Home » Posts tagged 'Race Realism' (Page 3)
Tag Archives: Race Realism
It Makes Logical Sense for Santa Claus to Be a White Man
1100 words
Of course, with Christmas just around the corner, it is getting attacked like it does every year. The song ‘White Christmas‘ got attacked a few years back (a personal favorite of mine during the Holiday season). I recall the attacks on the song a few years back, I used to live in the NYC metro area and I remember very clearly that the song would get strongly attacked by ‘PoCs’ because it was ‘racist’ because it was talking about a ‘white Christmas’. Well, there has been even more crazy attacks against Christmas and this time, it’s against Santa!
This attack on ol’ Saint Nick leads to him having homosexual relations with a black man, which brings me to the point of this article: Santa is being attacked now for being white and it’s clear that people don’t know a thing about skin color and cold adaptations when it comes to skin color. Of course, people choose ideology before science. It’s ridiculous that I have to write an article like this but in #2017 I’m not too surprised.
A writer for Slate, Aisha Harris, published an article back in 2013 titled “Santa Claus Should Not Be a White Man Anymore: It’s time to give St. Nick his long overdue makeover“. In the article, Harris states that she saw two Santas while growing up: one black and the other white. Her father stated that Santa came in every color. She states that decades later America is “less and less white” and that “a melanin-deficient Santa remains the default in commercials, mall castings, and movies”. The author goes on to state that we should replace white Santa with a penguin, and call it penguin Claus. But penguins live in the South Pole, not the North Pole, so the author’s contention here, again, doesn’t make sense.
Megyn Kelly discussed this article where she brings up good points that just because white Santa makes you uncomfortable that doesn’t mean that it has to change. She’s right. Your feelings don’t really matter to a long-standing tradition; if you want to make Santa black, that’s your right to do so in your household just know that 1) it doesn’t make logical sense and 2) you can’t impose your will on what you believe Christmas should or should not be like based on your feelings. I know the world is beginning to work like that today (changes based on people’s feelings), but people need to really grow up and accept certain things, especially if these things are sound and logical.
Talking about illogical statements, Andy Ostroy in HuffPo (low-hanging fruit, I know) writes an article in response to Megyn’s small tirade and states: “Yes it does, Megyn. Just because white people have concluded that Santa is white doesn’t make it right, a fact or a status that’s immune from change. It doesn’t matter what he’s ‘always been.’ I’m sure prior to 1865 there were a lot of white folks who said about slaves, “but they’ve always been slaves!”” Here’s another guy who doesn’t logic. Sure, it ‘may not matter what he’s ‘always been”, howeber if you’re looking for logical consistency with what we know about human skin variation then you will see that, even though ‘white people have concluded that Santa is white’ literally makes logical sense due to how human skin variation has evolved. We have scientific evidence for that, as you say in your piece in regard to one of Megyn’s contributors saying that it wouldn’t work because penguins live in the South Pole.
So, sorry Andy Ostroy, but Santa Claus is white.
However, you have articles like this one from The Atlantic titled “Megyn Kelly Assures Everyone That Santa Is White Even Though Santa Does Not Exist“, well I’m here to tell you that I assure everyone that Santa is white even though he doesn’t exist because logical deductions can be made based on where he lives.
This article talks about where to find black Santas that are ‘peppered’ all over the country (do you think the author of this article realizes what he wrote there?). Even former NBA all-star Baron Davis states that “his eyes see no color”. A man was teaching that “Santa comes in all colors“. People need to be logical when talking about skin color and Santa Claus, because by making ol’ St. Nick have dark skin, they’re really showing absolutely no logical thought at all.
In my article The Evolution of Human Skin Variation, I discussed how and why those people who migrated out of Africa evolved lighter skin due to migrating into high latitudes: vitamin D production. People with lighter skin can synthesize the steroid whereas people with darker skin, for instance, get diseases like rickets from not having much vitamin D. Though, logical thought such as this escapes people when they assert that Santa should be black or a ‘PoC’, they show that they do not have any knowledge of latitude, UV rays and skin color which evolves due to the intensity of UV rays.
Santa is based on St. Nicholas, a man who lived during the third century from the village Patara, which is now modern-day Turkey. This is the basis for the Santa Claus we all know and love today, and he was a white man. Santa Claus has his origins being brought to the New World by the first European settlers. Others have claimed that Santa borrows ideas from the Germanic god Wodan and other Pagan figures. Whatever the case may be, we have a few lines of evidence that he is white: 1) the man he was based off was European; 2) he was based on European legends and gods; and perhaps most importantly, 3) he lives at the damn North Pole where it makes sense to be white and have light skin to better produce vitamin D! This attack on Santa being white literally makes no sense at all.
Santa being white is logical, if a human lives at the North Pole for an extended amount of time, he will definitely be a white man due to how skin evolves in those latitudes. If you want to create a black Santa, that’s you’re right to do so. People really should stop letting their shitty ideologies permeate into everything we as a society do in America. The people who push a black Santa should know that if this version of Santa lives at the North Pole he’d quickly die due to lack of vitamin D production. Can’t let logic get in the way of a feel-good story though! Logic and reason is a white male construct anyway!
Rebutting Ross et al (1986) on Testosterone
1300 words
Ross et al (1986) is one of the most oft-cited papers that HBDers use to attempt to show that blacks have higher levels of testosterone than whites, which then—supposedly—goes on to explain higher rates of crime, aggression, and prostate cancer. However, people 1) say this only from reading the abstract (and not reading the full paper) and 2) even if they could read the paper they would not know where the flaws were to point them out and discredit the study based on flawed methodology. I see this study getting cited every now-and-then and I’m sick of seeing it.
Ross et al (1986: 45) state that they “recently reviewed the evidence that endogenous levels of certain steroid and polypeptide hormones are causally related to a group of human cancers, including cancer of the prostate gland.” I’ve shown how even injecting a man with exogenous testosterone does not worsen his prostate cancer (Eisenberg et al, 2015; Boyle et al, 2016) and testosterone doesn’t cause prostate cancer (Stattin et al, 2003; Michaud, Billups, and Partin, 2015). So this has been falsified. Even if blacks had the testosterone levels that they claimed it still would not cause higher rates of PCa (prostate cancer) incidence.
They solicited study participants from two colleges around the Los Angeles metro area. The two universities they got their sample from were the University of Southern California and California State University of Los Angeles. They recruited individuals through postings on the school bulletin board in in the school newspaper. They got 50 blacks and 50 whites. They then write something that’s troubling to me: “A convenient time for blood collection was arranged, and students were met by a nurse epidemiologist (R. H.) at either the Student Health Center or another mutually convenient location” (Ross et al, 1986: 45). This is dumb. The students were assayed at all times between 10 am and 3 pm; testosterone levels are highest at 8 am though one study on older men shows that assaying between 8 am and 2 pm doesn’t matter (Crawford et al, 2015). However, for the purposes of discussing this paper this is irrelevant.
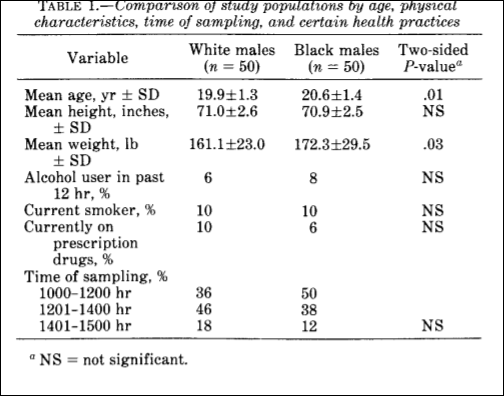
Table 1 from Ross et al (1986) tells us a lot about the flaws in the study—most importantly, the assay times. A majority were assayed between 10 am and 2 pm—which would depress testosterone though people assayed nearer to 10 am would have higher levels than people assayed nearer to 2 pm. Alcohol consumption only decreases testosterone while drunk, and a majority of the cohort did not consume alcohol within 12 hours of being assayed.
They come to the conclusion that the mean total testosterone level was 19 percent higher than whites whereas free testosterone was 21 percent higher. In regard to the assay collection times, Ross et al (1986: 47) write:
There was a negative correlation between time of sampling (No. of min elapsed since 0600 hr) and testosterone levels for whites (r=-O.4I) but not for blacks (r = -0.08). Adjustment for this variable caused a small reduction in geometric mean differences in levels of testosterone and free testosterone between blacks and whites. After simultaneous adjustment by analysis of covariance for time of sampling and age, weight, alcohol use, smoking, and use of prescription drugs, there
remained a 15% difference in total testosterone levels and a 13% difference in free testosterone levels between blacks and whites.
Even though they ‘adjusted for this variable’, it’s still a huge confound. Testosterone assays must be taken nearer to 8 am; the fact that people were assayed all over the place in the span of a 5 hour time period while testosterone levels decrease throughout the day is a huge red flag.
They then say that they are “uncertain why young black men have higher levels of circulating testosterone than white men“, though small sample sizes, a large range of variation in assay time, and a nonrepresentative sample is why. Other, more robust, analyses show a smaller ‘gap’, about 2.5 to 4.9 percent, favoring blacks (Richard et al, 2014). All in all, this study has huge flaws and should not be pointed to—especially today in 2017—because much larger analyses with much better methodologies have been carried out and some studies show no difference while others show a small difference favoring blacks but that still would not explain higher rates of testosterone, aggression and crime.
Ross et al (1986) is used by hereditarians such as Lynn (1990), Rushton (1997) and Hart (2007). Lynn (1990) states that these large testosterone differences discovered by Ross et al (1986) lend credence to Rushton’s r/K selection theory in which blacks have more children than whites who have more children than East Asians. Evidence for this assertion, states Lynn (1990) is the fact that blacks have higher rates of prostate cancer than whites who have higher levels of testosterone than East Asians, however this has been disproven by ethnicmuse.
Rushton (1997: 170) states that blacks had 19 percent higher levels of testosterone citing Ross et al (1986), however, Rushton didn’t cite the adjusted level which ended up being 15 percent, and, again, doesn’t mean anything to their hypothesis.
And Hart (2007) yet still repeats the same old stuff that “these differences in sexual behavior may be a consequence of the fact that blacks, on average, have higher levels of testosterone than whites“. These three researchers, clearly, are citing this study uncritically because it fits with their ‘racial hierarchy’. In fact, Rushton (1999) asked if testosterone was a ‘master switch’. In this paper, he cites Ellis and Nyborg (1992) who find that blacks had 3 percent higher levels of testosterone than whites. They gave the following values:
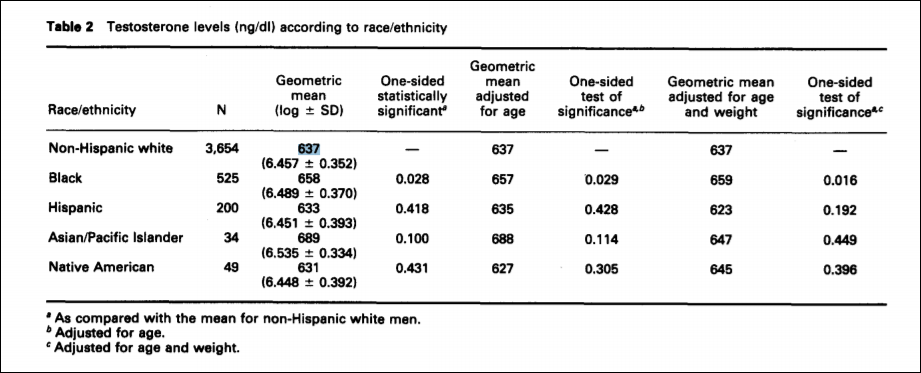
For the purposes of Rushton’s interpretation, writes Fish (2013), “These uncorrected figures are, of course, not consistent with their racial r- and K-continuum.” This, of course, is a big deal. Rushton cites this study as if it lends credence to his claims but it actually found the same result as Richard et al (2014). Thirty years after Ross et al (1986) we have numerous other studies showing a small gap between the races or no gap at all. We have numerous other studies showing that testosterone does not cause aggression, crime or violent behavior. However, people will still point to the abstract of Ross et al (1986) and think that they have proven that blacks have higher levels of testosterone than whites which proves how and why they have higher levels of testosterone, commit more crime and are all around more violent.
Though, as I have written about before, what Ross et al (1986) set out find the answer for (testosterone influencing higher levels of prostate cancer) can most definitely be explained by diet and lack of certain vitamins such as vitamin D, since low levels of this steroid hormone (it’s not a vitamin) cause prostate cancer (Schwartz and Hulka, 1990; Zhao and Feldman, 2001; Khan and Partin, 2004; Garland et al, 2006). Diet can explain a lot of the variation, as I have argued in the past.
In sum, Ross et al (1986) is the only study that I’ve found on racial testosterone differences that shows that extreme directionality favoring blacks over whites. This should set off some alarms in some people’s heads. People—psychologists included—need to learn about these hormones, how they’re produced in the body, and what they’re used for. Hormones don’t cause behavior, hormones influence behavior.
This fear of testosterone is largely overblown. We need testosterone for proper normal functioning. We need testosterone to be socially dominant; if you have lower levels you’ll be less socially dominant. This fear of testosterone—especially when it comes to race and it’s so-called causes—is largely pushed by Lynn, Rushton, Hart, and Ellis. I have spent a lot of time and thousands of words showing that they are wrong and testosterone is not a hormone to fear. It does not cause crime. It does not cause aggression. It does not cause prostate cancer. I’ve rebutted quite a few hereditarians on testosterone as well as testosterone and race, and if I come across more I will rebut them as well.
Differing Race Concepts and the Existence of Race: Biologically Scientific Definitions of Race
2700 words
Do you need to look at genetic differences between races to see if race is real? Some may argue that you do, and when you do you’ll see that genetic variation is too small to say that race exists. However, other arguments exist that do not look at genetic differences between races, but look at geographic ancestry, reproductive isolation between races, and morphologic differences. Those three variables are enough to prove the existence of race without looking at genetic differences between races. They do correspond to genetic differences between races. The four concepts I will briefly lay out are from Michael Hardimon, professor of philosophy at University of California, San Diego. The concepts are the racialist concept of race, minimalist concept of race concept, populationist concept of race, and the socialrace concept of race. One doesn’t need to look at the racialist concept of race to prove the existence of race, which I will prove below.
Michael Hardimon published Rethinking Race: The Case for Deflationary Realism earlier this year. In the book, he makes the case that race exists if minimalist race exists (I will get into what minimalist race entails below). Nevertheless, race deniers will say that even by looking at variables such as morphology, reproductive isolation, and geographic ancestry, race as a concept is scientifically invalid. This is patently false.
Concepts of race
The racialist concept of race
Hardimon’s first race concept is the racialist concept. The racialist concept (keep in mind, this is, as Hardimon writes on page 17 of his book Rethinking Race “the specific concept I have dubbed “the racialist concept” which “is hierarchal“) as defined by Hardimon holds that “racialist race is the idea of a fundamental division between groups and individuals” (Hardimon, 2017: 17). I think that Hardimon strawmans the racialist concept as he as defined it, but that’s for another day.
He also says that the racialist concept “is closely associated with racism” while the terms racialism and racism are “sometimes used interchangeably” (Hardimon, 2017: 17).
His argument against the racialist concept of race (as he defines it) is as follows (Hardimon, 2017: 21):
A third line of argument starts from the idea that in order for racialist races to exist, certain things must be true of human genetics, namely the following:
(a) The fraction of human genetic diversity between populations must exceed the fraction of diversity between them.
(b) The fraction of human genetic diversity within populations must be small.
(c) The fraction of diversity between populations must be large.
(d) Most genes must be highly differentiated by race.
(e) The variation in genes that underlie obvious physical differences must be typical of the genome in general.
(f) There must be several important genetic differences between races apart from the genetic differences that underlie obvious physical differences.
Note: (b) says that racialist races are genetically racially homogeneous groups; (c)-(f) say that racialist races are distinguised by major biological differences.
Call (a)-(f) the racialist concept of race’s genetic profile.
Now that his argument against the racialist concept (as he defines it) is laid out, you can see why I said that I think he strawmans the racialist concept. But I’ll get into that another day.
He then cites Lewontin’s (1972) analysis of blood groups by race as evidence against the racialist concept. Lewontin found that 85.4 percent of total human variation fell within populations. He also found that populations that populations classically defined as human races (Caucasians, Africans, Mongoloids, South Asian Aborigines, American Indians, and Oceanians) accounted for 8.3 percent of total human variation. Total variation between the classically defined races accounted for 6.3 percent of the variance.
It’s worth noting that the numbers given by Lewontin are true; where he goes wrong is assuming that there is no taxonomic significance for race based on the data he got from his analysis. “Call this Lewontin’s cleaver,” writes Hardimon on page 22.
Then in 2002, 31 years after Lewontin published his analysis, A.W.F. Edwards published his paper Human Genetic Diversity: Lewontin’s Fallacy. (Edwards, 2003). In the paper, Edwards argues that Lewontin’s conclusion is incorrect. Edwards (2003: 800-801) writes in his conclusion (emphasis mine):
There is nothing wrong with Lewontin’s statistical analysis of variation, only with the belief that it is relevant to classification. It is not true that ‘‘racial classification is … of virtually no genetic or taxonomic significance’’. It is not true, as Nature claimed, that ‘‘two random individuals from any one group are almost as different as any two random individuals from the entire world’’, and it is not true, as the New Scientist claimed, that ‘‘two individuals are different because they are individuals, not because they belong to different races’’ and that ‘‘you can’t predict someone’s race by their genes’’. Such statements might only be true if all the characters studied were independent, which they are not.
Of course, Lewontin’s conclusion is fallacious because small genetic differences do not entail that racial classification that race has no taxonomic significance (Richard Dawkins accepts the taxonomic existence of race). As you can see from the quote from Edwards, he does not object to Lewontin’s analysis of the races, he objects to his conclusion—namely that races do not exist based on the within-race variation being greater than between-race variation.
On page 22-23, Hardimon writes about Edwards’ objection to Lewontin’s conclusion:
Lewontin’s locus-by-locus analysis (which does not consider the possibility of a correlation between individual loci) does not preclude the possibility that individual loci might be correlated in such a way that people could be grouped into traditional racial categories. The underlying thought is that racial classification would have “taxonomic significance” were it possible to group people into traditional racial categories by making use of correlations between individual loci. However, Lewontin’s argument that there are no racialist races because the component of within-race genetic variation is larger than the component of between-race variation is untouched by Edwards’s objection.
In 2002, Rosenberg et al, in their paper Genetic Structure of Human Populations confirmed Lewontin’s analysis. They looked at 377 autosomal loci in 1,056 individuals from 52 populations and found that within-population differences between major groups (Africa, Europe, Asia, the Middle East, Central and South Asia, East Asia, Oceania, and America) accounted for 3-5 percent of genetic variation while genetic differences between individuals accounted for 93-95 percent of genetic variation. So Rosenberg et al (2002) confirmed Lewontin’s (1972) analysis—though do recall that Lewontin’s conclusion is incorrect. According to Hardimon’s interpretation of the racialist concept of race, both Lewontin’s and Rosenberg et al’s analysis disprove the racialist concept of race, but that doesn’t mean that there is no scientific basis for the biological reality of race (Hardimon, 2012).
The minimalist concept of race
The minimalist concept of race is similar to the racialist concept, though there are some stark differences. It does not say that there are intrinsic differences between races—call them essences if you will), but it does say that you can distinguish races by patterns of different physical features such as skin color, hair type, nose shape, morphology, etc, which then correspond to differences in geographic ancestry in geographically, genetically isolated breeding populations.
The minimalist concept of race further states that (i) races are distinguised from other races by patterns of visible physical features; (ii) the members are linked by a common ancestry which is peculiar to members of the group; and (iii) this group must originate from a distinct location.
The minimalist concept of race does not require: that the fraction of human genetic diversity between minimalist races is larger than the fraction of diversity within them; it is compatible with within-race diversity being large and between-race diversity being small; it does not require most genes to be highly differentiated by race; it does not require the existence of a lot genetic differences between races that underlie more than the phenotypic differences already noticed; the concept does not imply that there can be predictions made from yet unstudied characteristics; it finally does not require any genetic differences between races other than those found in the genes that underlie differences in physical appearance between race. This is called the minimalist concept of biological race (Hardimon, 2017: 66) and it survives all objections from Lewontin’s and Rosenberg et al’s analysis of between-race genetic variation.
This is my favorite race concept, personally, because it covers any and all objections from the race-denialist crowd—people who deny any genetic differences between races—because the only genetic differences it counts on are those physical traits that are already noticed.
Hardimon (2017: 29) writes:
Such readers should feel free to regard the minimalist concept of race, that is, as a concept that, though in many respects similar to the ordinary concept, is nonetheless distinct from it. What I would insist on is that minimalist races (groups satisfying the minimalist concept of race) are *races* (that is races so properly called)—either because the minimalist concept of race just is the ordinary concept of race or because it captures enough of the ordinary concept of race for minimalist races to be counted as races. My view is that if it can be shown that minimalist races exist, races exist. And if it can be shown that *minimalist race* is real, race is real.
The populatonist concept of race
The populationist concept of race is a nonessentialist, non-hierarchical concept of race that slightly differs from the minimalist concept of race. The populationist concept of race can be said to be a scientific concept of race (as can the minimalist concept) because it characterizes races as groups belonging to different groups of biological descent, they are distinguished by patterns of phenotypic differences, and these phenotypic differences trace back to geographically separated and genetically isolated founding populations.
The populationist concept of race also holds that “A race is a subdivision of Homo sapiens—a group or population that exhibits a distinctive pattern of genetically transmitted phenotypic characters that corresponds to the group’s geographical ancestry and belongs to a biological line of descent initiated by a geographically separated and reproductively isolated founding population” (Hardimon, 2017: 99). So with these criteria, you can see that even if you do not accept the racialist concept of race (as Hardimon defines it), you can still be a race realist. The populationist concept is likely to exist, and if the populationist concept of race exists then race is real.
Defining race as geographically and reproductively isolated breeding populations that share a common line of biological descent with similar phenotypic characters is as barebones a concept of race as you can get—and it is perfectly in line with how most people view races on the basis of phenotypic characterization. The populationist concept of race supposes that numerous concepts from the racialist concept of race are true—but do not presuppose any to-be-studied differences between those races. The strength of the populationist argument, as you can see, is very strong and it holds up to numerous lines of criticism very well. Although both the populationist and minimalist race concepts do not presupposed any to-be-studied differences between races, this still is not good enough for race deniers.
It is clear that without even looking at the brain and physiological differences between races, that race does indeed exist and it does—contrary to popular belief—have implications for people’s health of certain races.
The socialrace concept of race
Finally, the last concept of race laid out by Hardimon is the concept of socialrace. The concept of socialrace takes a race to be a racialist race, it refers to a position that is occupied by a social group that is a socialrace, and the socialrace concept refers to the system of social positions that are socialraces. This concept of race is, clearly, different from the minimalist and populationist race concepts but does indeed correlate with popular notions of race (and would correlate with the minimalist and populationist concept of race very well). The socialrace concept is, basically, what is believed to be racialist races.
The concept of socialrace is a concept of race as a social group (Hardimon, The Ontology of Race: 31)
The socialrace concept differs from the minimalist and populationist concept of race in that it looks at so-called social—not biological—correlates of race. Though, still, the socialrace concept can be said to show the reality of race since how one socially defines themselves correlates almost perfectly with geographic ancestry (which is a prerequisite for the existence of the minimalist concept of race and the populationist concept of race) (Tang et al, 2005). They showed that self-identified racial categories lined up almost perfectly with geographic ancestry (99.86 percent of the time). So, as you can see, the concept of socialrace also gives credence to the existence of the minimalist and populationist concepts of race.
This concept of race—as its name implies—does not talk race is a biological manner, but a social one, as its name implies. However, due to the extremely high chance that one’s self-identified race (their socialrace) lines up with the geographic ancestry of the classical races, we can see that the socialrace concept further buttresses the argument for the existence for the reality of the minimalist concept of race and the populationist concept of race.
The socialrace concept is kind of like Templeton (2014) defines race: that human races exist in a cultural sense, but not biologic sense. I have shown, though, that races exist in a cultural, social, and biological sense with the arguments presented in this article. Socialrace, culturalrace, whatever you want to call it, it is evidence for the existence of race.
Conclusion
Race exists whether or not the racialist position of race (as Hardimon defines it) is true or not. The minimalist concept of race and populationist concept of race show that race is real while the concept of socialrace further lends credence to the biological models of the minimalist and populationist concept of race. Even still, people who deny race because the genetic distance between races is too small for their to be any meaningful differences between them do not accept that three arguments above (sans the racialist concept) for the existence of race. They’ll still talk about the genetic differences between them and, say, morphology, but the minimalist concept of race and the populationist concept of race define race in enough of a way that genetic differences do not need to be looked at—we can only look at reproductive isolation, morphology, geographic ancestry and physical differences between minimalist and populationist races such as hair, nose, and skin color along with morphological differences.
Minimalist and populationist races exist and are a biological reality. We can take those two concepts to be a scientific basis for race. While we can take the concept of socialrace not as a biological concept, but as a social concept and we can then say that socialrace is socially real while being a significant social reality. That social reality is manifested by noticing different racial phenotypes, along with differences in SES, educational attainment, etc, and placing different races in different average social positions, which would correlate with the concepts of race mentioned above. This also correlated nearly perfectly with geographic ancestry. So, I’m saying it again, the existence of race as a social reality is real; the existence of socialrace buttresses the arguments for both the existence of the minimalist concept of race and the populationist concept of race—both of which are scientific concepts of race.
Minimalist races exist, and is a superficial biological reality, populations races may exist and if they exist, they are a relatively superficial biological reality. Socialraces exist and are a social reality which also lend credence to the minimalist and populationist concepts. I personally am privy to the minimalist race concept because it is shown to be real, so race is real.
In sum, race exists whether you look at genetic differences between races or not, morphology, geographic ancestry, reproductive and genetic isolation are all you need to prove the existence of race. There is a scientific concept of race, and the minimalist and populationist race concepts provide the existence for it, while the socialrace concept does as well. It is clear that for a scientific concept of race, you only need phenotypic variation, morphologic variation between races,
(Also read the American Rennaisance review for the book, A Tactical Retreat for Race Denial. I think it is balanced and fairly written, though a bit biased and doesn’t account for Hardimon’s views well enough in my opinion.)
Evidence for Natural Selection in Humans: East Asians Have Higher Frequency of CASC5 Brain Size Regulating Gene
1500 words
Brain size is one physical difference that the races differ on. East Asians have bigger brains than Europeans who have bigger brains than Africans (Beals et al, 1984; Rushton, 1997). What caused these average differences and the ultimate causes for them have been subject to huge debate. Is it drift? Natural/sexual selection? Mutation? Gene flow? Epigenetic? One reason why brains would need to be large in colder climates is due to heat retention, while in tropical climates heads need to be smaller to dissipate heat. One of the biggest criticisms of HBD is that there is no/little evidence of recent natural selection between human races. Well, that has changed.
CASC5 “performs two crucial functions during mitosis, being required for correct attachment of chromosome centromeres to the microtubule apparatus, and also essential for spindle-assembly checkpoint (SAC) signaling” (Shi et al, 2016). The gene has been found to be important in recent human evolution along with neurogenesis.
Shi et al (2016) genotyped 278 Han Chinese (174 females and 104 males with a mean age of 36) who were free of maladies or genetic defects. They had the coding sequences of CASC5 for humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, baboons, gibbons, orangutans, tarsiers, Denisovans, and Neanderthals. They downloaded genotypes from the Human Genome Project for their analysis.
They compared CASC5 among three human species: humans, Neanderthals, and Denisovans. Using chimpanzees as an outgroup, they discovered 45 human-specific mutations, 48 Neanderthal-specific mutations, and 41 Neanderthal-specific mutations. Further, when one exon region was aligned among modern humans, non-human primates and other mammalian species, 12 amino acid sites showed divergence between modern humans, Neanderthals, and Denisovans with 8 occurring in modern humans. Of the 8 sites in humans, 6 are preserved which implies that they were important in our evolutionary history.
Shi et al (2016) write:
At the population level, among the 8 modern human amino acid changes, two (H159R and G1086S) are fixed in current human populations, and the other six are polymorphic Fig. 1). Surprisingly, 5 of the 6 amino acid polymorphic sites showed deep between-population divergence in allele frequencies. East Asians possess much higher frequencies of the derived alleles at four sites (T43R-rs7177192, A113T-rs12911738, S486A-rs2412541 and G936R-rs8040502) as compared to either Europeans or Africans (Fig. 1), while E1285K-rs17747633 is relatively enriched in Europeans (46%), and rare in East Asians (10%) and Africans (3%). No between-population divergence was observed for T598 M-rs11858113 (Fig. 1).
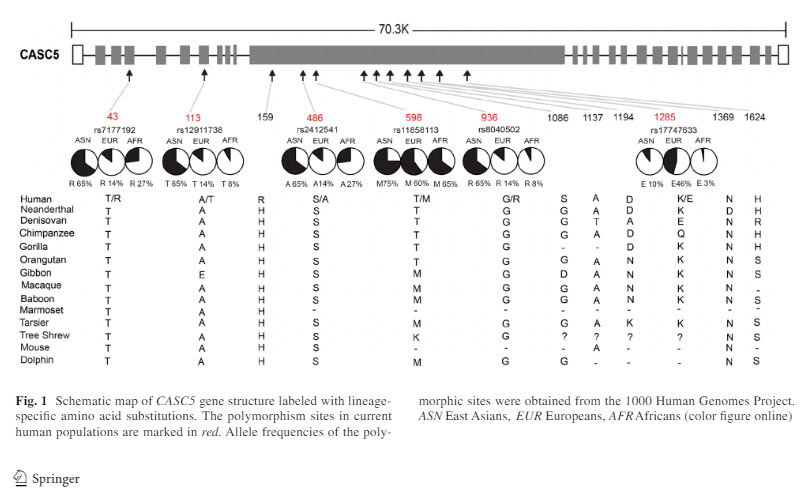
So East Asians have a much higher frequency of this derived trait. This is direct evidence for natural selection in recent human evolution in regards to the physical structure of the brain.
Since most of the amino acid polymorphic sites showed between-population divergence, they decided to analyze the three classical races using 1000 genomes. The variation between the races could be due to either genetic drift or natural selection. When they analyzed certain gene regions, they observed a signal of positive selection for East Asians but not Europeans or Africans. They further tested this selection signal using “the standardized integrated haplotype score (iHS) which is used for detecting recent positive selection with incomplete sweep (i.e. the selected allele is not yet fixed)” (Shi et al, 2016). Using this method, they discovered a few SNPs with large iHS values in Europeans (7 SNPs at 4.2 percent) and none in Africans.
They also conducted a genome-wide scan of Fst, iHS, and “XPCLR (searching for highly differentiated genomimc regions as targets of selective sweeps)” (Shi et al, 2016). Several SNPs had high Fst, iHS and XPCLR scores, which indicate that these alleles have been under positive selection in East Asians. Among the fixed amino acid sites in human populations, East Asians showed 5, Europeans showed 1, and Africans showed 0 which, the authors write, “[imply] that these amino acid changes may have functional effects” (Shi et al, 2016). Furthermore, using the HDGP, they obtained the frequency of the 6 amino acid sites in 53 populations. This analysis showed that 4 of the 6 amino acid sites are “regionally enriched in East Asia .. in line with the suggested signal of population-specific selection in this area” (Shi et al, 2016).
Then, since CASC5 is a brain size regulating gene, they looked for phenotypic effects. They recruited 167 Han Chinese (89 men, 178 women) who were free of maladies. They genotyped 11 SNPs and all of the frequencies followed Harvey-Weinberg Equilibrium (which states that allele and genotype frequencies will remain constant in a population from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary pressures; Andrews, 2010). In the female sample, 5 regions were related to gray matter volume and four were on the amino acid polymorphic sites. Interestingly, the four alleles which showed such a stark difference between East Asians and Europeans and Africans showed more significant associations in Han Chinese females than males. Those carrying the derived alleles had larger brain volumes in comparison with those who had the ancestral alleles, implying recent natural selection in East Asia for brain size.
Shi et al (2015) also attempted two replications on this allele writing:
We further conducted a replication analysis of the five significant CAC5 SNPs in two other independent Han Chinese samples (Li et al. 2015; Xu et al. 2015). The results showed that three SNPs (rs 7177192, rs11858113 and rs8040502) remained significant in Replication-1 for total brain volume and gray matter volume (Xu et al. 2015), but no association was detected in Replication-2 (Li et al. 2015) (Table S4).
It is very plausible that the genes that have regulated brain growth in our species further aid differences in brain morphology within and between races. This effect is seen mostly in Han Chinese girls. Shi et al (2016) write in the Discussion:
If this finding is accurate and can be further verified, it suggests that that [sic] after modern humans migrated out of Africa less than 100,000 years ago, the brain size may still be subject to selection.
I do believe it is accurate. Of course, the brain size could still be subject to selection; there is no magic field shielding the brain against selection pressure. Evolution does not stop at the neck.
So Shi et al (2016) showed that there were brain genes under recent selection in East Asians. What could the cause be? There are a few:
- Climate: In colder climates you need a smaller body size and big brain to survive the cold to better thermoregulate. A smaller body means there is less surface area to cover, while a larger head retains heat. It, obviously, would have been advantageous for these populations to have large brains and thus get selected for them—whether by natural or sexual selection. This could also have to do with the fact that one needs bigger eyes in colder environments, which would cause an increase in the size of the brain for the larger eyes, as well as being sharper visio-spatially.
- Intelligence: East Asians in this study showed that they had high levels of gray matter in the skull. Further, large brains are favored by an intermediately challenging environment (Gonzalez-Forero, Faulwasser, and Lehmann, 2017).
- Expertise: I used Skoyle’s (1999) theory on expertise and human evolution and applied it to racial differences in brain size and relating it to the number of tools they had to use which differed based on climate. Now, of course, if one group uses more tools then, by effect, they would need more expertise with which to learn how to make those tools so large brains would be selected for expertise—especially in novel areas.
- Vision: Large brains mean large eyes, and people from cold climates have large eyes and large brains (Pearce and Dunbar, 2011). Decreasing light levels select for larger eye size and visual cortex size in order to “increase sensitivity and maintain acuity“. Large eyeballs mean enlarged visual cortices. Therefore, in low light, large brains and eyes get selected for so one can see better in a low light environment.
Of course, all four of the examples below could (and probably do) work in tandem. However, before jumping to conclusions I want to see more data on this and how the whole of the system interacts with these alleles and these amino acid polymorphic sites.
In sum, there is now evidence for natural selection on East Asians (and not Africans or Europeans) that favored large brains, particularly gray matter, in East Asians with considerable sexual dimorphism favoring women. Four of the genes tested (MCPH1, ASPM, CDK5RAP2, and WDR62) are regulated by estradiol and contribute to sexual dimorphism in human and non-human primates (Shi et al, 2016). Though it still needs to be tested if this holds true for CASC5.
This is some of the first evidence that I have come across for natural selection on genes that are implicated in brain evolution/structural development between and within populations. It does show the old “Rushton’s Rule of Three“, that is, Mongoloids on top, Caucasians in the middle, and Negroids on bottom, though Caucasians were significantly closer to Africans than Mongoloids in the frequency of these derived alleles. I can see a HBDer going “They must be related to IQ”, I doubt it. They don’t ‘have’ to be related to IQ. It just infers a survival advantage in low light, cold environments and therefore it gets selected for until it reaches a high frequency in that population due to its adaptive value—whether spreading by natural or sexual selection.
No, Black Women Do Not Have Higher Testosterone than White Women (And More On Hereditarian Claims on Racial Testosterone Differences)
1850 words
It has been over a year since I wrote the article Black Women and Testosterone, and I really regret it. Yes, I did believe that black women had higher levels of testosterone than white women due to one flimsy study and another article on pregnant black women. I then wised up to the truth about testosterone and aggression/crime/race/sex and revised the articles (like I have done with r/K selection theory). However, after I revised my views on the supposed differences in testosterone between black men/white men and black women/white women, people still cite the article, disregarding the disclaimer at the top of the article. I quoted Mazur (2016), who writes (emphasis mine):
The pattern [high testosterone] is not seen among teenage boys or among females.
…
There is no indication of inordinately high T among young black women with low education.
…
Honor cultures are cast as male affairs, but with T data in hand for both sexes, it is worth exploring whether or not a similar pattern exists among women. Mean T was calculated as a function of age for the four combinations of race and education used in Table 1 but now for women. All plots show T declining with age, from about 35 ng/dL in the 20–29 age group to about 20 ng/dL among women 60 years and older. The four plots essentially overlap without discernible differences among them. Given the high skew of T among adult females, both raw and ln-transformed values were analyzed with similar results. There is no indication of inordinately high T among young black women with low education.
…
In the present study, at least, the sexes differ because the very high T seen among young black men with low education does not occur among young black women with low education.
This is very clear… Mazur (2016) analyzed the NHANES 2011-2012 data and this is what he found. I understand that most HBD bloggers do believe this, well, like a lot of their strong assertions (which I have rebutted myself), they’re wrong. They don’t get it. They do not understand the hormone.
The reason why I’m finally writing this (which is long overdue) is that I saw a referral from this website today: https://www.minds.com/RedPillTV who writes about the aforementioned black women and testosterone article:
It is known that blacks have the highest levels of testosterone out of the major races of humanity. However, what’s not known is that black women have higher rates than white women. The same evolutionary factors that make it possible for black men to have high testosterone make it possible for women as well.
https://notpoliticallycorrect.me/2016/09/06/black-women-and-testosterone/
…..No. It seems that people just scroll on by the disclaimer at the top that is bolded and italicized and just go to the (now defunct) article and attempt to prove their assertion that black women have higher testosterone than white women with an article that I have stated myself I no longer believe and have provided the rationale/data for the position. This shows that people have their own biases and no matter what the author writes about their views that have changed due to good arguments/data, they will still attempt to use the article to prove their assertion.
I’ve written at length that testosterone does not cause 1) aggression, 2) crime and 3) prostate cancer. People are scared of testosterone mostly due to the media fervor of any story that may have a hint of ‘toxic masculinity’. They (most alt-righters) are scared of it because of Lynn/Rushton/Templer/Kanazawa bullshit on the hormone. Richard Lynn doesn’t know what he’s talking about on testosterone. No, Europeans did not need lower levels of aggression in the cold; Africans didn’t need higher levels of aggression (relative to Europeans) to survive in the tropics. The theory that supposed differential testosterone differences between the races are “the physiological basis in males of the racial differences in sexual drive which form the core of the different r/K reproduction strategies documented by J.P. Rushton” (Lynn, 1990: 1203). The races, on average, do not differ in testosterone as I have extensively documented. So hereditarians like Lynn and others need to look for other reasons to explain blacks’ higher rate of sexual activity.
Rushton’s views on the testosterone and supposed r/K continuum have been summarily rebutted by me. These psychologists’ views on the hormone (that they don’t understand the production of nor do they understand the true reality of the differences between the races) are why people are afraid of testosterone. No, testosterone is not some ‘master switch’ as Rushton (1999) asserts. Rushton asserts that racial differences in temperament are mediated by the hormone testosterone. He further dives into this assertion stating “Testosterone level correlates with temperament, self-concept, aggression, altruism, crime, and sexuality, in women as well as in men (Harris, Rushton, Hampson, & Jackson, 1996). It may ‘correlate’ with aggression and crime, but as I have documented, they do not cause either.
The aggression/testosterone correlation is only .08 (Archer, Graham-Kevan, and Davies, 2005). Furthermore, the diurnal variation in testosterone does not directly correlate to when testosterone levels are highest in the day (at 8 am and drop thereafter), with adults peaking in crime at 10 pm and kids at 3 pm, with rises at 8 pm and 12 pm (not surprisingly, kids go in to school around 8 am, go to recess at 12 and leave at 3).

(Source: The Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP))
If you’ve read as much Rushton as I have, you’ll notice that he begins to sound like a broken record when talking about certain things. One of the most telling is Rushton’s repeated assertions that blacks average 3-19 percent higher testosterone than whites. The 3 percent number comes from Ellis and Nyborg (1992) and the 19 percent number comes from Ross et al (1986) (which Rushton should know that after adjustments for confounding, it decreased to 13 percent). These are the only studies that hereditarians ever cite for these claims that blacks average higher testosterone than whites. That seems a bit fishy to me. Cite a 30-year-old study along with a 25-year-old study (with such huge variation from Rushton and those who cite him for this matter—3-19 percent!!) as ‘proof’ that blacks average such higher levels of testosterone in comparison to whites.
Ross et al (1986) is one of the most important studies to rebut for this hereditarian claim that testosterone causes all of these maladies in black American populations. Ross et al (1986) propose that higher levels of the hormone lead to the higher rates of prostate cancer in black American populations. However, meta-analyses do not show this (Zagars et al, 1998; Sridhar et al, 2010).
Rushton et al’s assertions—largely—lie on this supposed testosterone difference between the races and how it supposedly leads to higher rates of crime, prostate cancer, aggression, and violence. However, the truth of the matter is, this is all just hereditarian bullshit. Larger analyses—as I have extensively documented—do not show this trend. And even accepting the claim that blacks have, say, 19 percent higher levels of testosterone than whites, it still would not explain the supposed prostate cancer rates between the races (Stattin et al, 2003; Michaud, Billups, and Partin, 2015). Even if blacks had 19 percent higher testosterone than whites, it would not explain higher levels of crime nor aggression due to such a hilariously low correlation of .08 (Archer, Graham-Kevan, and Davies, 2005).
Finally, I have a few words for Michael Hart and his (albeit sparse) claims on testosterone in his 2007 book Understanding Human History.
Hart (2007) writes:
(Many of these differences in sexual behavior may be a consequence of the fact that
blacks, on average, have higher levels of testosterone than whites.7) (pg. 127)
And….. footnote number 7 is…. surprisingly (not): 7) Ross, R., et al. (1986). Not going to waste my time on this one, again. I’ve pointed out numerous flaws in the study. (I will eventually review the whole thing.)
It seems unlikely, though, that the higher testosterone level in blacks — which is largely genetic in origin — has no effect on their sexual behavior (pg. 128; emphasis mine)
This is bullshit. People see the moderately high heritability of testosterone (.60; Harris, Vernon, and Boomsma, 1998) and jump right to the “It’s genetics!!!” canard without even understanding its production in the body (it is a cholesterol-based hormone which is indirectly controlled by DNA, there are no ‘genes for’ testosterone). Here are the steps: 1) DNA codes for mRNA; 2) mRNA codes for the synthesis of an enzyme in the cytoplasm; 3) luteinizing hormone stimulates the production of another messenger in the cell when testosterone is needed; 4) this second messenger activates the enzyme; 5) the enzyme then converts cholesterol to testosterone
I have documented numerous lines of evidence showing that testosterone is extremely sensitive to environmental factors (Mazur and Booth, 1998; Mazur, 2016), and due to the homeodynamic physiology we have acquired due to ever-changing environments (Richardson, 2017), this allows our hormones to up- or down-regulate depending on what occurs in the environment. The quote from Hart is bullshit; he doesn’t know what he’s talking about.
For females in Siberia, the disadvantages of failing to find a man who would
provide for her and her children during their childhood were much greater than they were in tropical climates, and females who were not careful to do so were much less likely to pass on their genes. Furthermore, because females in harsh climates were so demanding on this point, males who seemed unlikely to provide the needed assistance found it hard to find mates. In other words, there was a marked sexual selection against such males. Such selection could result, for example, in the peoples living in northerly climates gradually evolving lower levels of testosterone than the peoples living in subSaharan Africa. (pg. 131)
This is a bullshit just-so story. Africans in Africa have lower levels of testosterone than Western men (Campbell, O’Rourke, and Lipson, 2003; Lucas and Campbell, and Ellison, 2004; Campbell, Gray, and Ellison, 2006).
Note also that a difference in testosterone level frequently affects not
only the sexual behavior of a young male, but also his aggressiveness.
No it does not (Archer, Graham-Kevan, and Davies, 2005).
Thankfully, that’s all he wrote about testosterone. There is so much bullshit out there. Though, people who like and seek out the truth will learn that there are no racial differences and that testosterone does not cause crime/aggression/prostate cancer and that it’s just hereditarian bullshit.
The evidence I have amassed and the arguments I have given point to a few things: 1) the races do not differ in testosterone/there is a small negligible difference; 2) testosterone does not cause crime; 3) testosterone does not cause aggression; 4) black women do not have higher levels of testosterone than white women; 5) high levels of testosterone do not cause prostate cancer; and 6) even allowing a 19 percent black/white difference will not have hereditarian claims hold true.
So for anyone who comes across my old articles on testosterone and sex/race, do a bit more reading of my newer material here to see my new viewpoints/arguments. DO NOT cite these articles as proof for your claims of higher levels of black men/women. DO cite the old articles ALONG WITH the new ones to show how and why my views changed along with the studies I have cited that changed my view. (Actually understanding the production of testosterone in the body was a huge factor too, which I talk about in Why Testosterone Does Not Cause Crime.)
Why Are People Afraid of Testosterone?
1100 words
The answer to the question of why people are afraid of testosterone is very simple: they do not understand the hormone. People complain about birth rates and spermatogenesis, yet they believe that having high testosterone makes one a ‘savage’ who ‘cannot control their impulses’. However, if you knew anything about the hormone and how it’s vital to normal functioning then you would not say that.
I’ve covered why testosterone does not cause crime by looking at the diurnal variation in the hormone, showing that testosterone levels are highest at 8 am and lowest at 8 pm, while children commit the most crimes at 3 pm and adults at 10 pm. The diurnal variation is key: if testosterone truly did cause crime then rates of crime would be higher in both children and adults in the morning; yet, as can be seen with children, there are increases in amounts of violence committed when they enter school, go to recess, and exit school. This shows why those times are related to the spike in crime in children.
I have wrote a previous article citing a paper by Book et al (2001) in which they meta-analyzed testosterone studies and found that the correlation between testosterone and aggression was .14. However, that estimate is too high since they included 15 studies that should have not been included in the analysis. The true correlation is .08 (Archer, Graham-Kevan, and Davies, 2004). So, clearly, along with the fact that the diurnal variation in testosterone does not correlate with crime spikes, it shows that testosterone has no relationship to the cause of crime; it’s just always at the scene because it prepares the body to deal with a threat. That does not mean that testosterone itself causes crime.
One main reason people fear testosterone and believe that it causes crime and by extension aggressive behavior is because of racial crime disparities. According to the FBI, black Americans by and large commit the most crime, despite being 13 percent of the US population. And since it has been reported that blacks have higher levels of testosterone (Ross et al, 1986; Lynn, 1992; Rushton, 1997; Ellis, 2017), people believe that the supposed higher levels of testosterone that blacks, on average, have circulating in their blood is the ultimate cause of the crime disparities in America between races. Though see above to see why this is not the ultimate cause.
Blacks, contrary to popular belief, don’t have higher levels of testosterone (Gasper et al, 2006; Rohrrman et al, 2007; Lopez et al, 2013; Richard et al, 2014). Even if they did have higher levels, say the 13 percent that is often cited, it would not be the cause of higher rates of crime, nor the cause of higher rates of prostate cancer in blacks compared to whites. What does cause part of the crime differential, in my opinion, is honor culture (Mazur, 2016). The blacks-have-higher-testosterone canard was pushed by Rushton and Lynn to explain both higher rates of prostate cancer and crime in black Americans, however I have shown that high levels of testosterone do not cause prostate cancer (Stattin et al, 2003; Michaud, Billups, and Partin, 2015). Looking to testosterone as a ‘master switch’ as Rushton called it is the wrong thing to research because, clearly, the theories of Lynn, Rushton, and Ellis have been rebutted.
People are scared of testosterone because they do not understand the hormone. Indeed, people complain about lower birth rates and lower sperm counts, yet believe that having high testosterone will cause one to be a high T savage. This is seen in the misconception that injecting anabolic steroids causes higher levels of aggression. One study looked at the criminal histories of men who self-reported drug use and steroid use Lundholm et al (2014) who conclude: “We found a strong association between self-reported lifetime AAS use and violent offending in a population-based sample of more than 10,000 men aged 20-47 years. However, the association decreased substantially and lost statistical significance after adjusting for other substance abuse. This supports the notion that AAS use in the general population occurs as a component of polysubstance abuse, but argues against its purported role as a primary risk factor for interpersonal violence. Further, adjusting for potential individual-level confounders initially attenuated the association, but did not contribute to any substantial change after controlling for polysubstance abuse.“
The National Institute of Health (NIH) writes: “In summary, the extent to which steroid abuse contributes to violence and behavioral disorders is unknown. As with the health complications of steroid abuse, the prevalence of extreme cases of violence and behavioral disorders seems to be low, but it may be underreported or underrecognized.” We don’t know whether steroids cause aggression or more aggressive athletes are more likely to use the substance (Freberg, 2009: 424). Clearly, the claims of steroids causing aggressive behavior and crime are overblown and there has yet to be a scientific consensus on the matter. A great documentary on the matter is Bigger, Stronger, Faster, which goes through the myths of testosterone while chronicling the use of illicit drugs in bodybuilding and powerlifting.
People are scared of the hormone testosterone—and by extent anabolic steroids—because they believe the myths of the hulking, high T aggressive man that will fight at the drop of the hat. However, reality is much more nuanced than this simple view and psychosocial factors must also be taken into account. Testosterone is not the ‘master switch’ for crime, nor prostate cancer. This is very simply seen with the diurnal variation of the hormone as well as the peak hours for crime in adolescent and adult populations. The extremely low correlation with aggression and testosterone (.08) shows that aggression is mediated by numerous other variables other than testosterone, and that testosterone alone does not cause aggression, and by extension crime.
People fear things they don’t understand and if people were to truly understand the hormone, I’m sure that these myths pushed by people who are scared of the hormone will no longer persist. Low levels of testosterone are part of the cause of our fertility problems in the West. So does it seem logical to imply that high testosterone is for ‘savages’, when, clearly, high levels of testosterone are needed for spermatogenesis which, in turn, would mean a higher birth rate? Anyone who believes that testosterone causes aggression and crime and that the injection of anabolic steroids causes ‘roid rage’ should do some reading on how the production of the hormone in the body as well as the literature on anabolic steroids. If one wants birth rates to increase in the West, then they must also want testosterone levels to increase as well, since they are intimately linked.
Testosterone does not cause crime and there is no reason to fear the hormone.
Homo Neanderthalis vs. Homo Sapiens Sapiens: Who is Stronger? Implications for Racial Strength Differences
1300 words
Unfortunately, soft tissue does not fossilize (which is a problem for facial reconstructions of hominins; Stephan and Henneberg, 2001; I will cover the recent ‘reconstructions’ of Neanderthals and Nariokotome boy soon). So saying that Neanderthals had X percent of Y fiber type is only conjecture. However, to make inferences on who was stronger, I do not need such data. I only need to look at the morphology of the Neanderthals and Homo sapiens, and from there, inferences can be made as to who was stronger. I will argue that Neanderthals were stronger which is, of course, backed by solid data.
Neanderthals had wider pelves than Homo sapiens. Wider pelves in colder climes are due to adaptations. Although Neanderthals had wider pelves than ours, they had infants around the same size as Homo sapiens, which implies that Neanderthals had the same obstetric difficulties that we do. Neanderthals also had a pelvis that was similar to Heidelbergensis, however, most of the pelvic differences Neanderthals had that were thought to be derived traits are, in fact, ancestral traits—except for the cross-sectional shape of the pubic ramus (Gruss and Schmidt, 2015). Since Neanderthals had wider pelves and most of their pelvis were ancestral traits, then wide pelves may have been a trait of ancestral Homo (Trinkaus, Holliday, and Aurbach, 2014).
Hominins do need wider pelves in colder climates, as it is good for heat retention, however (see East Asians and Northern Europeans). Also, keep in mind that Neanderthals were shorter than us—with the men averaging around 5 feet five inches, and the women averaging about 5 feet, about 5.1 inches shorter than post-WW II Europeans (Helmuth, 1998).
So what does a wider pelvis mean? Since the Neanderthals were shorter than us and also had a wider pelvis, they had a lower center of gravity in comparison to us. Homo sapiens who came Out of Africa, had a narrower pelvis since narrow pelves are better to dissipate heat (Gruss and Schmidt, 2015). Homo sapiens would have been better adapted to endurance running and athleticism, in comparison to the wide-pelved Neanderthals.
People from tropical climates have longer limbs, and are tall and narrow (which is also good for endurance running/sprinting) while people from colder climates are shorter and more ‘compact’ (Lieberman, 2015: 113-114) with a wide pelvis for heat retention (Gruss and Schmidt, 2015). So, clearly, due to the differences in pelvic anatomy between Homo sapiens and Neanderthals,
Furthermore, due to the length of Neanderthal clavicles, it was thought that they had long clavicles which would have impeded strength. However, when the clavicles were reanalyzed it was discovered that when the clavicles were adjusted with the body size of Neanderthals—and not compared with the humeral lengths—Neanderthals had a similar clavicular length, which implies a similar shoulder breadth as well, to Homo sapiens (Trinkaus, Holliday, and Aurbach, 2014). This is another clue that Neanderthals were stronger.
Yet more evidence comes from comparing the bone density of Neanderthal bones to that of Homo sapiens. Denser bones would imply that the body would be able to handle a heavier load, and thusly generate more power. In adolescent humans, muscle power predicts bone strength (Janz et al, 2016). So if the same holds true for Neanderthals—and I don’t see why not—then Neanderthals would have higher muscle power since it predicts bone strength.
Given the “heavy musculature” of Neanderthals, along with high bone robusticity, then they must have had denser bones than Homo sapiens (Friedlander and Jordan, 1994). So since Neanderthals had denser bones, then they had higher muscle power; they had a lower center of gravity due to having a wider pelvis and being shorter than Homo sapiens whose body was heat-adapted. Putting this all together, the picture is now becoming clearer that Neanderthals were, in fact, way stronger than Homo sapiens.
Another cause for these anatomical differences between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens is completely independent of cold weather. Neanderthals had an enlarged thorax (rib cage), which evolved to hold an enlarged liver, which is responsible for metabolizing large amounts of protein. Since protein has the highest thermic effect of food (TEF), then they would have had a higher metabolism due to a higher protein diet which would also have resulted in an enlarged bladder and kidneys which are necessary to remove urea, which possibly would have also contributed to a wider pelvis for Neanderthals (Ben-Dor, Gopher, and Barkai, 2016).
During glacial winters, Neanderthals would have consumed 74-85 percent of their calories from fat, with the rest coming from protein (Ben-Dor, Gopher, and Barkai, 2016). Neanderthals also consumed around 3,360-4,480 kcal per day (Steegman, Cerny, and Holliday, 2002). Let’s assume that Neanderthals averaged 3800 kcal per day. Since the upper limit of protein intake is 3.9 g/bw/day (erectus) and 4.0 g/bw/day for Homo sapiens (Ben-Dor et al, 2011), then Neanderthals would have had a theoretical higher upper limit due to having larger organs, which are useful in processing large amounts of protein. The protein intake for a Neanderthal male was between estimated to be between 985 kcal (low end) to 1170 kcal (high end). It was estimated that Neanderthal males had a protein intake of about 292 grams per day, or 1,170 kcal (Ben-Dor, Gopher, and Holliday, 2016: 370).
Assuming that Neanderthals did not eat carbohydrates during glacial winters (and even if a small amount were eaten, the model would not be affected) and an upper limit of protein intake of 300 grams per day for Neanderthal males, this implies that 74-85 percent of their diet came from animal fat—the rest being protein. Protein is the most thermogenic macro (Corvelli et al, 1997; Eisenstein et al, 2002; Buchholz and Schoeller, 2004; Halton and Hu, 2004; Gillingham et al, 2007; Binns, Grey, and Di Brezzo, 2014). So since Neanderthals ate a large amount of protein, along with their daily activities, they had to have had a high metabolic rate.
To put into perspective how much protein Neanderthals ate, the average American man eats about 100 grams of protein per day. In an analysis of the protein intake of Americans from 2003-2004, it was found that young children ate about 56 grams of protein per day, adults aged 19-30 ate about 91 grams of protein per day, and the elderly ate about 56 grams of protein per day (Fulgoni, 2008). Neanderthals ate about 3 times the amount of protein than we do, which would lead to organ enlargement since larger organs are needed to metabolize said protein as well. Another factor in the increase of metabolism for Neanderthals was the fact that it was, largely, extremely cold. Shivering increases metabolism (Tikuisis, Bell, and Jacobs, 1985; van Ooijen et al, 2005). So the Neanderthal metabolism would have been revved up close to a theoretical maximum capacity.
The high protein intake of Neanderthals is important because high amounts of protein are needed to build muscle. Neanderthals consumed a sufficient amount of kcal, along with 300 grams of protein per day on average for a Neanderthal male, which would have given Neanderthals yet another strength advantage.
I am also assuming that Neanderthals had slow twitch muscle fibers since they have wider pelves, along with evolving in higher latitudes (see Kenyans, East Asians, European muscle fiber distribution), they would have an abundance of type slow twitch muscle fibers, in comparison to fast twitch muscle fibers, however, they also have more slow twitch fibers which Europeans have, while African-Americans (West-African descendants) have a higher amount of fast twitch fibers. (Caesar and Henry, 2015). So now, thinking of everything I explained above and replacing Neanderthals with Europeans and Homo sapiens with Africans, who do you think would be stronger? Clearly, Europeans, which is what I have argued for extensively. African morphology (tall, lanky, high limb ratio) is not conducive to strength; whereas European morphology (wide pelvis, low limb ratio, an abundance of slow twitch fibers) is.
The implications for these anatomic differences between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens and how it translates into racial differences will be explored more in the future. This was just to lay the anatomic and morphologic groundwork in regards to strength and cold weather adaptations. Nevertheless, the evidence that Neanderthals were stronger/more powerful than Europeans stands on solid ground, and the same does hold for the differences in strength between Africans and Europeans. The evolution of racial pelvic variation is extremely important to understand if you want to understand racial differences in sports.
r/K Selection Theory: A Response to Anonymous Conservative
2800 words
I knew the article about r/K selection would stir a bit of debate. Anonymous Conservative has replied to both articles that were published the other day. However, he seems confused. He doesn’t talk about r/K selection theory in terms of density-dependence/independence. That’s what r/K theory was based on before it was discredited for age-specific mortality (Reznick et al, 2002). The theory was discredited decades ago. This article will be a response to him. How can you use age-specific mortality for your theory?
Combining all African and all European populations probably dulls the degree to which certain populations are r and K.
Combining the ethnies of all three populations makes no sense if you’re attempting to infer how behavior X evolved in ecosystem Y using r/K selection theory. To conduct such a study, you would need to study the races in the ecosystem that the selection was hypothesized to have occurred. r/K selection is—as I’ve already brought up—proven false. I will get to that below.
If r/K selection did apply to humans, then since Africans have been in their habitat—according to Rushton—for 140ky and Mongoloids have been in their habitat for 40ky, then Africans would have had more opportunity to approach the environmental carrying capacity while Mongoloids who migrated into novel environments (cold weather, as mentioned above) would experience r-selected traits since they are in a novel environment (r pressure) and facing cold weather (another r pressure). Per Rushton’s own arguments—along with how r/K theory was really used—Africans are K and Mongoloids are r.
Take the most r populations in Africa and you would also see highly obvious differences deviating from normal human behavior.
Which populations in Africa are ‘the most r’? What is ‘normal human behavior’?
Goal number one should be to get people forced to acknowledge that some humans are exhibiting the r-strategy compared to others.
If this were the case, then Mongoloids would be r while Africans would be K—if r/K selection theory weren’t discredited and if human races qualified as local populations. This, of course, comes from Rushton own words, who asserts that Mongoloids have cold-weather adaptations. So if Mongoloids have cold-weather adaptations and cold weather is an agent of r-selection as described previously, then Mongoloids are r-selected. This argument comes straight from Rushton’s own theory. Furthermore, Africans would be K-selected since endemic disease is an agent of K-selection. This is simple enough to understand, especially if you read a few papers on r/K selection.
I get the impression the author is a pot-stirrer ginning up debate, which I can respect. But I would counter that I think this argument requires a slightly more complex view on a few points, and it seeks to cite the established literature on r/K a little too much.
Citing papers is what’s needed when discussing scientific matters. If your arguments are not backed by scientific papers then your argument is pretty much moot.
Most of the literature on r/K is incredibly shallow in its analyses. I suspect nobody really cared about the theory on an emotional level, so nobody really bothered to look too closely at it, or tried to understand why some arguments would seemingly violate simple common sense. One person would assert things that would make no sense in certain contexts, and nobody would ever try to highlight the complexity required for a fuller understanding of the issue. It is either that, or the more powerful minds gravitated somewhere else in the sciences with more practical application.
This looks pretty clear-cut to me. r/K selection theory has been extensively tested and falsified. Of course people cared about it, it dominated biology and ecology literature for about twenty years after Pianka’s (1970) paper where he proposed his now debunked ‘r/K continuum’. As I have said, Pianka gave no experimental rationale on why he chose the traits he did for the continuum (Graves, 2002: 135). This is simple enough to understand on its own.
As an example, the author cites papers that say drought is an r-selective pressure. Drought can be r or K, depending on the abilities of the organisms confronted with it. Mice will die in a drought, and have short enough life cycles to reproduce in the wet periods following it. So with mice, after the drought, there will be free resources and that makes drought a huge r-selection pressure.
But suppose you have an organism with the intelligence to envision how to survive the drought, and which thinks in terms of long time frames. Now that drought will cull the relatively r-selected individuals who are designed to exploit a glut with no thought of the future, while favoring those who planned for the drought and stockpiled water, or organized a way to acquire it. Is the drought still an r-selective pressure? Being human, with a high IQ and an ability to plan for the future changes a lot of these rules.
Drought is an agent of r-selection. How about earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? Are those agents of K-selection as well if you can ‘plan for the future changes’? Provide references for your assertion or your claim is unfounded.
On the issue of colder climates being K, the author cites research which makes the case that cold climates kill back the population in the winter, and then allow explosive growth in the summer, and thus are r-selecting.
This will be true in things like insects with short lifespans and no ability to plan for the winter. But in humans, this will favor those who can defer pleasures in the summer, looking forward to the winter and sacrificing by setting aside resources to get themselves through the colder period. It will also favor groups which can work together in pursuit of common goals.
You don’t get it. Mongoloids being r-selected is straight from Rushton. He asserts that they have cold-adaptations. Cold adaptations are due to cold weather. Cold weather is an agent of r-selection (temperature extreme). If cold weather is an agent of r-selection and Mongoloids further migrated into a novel environment (another agent of r-selection), then, per Rushton’s own words, Mongoloids are r-selected. Conversely, Rushton describes endemic disease and drought in Africa (without references), but let’s assume it’s true. As described above, drought is an agent of r (see the table from Anderson above) while endemic disease is an agent of K-selection.
Endemic (native) disease is an agent of K-selection. Since the disease is constant, then the population under that agent of K-selection can prepare ahead for disease. Indeed, in Africa, measures can be taken to reduce the number of those infected with malaria, such as mothers shielding their babies from mosquitoes, to even herbal remedies which have been in use for thousands of years (Wilcox and Bodecker, 2004). If endemic disease is constant (and it is) and Africans are under that constant pressure, then they will be K-selected.
Do groups not work together in Africa to reach common goals? In the Pleistocene as well? Citations? Think before you write (and cite), because hunting bands in our species began with Homo erectus. The capacity for endurance running evolved in erectus which can be seen with the beginnings of our modern pelvis as well as the evolution of the gluteus maximus (Lieberman et al, 2006). So how can you assert that working together to reach common goals only occurred where it was cold—as if tropical environments don’t have their own challenges which require foresight and planning? Think about human evolution and how modern human cognition evolved in Africa.
This will be true of most hardships to some degree. Where they kill back the population massively and randomly, and then allow explosive regrowth, they are r-pressures. But where they are challenges that select for those who can prepare and overcome them, they will tend to favor K, even if they may, strictly by the numbers, appear to be r.
How can you prepare and overcome a violent winter storm, volcanic eruption, earthquake, and drought (which vary wildly)? At a certain point, you can be the smartest one around but one would still succumb to the elements.
He also speaks of aggression. There the question is, is aggression borne of a competitive psychology that embraces risk innately because it evolved to embrace risk in a competitive environment where resources are scarce, or is aggression an opportunistic seizure of free resources from the weak and helpless.
A criminal who sees an old lady and pushes her to the ground to steal her purse is not the same as a Marine who proceeds to selflessly storm enemy lines and kill fifteen men with his bare hands simply to try and save his fellow Marines in battle. The criminal will seek out the weak and vulnerable to victimize safely for personal gain, while the Marine would find that in conflict with his nature. The Marine will sacrifice himself for his group and nothing more, while the criminal would view that as pointless and stupid. Those are two vastly different forms of aggression.
Aggression and violence can be principled and daring, or opportunistic and cowardly. Each is driven by a different psychology, and you can see this difference extend to sexual drive, promiscuity, and even rearing investments. I think there needs to be a difference cited there. One aggressive psychology is r and one is K. One is designed to take free resources in a world with no consequences, while the other is programmed to fight with anyone to try and get a share of scarce resources, because if they didn’t they would starve.
I speak of aggression in regards to testosterone and Richard Lynn’s claims that gonadotropin levels and testosterone lend further support for Rushton’s theory. However, I’ve falsified Ross et al (1986) numerous times. Further, the correlation between testosterone and physical aggression is a pitiful .08 (Archer, Graham-Kevan, and Lowe 2005). The point is that testosterone is not related to aggression, nor crime. Furthermore, the time of day that crime is committed at the highest rates for teens (3 pm) and adults (10 pm) discredit the testosterone-causing-crime theory since testosterone levels are highest at 8 am and lower at 8 pm. You did not address my arguments on testosterone—try again.
Then there is disease. Disease can be r or K, depending on epidemiology. If a disease is sexually transmitted, it is going to take out those with a high sex drive, promiscuity, and reduced disgust. That doesn’t means the disease is K-selecting, so much as it preferentially kills those with an r-selected psychology, and fosters the rise of K.
What about if a disease is endemic? Endemic disease (Rushton’s assertion) is an agent of K, this is not up for discussion. Endemic disease reduces carrying capacity and thusly is an agent of K-selection.
This is simple enough to understand, especially if you understand r/K selection theory.
On the other hand, if a disease infects and kills randomly, such as one transmitted by mosquito, then it will open up free resources by killing the population back below the carrying capacity. That will favor the rise of the r-selected psychologies.
Nope.
I have found the vast majority are written by individuals looking to create quick rules of thumb for much more complex variables that can only be looked at in the context of the mechanisms they are a part of. In many cases, I see authors claiming something is always r or K, when the truth is they are more often the opposite for reasons which the authors seem strangely blind to.
The vast majority of what was written about r/K in its heyday was written by biologists and ecologists. Why reduce a complex biological system interacting with its almost equally complex environment down to a discredited theory? It doesn’t make sense to reduce what organisms do to some ‘simple model’ when the real world—and by proxy ecological theories—are much more complex than a ‘simple model’.
r and K are simple adaptation to either free or limited resource availabilities. To understand how the environment affects the evolution of r and K psychologies, you have to understand that those adaptations to free or limited resources imbue certain psychological predispositions. Once imbued, all other selective pressures have to be examined with an eye to how they either confer advantage or disadvantage on those who express those psychological traits.
r/K selection theory is based on density-dependence and density-independence. As a matter of fact, searching for ‘density-dependent‘ brings up no hits and for ‘density-independent‘, the only hit is for your response to my article. Which makes me believe that you don’t understand r/K selection theory since it’s based on density-dependence and density-independence. It’s also impossible to predict which life history traits will be favored by selection unless you know which particular ecological factors influence life history traits as well as needing a model as to how they function (Anderson, 1991). Rushton did neither, and so he was wrong with his application of r/K to human races.
A sexually transmitted disease that savages a population will open up resource availability and reduce the population well below the carrying capacity, and thus could be mistaken for an r-selecting pressure. But if it wipes out every promiscuous r-strategist, and leaves behind only the monogamous K-strategists, then it is not an r-selective pressure at all. It is favoring the K-psychology, even as from a raw numerical standpoint it would appear an r-pressure.
Which STD? Which population(s)? Source? Even then, STDs such as chancroid (in the US and Europe) were endemic in the early 20th century (Aral, Fenton, and Holmes, 2007). Which populations are you describing? An event like that would be part of the density-dependence aspect of what r/K described. The population would dip and then go right back to environmental carrying capacity (K).
It is necessary—for a K-selected history—to have some sort of density-dependent pressure. Density-dependent pressures are things such as endemic disease in Africa—which is necessary for a K-selected history since density-dependent natural selection occurs at or close to the environmental carrying capacity (Anderson, 1991: 58). If you truly understood r/K selection theory, you’d understand how it’s based on density dependence. You’d understand that ‘r’ and ‘K’ are not adjectives.
(Indeed, I suspect a golden age in the context of human history will be found to often be such an unusual circumstance, where a population is K-ified, even as it is placed in an r-selected environment of free resource availability. The opposite, an r-ified population placed in a grossly overpopulated environment of shortage will be found to reliably be Hell on earth. Guess which one we have coming.)
You should learn about what r/K selection really is (it is density-dependent selection).
The complete absence of that type of detailed understanding of the effects of selective pressures in the literature about r/K Selection Theory is why I don’t waste extensive time here quoting the source texts on the subject. Most seem strangely shallow in their analyses.
It is detailed, see the table above. Where does alpha-selection fit into your theory? Are conservatives alpha-selected? Not speaking about alpha-selection throws a wrench into the theory. The r/K continuum doesn’t even exist!
I am amused to see the author mention r/K Selection Theory has been linked to ideology, without any mention of where. My greatest hope has always been that r/K Theory would become so ever present in the dialog that nobody would remember where it first arose. When that happens, r/K will be everywhere, and nobody will have any idea who to blame.
Well, the ‘one’s to blame’ would be the originators of the theory, MacArthur and Wilson. But r/K selection is a dead concept in biology and population ecology. Don’t worry, r/K selection is dead and isn’t coming back. I’ve shown how it’s a discredited model.
In regards to r/K being falsified, when the theory was tested, key life history variables did not conform to the predictions of the theory (Graves, 2002: 137). People should stop pushing discredited theories.
By the way, in regards to the one comment that was left, why breakdown complex biological interactions with the environment into something so simple? Can you explain to me how and why complex biological systems interacting with their environment can be broken down ‘simply’? You, as well, have no idea what r/K selection is either.
Anonymous Conservative should try to be aware of his political biases. That much is clear. Although, now I know what will happen. We will see a case of the backfire effect where these corrections will increase his misconceptions of r/K selection theory (Nyhan and Reifler, 2012). Everyone should try keep this quote in mind at all times:
When you are studying any matter, or considering any philosophy, ask yourself only what are the facts and what is the truth that the facts bear out. Never let yourself be diverted either by what you wish to believe, or by what you think would have beneficent social effects if it were believed. But look only, and solely, at what are the facts. That is the intellectual thing that I should wish to say. —Bertrand Russel, 1959
The ENA Theory: On Testosterone and Aggressive Behavior by Race/Ethnicity
3250 words
A commenter by the name of bbloggz alerted me to a new paper by Lee Ellis published this year titled Race/ethnicity and criminal behavior: Neurohormonal influences in which Ellis (2017) proposed his theory of ENA (evolutionary neuroandrogenic theory) and applied it to racial/ethnic differences in crime. On the face, his theory is solid and it has great explanatory power for the differences in crime rates between men and women, however, there are numerous holes in the application of the theory in regards to racial/ethnic differences in crime.
In part I, he talks about racial differences in crime. No one denies that, so on to part II.
In part II he talks about environmental causes for the racial discrepancies, that include economic racial disparities, racism and societal discrimination and subordination, a subculture of violence (I’ve been entertaining the honor culture hypothesis for a few months; Mazur (2016) drives a hard argument showing that similarly aged blacks with some college had lower levels of testosterone than blacks with less than high school education which fits the hypothesis of honor culture. Though Ellis’ ENA theory may account for this, I will address this below). However, if the environment that increases testosterone is ameliorated (i.e., honor culture environments), then there should be a subsequent decrease in testosterone and crime, although I do believe that testosterone has an extremely weak association with crime, nowhere near high enough to account for racial differences in crime, the culture of honor could explain a good amount of the crime gap between blacks and whites.
Ellis also speaks about the general stress/strain explanation, stating that blacks have higher rates of self-esteem and Asians the lowest, with that mirroring their crime rates. This could be seen as yet another case for the culture of honor in that blacks with a high self-esteem would feel the need to protect their ‘name’ or whatever the case may be and feel the need for physical altercation based on their culture.
In part III, Ellis then describes his ENA theory, which I don’t disagree with on its face as it’s a great theory with good explanatory power but there are some pretty large holes that he rightly addresses. He states that, as I have argued in the past, females selected men for higher rates of testosterone and that high rates of testosterone masculinize the brain, changing it from its ‘default feminine state’ and that the more androgens the brain is exposed to, the more likely it is for that individual to commit crime.
Strength
Ellis cites a study by Goodpaster et al (2006) in which he measured the races on the isokinetic dynamometry, pretty much a leg extension. However, one huge confound is that participants who did not return for follow-up were more likely to be black, obese and had more chronic disease (something that I have noted before in an article on racial grip strength). I really hate these study designs, but alas, it’s the best we have to go off of and there are a lot of holes in them that must be addressed. Though I applaud the researchers’ use of the DXA scan (regular readers may recall my criticisms on using calipers to assess body fat in the bench press study, which was highly flawed itself; Boyce et al, 2014) to assess body fat as it is the gold standard in the field.
Ellis (2017: 40) writes: “as brain exposure to testosterone surges at puberty, the prenatally-programmed motivation to strive for resources, status, and mating opportunities will begin to fully activate.” This is true on the face, however as I have noted the correlation between physical aggression and testosterone although positive is low at .14 (Archer, 1991; Book et al, 2001). Testosterone, as I have extensively documented, does cause social dominance and confidence which do not lead to aggression. However, when other factors are coupled with high testosterone (as noted by Mazur, 2016), high rates of crime may occur and this may explain why blacks commit crime; a mix of low IQ, high testosterone and low educational achievement making a life of crime ‘the smart way’ to live seeing as, as Ellis points out, and that intelligent individuals find legal ways to get resources while less intelligent individuals use illegal ways.
ENA theory may explain racial differences in crime
In part IV he attempts to show how his ENA theory may explain racial differences in crime—with testosterone sitting at the top of his pyramid. However, there are numerous erroneous assumptions and he does rightly point out that more research needs to be done on most of these variables and does not draw any conclusions that are not warranted based on the data he does cite. He cites one study in which testosterone levels were measured in the amniotic fluid of the fetus. The sample was 59 percent white and due to this, the researchers lumped blacks, ‘Hispanics’ and Native Americans together which showed no significant difference in prenatal testosterone levels (Martel and Roberts, 2014).
Umbilical cord and testosterone exposure
Ellis then talks about testosterone in the umbilical cord, and if the babe is exposed to higher levels of testosterone in vitro, then this should account for racial/ethnic differences in crime. However, the study he cited (Argus-Collins et al, 2012) showed no difference in testosterone in the umbilical cord while Rohrmann et al (2009) found no difference in testosterone between blacks and whites but found higher rates of SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin) which binds to testosterone and makes it unable to leave the blood which largely makes testosterone unable to affect organ development. Thusly, if the finding of higher levels of SHBG in black babes is true, then they would be exposed to less androgenic hormones such as testosterone which, again, goes against the ENA theory.
He also cites two more studies showing that Asian babes have higher levels of umbilical cord testosterone than whites (Chinese babes were tested) (Lagiou et al, 2011; Troisi et al, 2008). This, again, goes against his theory as he rightly noted.
Circulating testosterone
Next he talks about circulating differences in testosterone between blacks and whites. He rightly notes that testosterone must be assayed in the morning within an hour after waking as that’s when levels will be highest, yet cites Ross et al (1986) where assay times were all over the place and thusly testosterone cannot be said to be higher in blacks and whites based on that study and should be discarded when talking about racial differences in testosterone due to assay time being between 10 am and 3 pm. He also cites his study on testosterone differences (Eliss and Nyborg, 1993), but, however, just as Ross et al (1986) did not have a control for WC (waist circumference) Ellis and Nyborg (1993) did not either, so just like the other study that gets cited to show that there is a racial difference in testosterone, they are pretty hugely flawed and should not be used in discussion when discussing racial differences in testosterone. Why do I not see these types of critiques for Ross et al (1986) in major papers? It troubles me…
He also seems to complain that Lopez et al (2013) controlled for physical activity (which increases testosterone) and percent body fat (which, at high levels, decreases testosterone). These variables, as I have noted, need to be controlled for. Testosterone varies and fluctuated by age; WC and BMI vary and fluctuate by age. So how does it make sense to control for one variable that has hormone levels fluctuate by age and not another? Ellis also cites studies showing that older East Asian men had higher levels of testosterone (Wu et al, 1995). Nevertheless, there is no consensus; some studies show Chinese babes have higher levels of testosterone than whites and some studies show that whites babes have higher levels of testosterone than Chinese babes. Indeed, this meta-analysis by Ethnicmuse shows that Asians have the highest levels, followed by Africans then Europeans, so this needs to be explained to save the theory that testosterone is the cause of black overrepresentation of violence (as well as what I showed that testosterone is important for vital functioning and is not the boogeyman the media makes it out to be).
Bone density and crime
Nevertheless, the next variable Ellis talks about is bone density and its relationship to crime. Some studies find that blacks are taller than whites while other show no difference. Whites are also substantially taller than Asian males. Blacks have greater bone density than the other three races, but according to Ellis, this measure has not been shown to have a relationship to crime as of yet.
Penis size, race and crime
Now on to penis size. In two articles, I have shown that there is no evidence for the assertion that blacks have larger penises than whites. However, states that penis length was associated with higher levels of testosterone in Egyptian babes. He states that self-reported penis size correlates with self-reports of violent delinquency (Ellis and Das, 2012). Ellis’ main citations for the claim that blacks have larger penises than other races comes from Nobile (1982), the Kinsey report, and Rushton and Boagert (1987) (see here for a critique of Rushton and Boagert, 1987), though he does cite a study stating that blacks had a longer penis than whites (blacks averaging 5.77 inches while whites averaged 5.53 inches). An HBDer may go “Ahah! Evidence for Rushton’s theory!”, yet they should note that the difference is not statistically significant; just because there is a small difference in one study also doesn’t mean anything for the totality of evidence on penis size and race—that there is no statistical difference!
He then cites Lynn’s (2013) paper which was based on an Internet survey and thus, self-reports are over-measured. He also cites Templer’s (2002) book Is Size Important?, which, of course, is on my list of books to read. Nevertheless, the ‘evidence’ that blacks average larger penises than whites is extremely dubious, it’s pretty conclusive that the races don’t differ in penis size. For further reading, read The Pseudoscience of Race Differences in Penis Size, and read all of Ethnicmuses’ posts on penis size here. It’s conclusive that there is no statistical difference—if that—and any studies showing a difference are horribly flawed.
2d/4d ratio and race
Then he talks about 2d/4d ratio, which supposedly signifies higher levels of androgen exposure in vitro (Manning et al, 2008) however these results have been challenged and have not been replicated (Koehler, Simmons, and Rhodes, 2004; Yan et al, 2008, Medland et al, 2010). Even then, Ellis states that in a large analysis of 250,000 respondents, Asians had the lowest 2d/4d ratio, which if the hypothesis of in vitro hormones affecting digit length is to be believed, they have higher levels of testosterone than whites (the other samples had small ns, around 100).
Prostate-specific antigens, race, and prostate cancer
He then talks about PSA (prostate-specific antigen) rates between the races. Blacks are two times more likely to get prostate cancer, which has been blamed on testosterone. However, I’ve compiled good evidence that the difference comes down to the environment, i.e., diet. Even then, there is no evidence that testosterone causes prostate cancer as seen in two large meta-analyses (Stattin et al, 2003; Michaud, Billups, and Partin, 2015). Even then, rates of PCa (prostate cancer) are on the rise in East Asia (Kimura, 2012; Chen et al, 2015; Zhu et al, 2015) which is due to the introduction of our Western diet. I will cover the increases in PCa rates in East Asia in a future article.
CAG repeats
He then reviews the evidence of CAG repeats. There is, however, no evidence that the number of CAG repeats influences sensitivity to testosterone. However, intra-racially, lower amounts of CAG repeats are associated with higher spermatozoa counts—but blacks don’t have higher levels of spermatozoa (Mendiola et al, 2011; Redmon et al, 2013). Blacks do have shorter CAG repeats, and this is consistent with the racial crime gap of blacks > whites > Asians. However, looking at the whole of the evidence, there is no good reason to assume that this has an effect on racial crime rates.
Intelligence and education
Next he talks about racial differences in intelligence and education, which have been well-established. Blacks did have higher rates of learning disabilities than whites who had higher levels of learning disabilities then Asians in a few studies, but other studies show whites and South Asians having different rates, for instance. He then talks about brain size and criminality, stating that the head size of males convicted for violent crimes did not differ from males who committed non-violent crimes (Ikaheimo et al, 2007). I won’t bore anyone with talking about what we know already: that the races differ in average brain size. However, a link between brain size and criminality—to the best of my knowledge—has yet to been discovered. IQ is implicated in crime, so I do assume that brain size is as well (no matter if the correlation is .24 or not; Pietschnig et al, 2015).
Prenatal androgen exposure
Now to wrap things up, the races don’t differ in prenatal androgen exposure, which is critical to the ENA theory; there is a small difference in the umbilical cord favoring blacks, and apparently, that predicts a high rate of crime. However, as noted, blacks have higher levels of SHBG at birth which inhibits the production of testosterone on the organs. Differences in post-pubertal testosterone are small/nonexistent and one should not talk about them when talking about differences in crime or disease acquisition such as PCa. DHT only shows a weak positive correlation with aggression—the same as testosterone (Christiansen and Winkler, 1992; however other studies show that DHT is negatively correlated with measures of physical aggression; Christiansen and Krussmann, 1987; further, DHT is not so evil after all).
Summing it all up
Blacks are not stronger than whites, indeed evidence from the races’ differing somatype, grip strength and leverages all have to do with muscular strength. Furthermore, the study that Ellis cites as ‘proof’ that blacks are stronger than whites is on one measure; an isokinetic dynamometry machine which is pretty much a leg extension. In true tests of strength, whites blow blacks away, which is seen in all major professional competitions all around the world. Blacks do have denser bones which is due to androgen production in vitro, but as of yet, there has been no research done into bone density and criminality.
The races don’t differ on penis size—and if they do it’s by tenths of an inch which is not statisitcally significant and I won’t waste my time addressing it. It seems that most HBDers will see a racial difference of .01 and say “SEE! Rushton’s Rule!” even when it’s just that, a small non-significant difference in said variable. That’s something I’ve encountered a lot in the past and it’s, frankly, a waste of time to converse about things that are not statistically significant. I’ve also rebutted the theory on 2d/4d ration as well. Finally, Asians had a similar level of androgen levels compared to blacks, with whites having the least amount. Along with a hole in the theory for racial differences in androgen causing crime, it’s yet another hole in the theory for racial differences in androgens causing racial differences in penis size and prostate cancer.
On intelligence scores, no one denies that blacks have scored about 1 SD lower than whites for 100 years, no one denies that blacks have a lower educational attainment. In regards to learning disabilities, blacks seem to have the highest rates, followed by Native Americans, than non-Hispanic whites, East Asians and the lowest rates found in South Asians. He states only one study links brain size to criminal behavior and it showed a significant inverse relationship with crime but not other types of offenses.
This is a really good article and I like the theory, but it’s full of huge holes. Most of the variables described by Ellis have been shown to not vary at all or much between the races (re: penis size, testosterone, strength [whites are stronger] prostate cancer caused mainly by diet, 2d/4d ratio [no evidence of it showing a digit ratio difference], and bone density not being studied). Nevertheless, a few of his statements do await testing so I await future studies on the matter. He says that androgen exposure ‘differs by race and ethnicity’, yet the totality of evidence shows ‘not really’ so that cannot be the cause of higher amounts of crime. Ellis talks about a lot of correlates with testosterone, but they do not pass the smell test. Most of it has been rebutted. In fact, one of the central tenets of the ENA theory is that the races should differ in 2d/4d ratio due to exposure of differing levels of the hormone in vitro. Alas, the evidence to date has not shown this—it has in fact shown the opposite.
ENA theory is good in thought, but it really leaves a lot to be desired in regards to explaining racial differences in crime. More research needs to be looked into in regards to intelligence and education and its effect on crime. We can say that low IQ people are more likely to drop out of school and that is why education is related to crime. However, in Mazur (2016) shows that blacks matched for age had lower levels of testosterone if they had some college under their belt. This seems to point in the direction of the ENA theory, however then all of the above problems with the theory still need to be explained away—and they can’t! Furthermore, one of the nails in the coffin should be this: East Asian males are found to have higher levels of testosterone than white males, often enough, and East Asian males actually have the lowest rate of crime in the worle!
This seems to point in the direction of the ENA theory, however then all of the above problems with the theory still need to be explained away—and they can’t! Furthermore, one of the nails in the coffin should be this: East Asian males are found to have higher levels of testosterone than white males, often enough, and East Asian males actually have some of the lowest rate of crime in the world (Rushton, 1995)! So this is something that needs to be explained if it is to be shown that testosterone facilitates aggression and therefore, crime.
Conclusion
I’ve shown—extensively—that there is a low positive correlation between testosterone and physical aggression, why testosterone does not cause crime, and have definitively shown that, by showing how flawed the other studies are that purport to show blacks have higher testosterone levels than whites, along with citing large-scale meta-analyses, that whites and blacks either do not differ or the differences is small to explain any so-called differences in disease acquisition or crime. One final statement on the CAG repeats, they are effect by obesity, men who had shorter CAG repeats were more likely to be overweight, which would skew readings (Gustafsen, Wen, and Koppanati, 2003). So depending on the study—and in most of the studies I cite whites have a higher BMI than blacks—BMI and WC should be controlled for due to the depression of testosterone.
It’s pretty conclusive that testosterone itself does not cause crime. Most of the examples cited by Ellis have been definitively refuted, and his other claims lack evidence at the moment. Even then, his theory rests on the 2d/4d ratio and how blacks may have a lower 2d/4d ratio than whites. However, I’ve shown that there is no significant relationship between 2d/4d ratio and traits mediated by testosterone (Kohler, Simmons, and Rhodes, 2004) so that should be enough to put the theory to bed for good.
Why Testosterone Does Not Cause Crime
1900 words
Edit: (The correlation between aggression and testosterone isn’t .14 as Book et al (2001) state; the true correlation is .08 (Archer, Graham-Kevan and Davies, 2005) So it’s even lower than I thought. This is one of the many reasons why testosterone does not cause crime. It’s just feminist bullshit and fear mongering from people who do not understand the hormone and what it does in the body. The misconceptions come from Rushton’s r/K selection bullshit which has been summarily refuted.)
Recently, I’ve written at length on racial differences in testosterone and how the correlation between testosterone and physical aggression is .14. Pitifully low to account for the cause of crime and any overall differences in racial crime (that will be touched on at length in the future). Tonight I will show, yet again, why testosterone does not cause crime by looking at what times most crimes are committed by both adults and children under the age of 18. This will definitively put the ‘testosterone causes crime’ myth to bed for good.
Before I get into the time of day that most crimes are committed, I must talk about the production of testosterone in the body. There are no ‘genes for’ testosterone (although men who had three certain alleles had a 6.5 fold higher risk of having low testosterone; Ohlsson et al, 2011, I am unaware of there being a variation by race; over 10,000 Caucasian men were studied). There is, however, an indirect control of testosterone synthesis by DNA. DNA regulates the production of testosterone by coding for enzymes that convert cholesterol to testosterone (testosterone is a cholesterol-based hormone).
There are five simple steps to the production of testosterone: 1) DNA codes for mRNA; 2) mRNA codes for the synthesis of an enzyme in the cytoplasm; 3) luteinizing hormone stimulates the production of another messenger in the cell when testosterone is needed; 4) this second messenger activates the enzyme; 5) the enzyme then converts cholesterol to testosterone (Leydig cells produce testosterone in the presence of luteinizing hormone). That’s how testosterone is produced in the body. It is indirectly controlled by DNA.

Above is a graph from the Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention which shows the time of day that most crimes are committed. Notice how crime goes up as the time of day goes on and since kids are at school, they’re more likely to fight. This then peaks at 3 pm when kids are getting out of school.
Now look at rates of crime for adults. At its peak of 10 pm, it’s vastly lower than that of people under the age of 18, which is important to keep in mind. You can see how at 8 am that rates of crime are low for adults and high for kids, right when they would be entering school so there would be a lot of other kids around and the chance for violence goes up. Keep the times of 8 am (kids when they enter school), 12 pm (when most kids go on lunch) and 3 pm (when most kids get out of school) along with the hours of 12 pm to 8 pm for adults (when 74 percent of crimes are committed by adults).
- In general, the number of violent crimes committed by adults increases hourly from 6 a.m. through the afternoon and evening hours, peaks at 10 p.m., and then drops to a low point at 6 a.m. In contrast, violent crimes by juveniles peak in the afternoon between 3 p.m. and 4 p.m., the hour at the end of the school day.
- Nearly one-third (29%) of all violent crime committed by juvenile offenders occurs between 3 p.m. and 7 p.m. In comparison, 26% of all violent committed by adult offenders occurs between 8 p.m. and 12 p.m.
So since testosterone varies by day and levels are highest at 8 am and lowest at 8 pm (Brambilla et al, 2009; however testing men aged 45 years of age and older is fine before 2 pm due to a blunted circadian rhythm; Long, Nguyen, and Stevermer, 2015), then how could testosterone account for why men commit most of their crimes at night and why the crime that children commit spikes when they go to school, go to lunch and get out of school? The answer is that it doesn’t because testosterone does not cause crime. What testosterone does cause, however, are feelings of confidence and dominance, which does not—surprisingly—lead to increased aggression and assault on others (Booth et al, 2006).
What testosterone does cause, however, is social dominance and success, not physical aggression and maladjustment (Shcaal et al, 1996). The effects of environment are also more notable on testosterone than are genetics at 5 months of age (Carmaschi et al, 2010). Furthermore, aggressive behavior is first noticed in infancy and reaches its peak before school age (Tremblay et al, 2004; Cote et al, 2006). Though testosterone does seem to have an effect on aggression in preschool boys, however genetic and environmental causality has not been established (Sanchez-Martin et al, 2000).
Nevertheless, the meta-analyses I cited last week show that testosterone has an extremely low correlation of .14, so other factors must be at play. However, Sanchez-Martin et al (2000:778-779) also note that “Tremblay et al (1998) suggested that associations between testosterone titer and physical aggression are likely to be observed in contexts where such attack leads to social dominance. This may be true of the preschool boys in the present study. The data generated in the present study generally support Scerbo and Kolko (1994), who studied older children (7 to 14 years of age). They found a significant relationship between testosterone levels and aggression (as assessed by clinical staff).”
It’s interesting to note that in the case of Scerbo and Kolko (1994) that after controlling for age and size, testosterone correlated with aggression when rated by staff but not parents or teachers. ‘Staff’ refers to clinic staff at a facility where the children were assessed for hyperactivity disorders. Of course, the staff would rate higher levels of aggression compared to parents of teachers—people who are around the children every day—since they would want a higher chance for diagnosis for certain drugs to ‘cure’ the hyperactivity, but I digress. Testosterone does not induce aggression in children, but it does induce social dominance and confidence which does not lead to aggression (Rowe et al, 2004; Booth et al, 2006).
There was also little difference in testosterone between socially dominant prisoners and aggressive prisoners (Ehrenkraz, Bliss, and Sheard, 1974). Furthermore, the testosterone increase leading to pubertal development in boys is not associated with increased aggression (Tremblay et al, 1998; Booth et al, 2006: 171). Indeed, increased body size is a marker for physical aggression in children, and I doubt these children have high muscle mass so, I assume, they have high levels of body fat and thusly lower levels of testosterone than they would have if they were leaner. Yet another strike against the ‘testosterone causes crime/physical aggression’ hypothesis.
Indeed, this has some implications for the honor culture hypothesis of why low-income blacks have higher levels of testosterone than similarly aged blacks with some college (Mazur, 2016). The patterns for crime as shown by the OOJDP shows that crime rises as the day progresses from the morning until its peak at 3 pm for children and then sharply declines while for adults it peaks at 10 pm.
Testosterone does increase when a challenge is issued; when one man feels his reputation is threatened, the propensity for violence is increased, but this was most notably seen in Southern men (Cohen et al, 1996). So the same would be said for this ‘culture of honor’ found in low-income black neighborhoods, the so-called ‘code of the street’ as stated by Anderson (1994: 88): “Moreover, if a person is assaulted, it is important, not only in the eyes of his opponent but in the eyes of his “running buddies,” for him to avenge himself. Otherwise, he risks being “tried” (challenged) or “moved on” by any number of others. To maintain his honor, he must show he is not someone to be “messed with” or “dissed.””
This culture of honor is found all over the world, including Brazil where homicide can be explained by the need to maintain honor and can be understood by taking into account cultural factors; biological, psychological and socioeconomic factors do not explain murder in Northeast Brazil as well as honor and culture (de Souza et al, 2015). People in honor cultures also have a higher chance of self-harm (Osterman and Brown, 2011) as well as a higher chance of committing violence in school (Brown, Osterman, and Barnes, 2009).
Testosterone does not cause crime; it does not cause aggression. Increases in testosterone before, during and after events are a physiologic process to prime the body for competition. As cited above, dominant behavior does not necessarily lead to violence in most cases, which may be surprising for some. Indeed, honor and culture may explain a nice amount of the homicide and violence rate in the South. Since testosterone is highest at 8 am and lowest at 8 pm and the rates of crime committed by adults and children are vastly different than the diurnal variance in the day, then testosterone does not cause crime and its increase is not associated with crime, but social dominance and confidence which does not lead to crime.
Hopefully—if anyone still believes testosterone to be the boogeyman its made out to be—I’ve put those misconceptions to rest. Racial differences in testosterone cannot be the cause of racial differences in crime—because there is either no statistical difference in testosterone between the races or the difference is non-existent. Testosterone is clearly a beneficial hormone—as I have extensively documented. Misunderstandings of the hormone are abound—especially in the HBD sphere—only due to literally a few paragraphs in a book (Rushton, 1997) and one study that showed blacks have higher testosterone than whites which was the cause of their higher rates of prostate cancer (Ross et al, 1986). The study is hard to find so I had to buy access to it. I will cover this in the future, but I discovered that they assayed the subjects when it was convenient for them—between the hours of 10 am and 3 pm—which is unacceptable. You cannot gauge racial differences in testosterone from a small study (n=50) and a non-representative sample (college students). For these reasons, the study should be thrown in the trash—especially when formulating evolutionary hypotheses.
Testosterone is one of the most important hormones for vital functioning. By knowing how it is processed in the body and that there are no ‘genes for’ testosterone (‘low testosterone genes’ notwithstanding) along with how testosterone has a low relationship with physical aggression one should not be scared of having high levels, on the contrary, one should be scared of having low levels. I have once again proven my case that testosterone is not related to violence in showing the diurnal variation in testosterone levels in adults, as well as the time of day that crimes are committed by both adults and children. High testosterone means high confidence and high dominance—and those two traits have a lot to do with masculinity—which do not lead to violence.
I know why testosterone does not cause crime—because I have an understanding of the hormone, how its produced in the body and what its effects on the body are. The most important thing to note here, is that even if blacks had 15 percent higher testosterone than whites, it still wouldn’t explain higher rates of crime or disease such as prostate cancer. So those who try so hard to prove that blacks have higher levels of the hormone do so in vain, because even if they did it wouldn’t mean anything for any theories they may have. The myth of testosterone causing aggression and crime need to be put to bed for good.