More g Denialism and more Gould Refuting
1750 words
It seems like every day something new comes out that attempts to discredit the reality of g (This paper came out in 2012.). Steven Jay Gould (in)famously wrote in The Mismeasure of Man:
The argument begins with one of the fallacies—reification, or our tendency to convert abstract concepts into entities (from the Latin res, or thing). We recognize the importance of mentality in our lives and wish to characterize it, in part so that we can make the divisions and distinctions among people that our cultural and political systems dictate. We therefore give the word “intelligence” to this wondrously complex and multifaceted set of human capabilities. (emphasis mine)
Which is the same thing that the researchers of the paper Fractioning Human Intelligence said to The Independent:
“The results disprove once and for all the idea that a single measure of intelligence, such as IQ, is enough to capture all of the differences in cognitive ability that we see between people,”
“Instead, several different circuits contribute to intelligence, each with its own unique capacity. A person may well be good in one of these areas, but they are just as likely to be bad in the other two,”
Just like The Mismeasure of Man is “the definitive refutation to the argument of The Bell Curve”, right?
In the above paper, they cite Gould twice writing:
It remains unclear, however, whether population differences in intelligence test scores are driven by heritable factors or by other correlated demographic variables such as socioeconomic status, education level, and motivation (Gould, 1981; . . .
They have been shown over numerous studies that population differences in intelligence are driven by heritable factors (Rushton and Jensen, 2005; Lynn and Vanhanen, 2006; Winick, Meyer, and Harris, 1975; Frydman and Lynn, 1988; Rushton, 2005)
More relevantly, it is questionable whether they relate to a unitary intelligence factor, as opposed to a bias in testing paradigms toward particular components of a more complex intelligence construct (Gould, 1981;
I will prove the existence of g in this article. There is also an empirical basis for the g factor.
It’s getting old now that researchers still think that they can “disprove g”, as a multitude of studies have already corroborated Spearman’s hypothesis as an empirical fact. That is, applying the scientific method, using the same hypothesis over a multitude of different studies and testing those predictions by experiment or further observation and modify the hypothesis when new information comes to light. Then, repeat the aforementioned steps until there are no discrepancies between the theory and experiment/observations.Then when consistency is obtained it then becomes a theory that provides a coherent set of premises that explain a class of events.
How many times has the Hampshire et al hypothesis been corroborated? I doubt it has been corroborated as many times as Spearman’s hypothesis has.
As I said the other day, Jensen tested Spearman’s hypothesis on 25 large independent samples, with each sample confirming Spearman’s hypothesis. Even matching blacks and whites for SES didn’t diminish the effect. Jensen then concludes that the overall chance for Spearman’s hypothesis being wrong is over 1 in a billion. Pretty high odds.
Even then, if this study were to be replicated the amount of times that Spearman’s hypothesis has, it still wouldn’t disprove g.
On page 558-559 of the Afterword to The Bell Curve, Charles Murray responds to many of Gould’s criticisms of the book. He writes:
He (Gould) continues: “The fact that Herrnstein and Murray barely mention the factor-analytic argument forms a central indictment around The Bell Curve and is an illustration of its vacuousness.” Where, Gould asks, is the evidence that g “captures a real property in the head?
Murray states that they “barely brought up the factor-analytical argument” because it was out of date; Gould was using statistics on g that were 50 + years old. Also, a reviewer of his book for the journal Nature said that Gould’s “discussion of the theory of intelligence stops at the stage it was more than a quarter of a century ago.” Gould was using old arguments, and, as Arthur Jensen states in his response to Gould:
Of all the book’s references, a full 27 percent precede 1900. Another 44 percent fall between 1900 and 1950 (60 percent of those are before 1925); and only 29 percent are more recent than 1950.
More than half of Gould’s references in The Mismeasure of Man are outdated by more than 50 years. Clearly, he was attempting to denigrate the old studies of intelligence, i.e., phrenology, even though this recent paper in the journal Nature recently said:
The genomic regions identified include several novel loci, some of which have been associated with intracranial volume
So, we have several loci that are associated with intracranial volume; this shows that those skull studies of yesteryear weren’t crazy. Moreover, the fact that Rushton and Ankney (1996) “reviewed 32 studies correlating measures of external head size with IQ scores or with measures of educational and occupational achievement, and they found a mean r .20 for people of all ages, both sexes, and various ethnic backgrounds, including African Americans” shows that there is a correlation of .20, albeit not too high but there, with external head size and IQ. This shows that Gould’s argument on phrenology is bunk, as modern studies confirm that there is a slight correlation between head size and IQ, and therefore g.
The fact that researchers are still bringing up Gould’s arguments on g show that there really is no good argument to discount it. Basically, any and all arguments that attempt to discredit g are bunk as Spearman’s hypothesis has been empirically verified:
Conclusion: Mean group differences in scores on cognitive-loaded instruments are well documented over time and around the world. A meta-analytic test of Spearman’s hypothesis was carried out. Mean differences in intelligence between groups can be largely explained by cognitive complexity and the present study shows clearly that there is simply no support for cultural bias as an explanation of these group differences. Comparing groups, whether in the US or in Europe, produced highly similar outcomes.
Along with Jensen’s 25 large independent studies that showed that the probability that Spearman’s hypothesis is false is 1 in a billion, this proves that Spearman’s hypothesis is an empirical scientific fact.
Newman and Just, (2005) state in verbal and spatial conditions that the frontal cortex revealed greater activation for high-g in comparison to low-g, supporting the idea that g reflects functions of the frontal lobe. The “seat” of general intelligence is the prefrontal cortex (Cole, et al, 2011, Roth, 2011). This can also be verified with MRI scans that show that those who have higher g have bigger prefrontal cortexes than those with lower g.
Moreover, the fact that Colom, et al (2006) show that in their sample that neuroanatomic areas underlying the g factor could be found across the entire brain including the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes, shows that this factor is present throughout the brain and all are correlated with g and work together in concert to manifest intellectual ability.
Other researchers have also used the method of correlated vectors on functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), which measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique is proven useful due to the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal action are correlated. Lee, et al write:
In conclusion, we suggest that higher order cognitive functions, such as general intelligence, may be processed by the coordinated ability may be attributable to the functional facilitation rather than the structural peculiarity of the neural network for g. In addition, our results demonstrated that the posterior parietal regions including bilateral SPL and right IPS could be the neural correlates for superior general intelligence. These findings would be the early step toward the development of biological measures of g which leads to new perspectives for behavior interventions improving general cognitive ability.
They also used the MCV to find that the frontal and parietal lobes are associated with g. Even these studies show that g shows up throughout the brain and not in one solitary spot (though, the PFC is still the seat of intelligence), this shows yet another biological basis for g.
Hampshire, et al write:
Thus, these results provide strong evidence that human intelligence is a construct that emerges from the functioning of anatomically dissociable brain networks.
However, with the above studies confirming that the seat of intelligence is the prefrontal cortex, along with great g ability possibly be attributable to the functional facilitation rather than the structural peculiarity of the neural network for g, this shows, along with the study proving Spearman’s hypothesis, that g is a real and measurable thing. g’s seat is the prefrontal cortex, and exceptional g may possibly be attributed to the functional facilitation of the neural network for g . What all of these studies show is that all though the Hampshire paper showed how they “demonstrate that different components of intelligence have their analogs in distinct brain networks.” that a) higher order cognitive functions may be processed by the coordinated activation of widely distributed brain areas (disproving the above quote), b) the seat of g is the prefrontal cortex, c) those with more g have bigger prefrontal cortexes and therefore bigger brains since the prefrontal cortex is the ‘seat’ of intelligence and d) Spearman’s hypothesis has been corroborated numerous times by many different researchers not named Arthur Jensen.
Highfield (one of the researchers in the study) ends the article as follows:
“We already know that, from a scientific point of view, the notion of race is meaningless. Genetic differences do not map on to traditional measurements of skin colour, hair type, body proportions and skull measurements.
This is something that never ends; it always comes up no matter how many times it’s been said. People can say “race is a social construct” all they want, it doesn’t make it true as there is a biological reality to race.
Now we have shown that IQ is meaningless too,” Dr Highfield said.
IQ is not biased, nor is it “meaningless“.
When will people learn not to cite men who have smeared their legacy in an attempt to defame men who they disagreed with ideologically? Citing Steven Jay Gould in 2016 shows a bias to want to discredit g as a main factor for many things in life including SES, educational attainment, wealth attainment and so forth. The g factor is a measurable thing, with the seat of the factor being the prefrontal cortex. No amount of attempting to dispute this factor can be done, as it’s been empirically verified numerous times.
Ethnic Genetic Interests and Group Selection Does Exist: A Reply to JayMan
6350 words
JayMan has said that ““Ethnic Genetic Interests” Do Not Exist (Neither Does Group Selection)“. It’s clear from what he says towards the end that he has some sort of bias to attempt to disprove Ethnic Genetic Interests and Group Selection. This will be a definitive refutation of JayMan’s belief of the non-existence of GST and GS. Along with Dr. Swaggins from the CoonU Blog, both of us today will prove that EGI and GS do in fact exist and that JayMan has an implicit bias in the denial of EGI and GS. I will also address JayMan’s comment to me in that same article that I never responded to save it for this article.
I first wrote an article, Genetic Similarity Theory, in reply to his denial of EGI. It was short, but I got my point across with the Price Equation. JayMan then comments:
Ethnic altruism can’t evolve through genetic similarity because the coefficient of relationship between co-ethnics (who aren’t close family) is pretty small. Even kin selection itself is pretty weak in general. How much time do you spend with your second and third cousins?
In-group favoritism likely evolved through individual selection for reciprocal altruism. Overall similarity simply allowed individuals to recognize likely partners for trading favors (shared language and customs may help). This may have even co-opted systems designed to act towards close kin – misfiring kin altruism, if you will.
Rebutting Jayman’s denial of the ethnic kinship coefficient requires an explanation of the concept of relatedness as a whole. How, for example, can I be 50% identical to my father if I’m 99.8% identical to all living humans? The answer is that I am not 50% identical to my father; rather, I am 50% identical to my father by comparison to the baseline level of relatedness of all living humans. If all living humans are 99.8% genetically identical then I’m 99.9% identical to my father. Jayman’s argument that two random co-ethnics aren’t related fails to factor this into account: a calculation of relation needs a baseline level of relatedness for comparison. So he’s correct in stating that two co-ethnics are not similar to one another- but only by comparison to the baseline level of relatedness of their entire population.
Since the ethnic kinship coefficient has been worked out to the equivalent of half siblings, it may be useful to frame the issue in those terms. If I am 25% identical to my half sibling by comparison to any other co-ethnic, it is because there is a quarter of my genome that I share with my half sibling due to our common descent. Specifically, our mutual descent from our mutual parent gives us a specific combination of genes that nobody else is likely to have. 25% of my genome is 100% identical to his alleles of the same genes and the other 75% is as similar to his as it is to any other co-ethnic, but taken as an average across my entire genome, any given allele is 25% more likely to be shared with him than it is everyone else in our race.
The ethnic kinship coefficient works in an uncannily similar way. Instead of inheriting those 25% identical genes from recent common ancestors, the two co-ethnics inherit the same genes due to the fact that people of their race usually have those genes (think melanin, keratin, microcephalin, EDAR, HERC2, or any other gene for which the frequency of alleles differs overpopulation). In spite of that difference in the origin of ethnic vs familial similarity, the mathematics are shockingly similar: according to Henry Harpending in his review paper Kinship and Population Subdivision, “Many studies agree that Fst [genetic distance between populations] in world samples of human populations is between ten and fifteen percent,” with “a conservative general figure” being 12.5%. What’s more, Fst “is computed for each allele at each locus, then averaged over all loci.” In other words, 1/8th of human genetic diversity is at the between-group level.
To put things into perspective, a 1/8th reduction in diversity within a family occurs when two half siblings (25% identical) have a child. There is a 1/16th chance that the common parent will pass a given allele to both children and that both children will pass that allele to their child, and a 1/16th chance for the same to occur for the other allele of the same gene; when computed allele for allele, “diversity” (odds of heterozygosity) goes down by 1/8th among a population that is 25% identical by descent.
One such calculation finds, for example, that a Frenchman is 24% identical to another Frenchman if your baseline for comparison is the genetic similarity between the French and Japanese.
This is the inevitable implication of the central tenet of HBD: that the various races of the world are genetically different from one another. It is also the inevitable implication of Lewontin’s famous finding that 15% of all human genetic variation is racial; if it were 100% then all co-ethnics would be identical and it were 0% then race wouldn’t exist at all. If it were 15%, though, then that 15% would be composed of genes whose alleles vary in frequency across populations; these are genes you share with co-ethnics much more often than you share with anyone else. If you’re more likely to share a lot of genes with co-ethnics than you are with anyone else, then you’re more genetically similar to co-ethnics than you are anyone else. When they sequence the genes of people of different races and compute the odds of similarity locus for locus, you’re much more likely to share some genes (ABCC11, MC1R, etc) with co-ethnics than you are others, but taken as an average across both copies of the entire genome, it’s about 25%. Apply those odds to the 20,000 or so genes in the human genome and the result will be consistent with the data that members of a given race are about 25% identical by comparison to members of other races.
We are not the first people to predict that these genetic differences would result in kin selection expressed as altruism towards co-ethnics and discrimination towards others; to quote an article by the late Henry Harpending posted in March 2012, “In the new diverse community the average person can find someone related as f~0.06, corresponding roughly to a great-grandchild at f=1/16. Suddenly there is a fitness payoff to discrimination.” (In this hypothetical population, an individual is 1/8th more related to a co-ethnic than to the average and 1/8th less related to some of a different race than to the average.) In an ethnically homogeneous population, discrimination of this kind will not occur because the fitness payoff of benefiting one co-ethnic or the other is the same, but in a heterogeneous population, you suddenly have people in whom you have comparatively more or less genetic interest. In December 2012, Harpending and Salter published “JP Rushton’s Theory of Ethnic Nepotism,” a paper predicting that the Fst data would support Rushton’s theory of ethnic genetic interest, by providing evidence for kin selection. Towards the end of this article, I will provide evidence for human altruistic behavior fitting the patterns predicted by kin selection, and I will present a likely animal model for subspecies competition over resources. In the meantime, however, there are more misconceptions to clear up.
JayMan says:
I suppose a key misunderstanding in the matter is the failure to realize that each individual gene contributes to fitness independently. Each gene is “out for itself”, so to speak. It just so happens that in any given organism, genes achieve success by working together (most of the time). As sucheach individual gene’s “aim” is to make more copies of itself. What’s going on in the rest of the genome is tangential to this. ((—>Each gene would be just as happy to mix with any other gene, so long as its own fitness is increased in the process.<—)) (Additions in last sentence for emphasis are mine)
Individual genes don’t always contribute to fitness independent of one another; the venerable Nicholas Wade has pointed out that there is at least one gene which confers different levels of selective disadvantage depending on the other genes they’re mixed up with: an allele that slightly increased risk of heart problems in Europeans causes big problems whenever it introgresses into Africans. Naturally, the population which has had this allele for longer has more genes elsewhere in the genome compensating for its negative effects, meaning that said allele will cause fitness problems after it introgresses into another population. Introgression is just a fancy word for race mixing, though, and there are other problems with it, as follows:
In a study of 100,000 mixed-race adolescent school children, those who identified themselves as such had higher health and behavior instances than those of one race. The effect was still observed even when SES and other factors were controlled for. A problem with an obvious genetic component.
Yet another study done on white-Asian mixes notes that they have a two times higher rate to be diagnosed with psychological problems such as anxiety, depression and substance abuse.
It was found, in agreement that black-white mixes engaged in more risky behavior than did monoracial children. They also observe that mixed-race adolescents are stark outliers in comparison to whites and blacks, which still holds true despite being raised in similar environments to monoracial children.
Fitness doesn’t look increased in that process, seeing how mulatto children show more health problems and negative behavior than monoracial children. And given the data relating to the allele mentioned above, we can’t rule out the possibility that health problems in biracial children arise because their parents’ genes don’t necessarily work together.
There is no impact on one’s fitness from the race of one’s mate (or an offspring’s mate) so long as close relatives are off the table as mates (aside from the fitness impact of the particular genes such mates were bringing in the environment in question). The fitness impact to a White man’s genes if his daughter marries a Black man is the same as if she married an unrelated White man (again, fitness from gene function notwithstanding).
Do you really believe that? As shown above, mixed-race children show more health and behavior problems than do monoracial children. Africans were not selected for resistance to the negative effects of certain European genes as Europeans were, and we have no reason to believe that any race is selected to compensate for the negative effects of genes they don’t even have.
Just the same, the inclusive fitness impact to a White American is the same whether he focuses his altruistic act on an unrelated White American or on a Namibian; it is zero in both cases. If you adopt children rather than have your own, the fitness hit to you is the same whether your adopted children are White, Black, Chinese, or Venezuelan.
Again, this assumes that there are no genetic differences between populations, but there are, so your fitness is probably higher if you adopt a co-ethnic than if you adopt someone else.
Hence, there is no human ethnic group that exhibits ethnic nepotism. This includes Ashkenazi Jews. But these have nothing to do with ethnic nepotism, didn’t arise via kin selection, and don’t depend on genetic relatedness per se. This includes Ashkenazi Jews.
Ashkenazi Jews evolved their nepotism through thousands of years of getting driven out of countries. Along with being barred from certain jobs, this led to them being only able to do banking jobs and those jobs that took more intellect, which they then evolved their higher IQ as well as more group favoritism to help them in societies where they are the minority. This is clearly evident today with Jewish overrepresentation at elite universities; their average IQ of 110 suggests that they shouldn’t be that much of the student body since they’re six times as likely to be geniuses but many more times likely to make it into the top institutions. Odds are pretty good that that’s ethnic nepotism in action. We’re talking about a group of people 38% likely to consider themselves religious but 70% likely to believe the old mythos that the omnipotent, omniscient creator of everything that ever existed prefers them to literally everyone else, and judge whether someone is worthy of this inconceivably lofty status purely on the basis of their genetics; before they had handy-dandy PCR machines and enzymes, Jews determined someone to be Jewish by matrilineal descent, not cultural custom. If the Ashkenazim lacked any ingroup preferences of any kind during their time in Europe, they would’ve literally copulated themselves to death by marrying Gentiles until their population was totally absorbed by ours. What would you call it then, JayMan, if not EGI? They’re one of the best examples FOR the existence of EGI. See, the thing is, if someone is an Ashkenazi Jew, more often than not, they will be more related to each other than some other random person from another population.
This particular fact – that co-ethnics share genes – is why they have a genetic interest in one another.
The Ethnic Kinship Coefficient has been corroborated literally every time anybody calculated Fst values between different human races, and by JayMan’s understanding of kin selection it disproves his assertion that ethnic genetic interests do not exist:
This [relatedness] is the probability that a given relative of an individual possesses a copy of an allele the individual possesses.
Co-ethnics are about 25% more likely to share the statistically average allele than people of different races are, so the Hamiltonian drive to confer benefit on co-ethnics is comparable to the drive to confer benefit on secondary relations (half siblings, grandchildren, etc). In other words, it doesn’t matter that the frequency of altruistic alleles is unaffected by the presence of outsiders, because people have a genetic imperative to assist the genes they share with their co-ethnics either way (and are therefore selected for altruism/ethnic nepotism either way); since they are related to their co-ethnics regardless of context, they are selected for the desire to confer benefit on co-ethnics regardless of context, and they only have a genetic interest in derogating an outgroup if doing so will increase the fitness of the ingroup. This is why Harpending and Salter observe, in the paper linked above, that racial solidarity “strengthens in response to attacks perceived to be aimed at group identity, especially invasion of the homeland and physical harm done to co-ethnics.” Observe Donald Trump or Marine Le Pen excoriating the bureaucrats they deem responsible for an alleged invasion, or Black Lives Matter being more enraged about a Hispanic killing a black than by thousands of blacks killing thousands of other blacks. A supposed shift in altruistic allele frequencies was never the point, and to argue against it is to battle with strawmen.
If altruism is the result of kin selection, then an organism will confer benefit on the criterion of relatedness. If a European man saves a daycare with 8 Asian babies in it from some freak accident, then he saves as much of his own genes as were shared by those babies. If he saves a daycare with 8 European babies in it, he just saved a collection of his own copies of HERC2 or ABCC11 or EDAR or some other such gene which he previously failed to save as well. If he saves 8 of his co-ethnic first cousins, the proportion again goes up, this time by 12.5%. By the same mathematical model we use to explain kin selection (Hamilton’s Rule), we predict and observe that altruism will be expressed to various degrees depending on the degree of relatedness.
The adaptation to this would have nothing to do with magical altruism genes which change in frequency when Japanese people arrive in France. Rather, the selection pressures predicted by the kin selection model would select for organisms that exhibited compassion and cooperation in proportion to relatedness.
The fact that co-ethnics share so many genes means that they do have a genetic interest in one another, if kin selection is real. I personally believe that kin selection is a clearer and more likely explanation for altruism than group selection in most cases, but due to the difficulty of determining causality in processes that occurred thousands if not millions of years ago (namely the original evolution of altruistic behavior), I doubt that the scientific community can put this one to bed yet. For the purposes of this issue, however, JayMan has already professed his belief that group selection has never occurred, meaning that one of a few different things must be true.
- Humans are not altruistic at all. Untrue.
- Humans are altruistic, but not due to kin selection or group selection. Unlikely; we can talk about mutual back-scratching all we want but the fact that people take bullets and jump on grenades for one another means that mutual benefit cannot be our only reason to confer benefit upon others.
- Humans are altruistic due to kin selection. This explanation is consistent with genetics and evolutionary theory; evolution holds that survival is a matter of passing on genes and genetics show that related organisms have many of the same genes. It also has pretty good predictive power (it predicts familial love, racism, and other real phenomena). For these reasons, I’m going to be arguing from the assumption that kin selection is a primary reason for human altruism, and that it, therefore, must exist in humans.
Due to the genetic similarity between co-ethnics, there is a genetic interest between them. Each has a Darwinian interest in the other comparable to roughly 25% of their own survival. Operating from the assumption that kin selection is the reason for human altruism, one would predict one of the following possibilities:
- Humans will prefer to confer benefit to their co-ethnics over others due to the fitness advantage gained by doing so,
- That humans cannot perceive genetic similarity and have therefore been selected to benefit one another regardless of genetic similarity in hopes that they hit the mark by accident,
- Humans do prefer those who are genetically similar but are incapable of perceiving the genetic differences between the various human subspecies, or
- Humans understand the genetic differences between themselves and others but for whatever reason will not take the 25% fitness advantage. I’m going to go ahead and throw this one out.
We know that humans prefer others on the basis of genetic similarity, and we know that nearly all human cultures have considered those of different ethnicities to be “the other,” or at least different in some significant way. We know that people can determine someone’s biological race based on their appearance, in any case, and in his 1996 book Race in the Making: Cognition, culture, and the child’s construction of human kinds, Lawrence Hirschfeld found that even children could do so. All of which means that humans can get a rough idea of genomic similarity (or difference) using phenotype and family history as a proxy, and that race is among the types of genetic difference that humans are capable of perceiving. If humans prefer one another based on the criterion of genetic similarity (they do), and race is a genetic difference that humans can perceive (it is), then we expect humans to generally prefer those of their own race (they do).
Even in studies of bereavement, Littlefield and Rushton (1986) put forth ten hypotheses (I will only bring the ones up that prove the case for EGI) to make the case for Genetic Similarity Theory:
- A mother will grieve more than the father: this is due to the mother having finite number of ova, have a more limited reproductive potential than do men and also bear the burden of bearing children, this shows that each offspring of a mother is more important to the overall success to her genes than the are to the father’s.
- Male children will be grieved for more intensely than female children. This is due to a male having a higher chance to have more children and spread his genes to more progeny.
- Similar children will be grieved for more intensely than dissimilar children. GST explains the phenomenon of assortative mating, the phenomenon that spouses will be genetically similar on those traits more influenced by genetics. One consequence of assortative mating is that one parent may be more similar to the child than the other. This can be illustrated as follows: Rushton and Littlefield: “If a father gives his child 50% of his genes, 10% of which are shared with the mother, and the mother gives the child 50% of her genes, 20% of which are shared with the father, the child would be 60% similar to the mother and 70% similar to the father (Rushton et al., 1984)”. So we can see that depending on the amount of genes a child gets from his parent will infer whether or not they are genetically similar to which parent, and in the case of a possible surprise death, the parent who believes the child looks (shares more alleles in common with) like their selves, will grieve longer and more intensely due to having a greater fitness hit due to the increased GST.
This study shows good evidence that the more genetically similar the child is to the grieving parent, the more strong and intense the grieving process will be. How mothers and fathers will risk their lives for their children, their genetic endowment, shows another truth to this phenomenon: altruism. Altruism for those who are genetically similar to yourself. We can then take this and show that since co-ethnics are closer to each other than they are to distant populations, and that since they are more genetically similar to themselves, the same kind of derogation and suspicion that parents give strangers who come around their children, co-ethnics will give to non-co-ethnics when they appear in their homeland. Robert Putnam’s research corroborates this.
Altruism/nepotism does increase when out-groups come to the land. When this occurs, the native population of the country will, in theory, become more altruistic to co-ethnics since their genetic interests are at stake. This is currently occurring in Eastern and Southern Europe in countries like Hungary, Poland, Spain, and Italy.
The model has pretty good predictive power since it predicts racism and other phenomena, which I’ll dive into now. Applying the kin selection model to humanity we expect that altruism will not only be doled out proportionally with respect to genetic similarity, but also to the number of babies the recipient is likely to have. I wouldn’t do as much for my DNA by saving the residents of a retirement home as I would by saving a daycare. And saving women is smarter than saving men. Hence, when the Titanic sinks, the rallying cry of the day is literally “save the women and children!” (Because the people who didn’t do that throughout our biological history had less of an impact on our gene pool than the ones who did.)
So you’re going to see innumerable charities for the benefit of children, and comparatively, nobody trying to solve the conundrum of how terrible life is in nursing homes for the elderly. On the Forbes list of top US charities, numbers 1-4 all frequently work with children (as do many others) and numbers 5, 6, 12, and 14 are specifically for children. None of them are specifically for the elderly; making sure that Grandpa isn’t miserable and alone registers nowhere in the top 50 items of our society’s to-do list.
And you’re going to see things like this, in spite of the fact that men are equally likely if not a hair more likely to get lung cancer and it’s a big killer in both sexes because people care more about “women” than they do about “people.” And I’m not joking or cherry-picking: Lung Force’s blog is seemingly more about women’s feelings than about lung cancer, no doubt because these people are aware that breast cancer research receives way more funding than prostate cancer research does in spite of similar death rates . In other words, it’s a well-known fact among people whose jobs are to stir up altruism that people will give more resources for the well-being of women than for the well-being of men.
All of which is just another case of altruism that “just so happens” to confer group and/or kin benefit, and does so proportionally to the expected increase in fitness, precisely as kin selection would predict. I would expect people to donate more to co-ethnics as well, were it not for the facts that:
a) It’s fashionable in our society to virtue signal niceness to swarthier folks, and
b-z) Haitian children literally eat dirt for breakfast.
In any case, you can look at where rich nonwhites send their donation dollars, be it the fitness benefit gained by JayZ when he donates to clean water causes in Africa, or by George Lopez in his “contributions to the Latino community“. This isn’t a cherry-picked trend of statistically irrelevant anecdotes: Blacks donate to other Blacks, “Identity-based giving is gaining momentum in the Latino, Asian American, Arab American, and Native American communities,” and “Latino’s motivation to give is embedded in a sense of responsibility and desire to give back to their community.” Much of the work of such people may end up benefiting Whites who happen to be there when a catastrophe hits a bunch of the donor’s co-ethnics (observe a Black donating to Hurricane Katrina; New Orleans is majority black, but not devoid of Whites), or occasionally they’ll donate to other nonwhites. But I’m not holding my breath for the day they raise awareness for the White squatter camps in South Africa.
Basically, any time that a person does a nice thing for another person, it will be proportional to any combination of three factors: genetic similarity, assumed number of offspring, and/or how bad the recipient needs help. All three of these are predicted by kin selection since all three are factors which predict the fitness gained by engaging in an altruistic act.
Importantly, virtually every culture on Earth preferred co-ethnics to others prior to the Communist subversion of the West, at which point accusations of racism became something of a social death sentence. (You don’t believe me on the Communist subversion thing- think it’s a conspiracy? Google up where all of this “social construct” ideology we keep encountering ultimately came from, and look up who’s promoting it today.) One could claim that whether a culture is “racist” or not depends on “culture” rather than biology, and point to the modern West as an example of an “anti-racist” culture, but in that case, it’s one hell of a coincidence that every race on Earth generally preferred themselves to everyone else, and did so for 10,000 years or more if you count prehistory. Considerably more likely is that populations with no ingroup preference are subsumed by other populations who gain a fitness advantage by doing so (they mounted no defense because they didn’t understand the need to do so) and that the majority of modern humans are therefore descended mostly from passionate racists.
Co-ethnics have a real genetic interest in one another due to large amounts of shared DNA, meaning that ethnic genetic interest is real. Humans do act on genetic interests in general, as the family studies show, and they are capable of perceiving racial genetic differences, as the ethnicity studies show; it is, therefore, likely that they will act on these ethnic genetic interests as they do with other genetic interests, because racism is caused by the innate preference for genetically similar people. In other words, racism is a biological phenomenon instead of a cultural one.
That, or nearly every culture ever in the history of forever was racist by pure coincidence.
To put subspecies competition into perspective, I will point out that wolves and coyotes have a Fst value between 0.056 and 0.121 and can interbreed. We can call subspecies and other taxonomic classification a social construct if we like; technically we’d be correct in the case of canids, to whom the words “species” and “subspecies” are doled out in a pretty arbitrary fashion. We can say that the admixture is proof that the wolf and coyote DNA doesn’t care about which other genes it’s combined with, if we like. But everything we say about it does absolutely nothing to change the fact that the biological fitness of coyotes massively drops when they share territory with wolves.
Understatement of the week: the implications of having to compete for the same resources is probably why canids fight for territory. Wolf packs, being direct family, would no doubt have a high Fst with other wolf packs, no different from how I’m more similar to my grandpa than I am my housemates. They fight for territory on a familial level because of genetic interest, and they have been observed fighting for territory on the level of subspecies as well, with a clear genetic interest in doing so. The only difference between them and us in this respect is that our method of acquiring resources relies on commerce rather than hunting, and so we weren’t selected for the propensity to wander around a given territory fighting off other families who intrude. That’s not good for business; in fact, I’d be willing to bet that warfare usually occurs in humans when the profit incentive for conquest is greater than the profit incentive for trade. Humans who don’t engage in a lot of commerce and belong to inbred populations, though, have fewer incentives towards peace and higher Fst values relative to others- and they aren’t above killing the guys from the next tribe over. What a surprise that these village’s conflicts had to do with territory and breeding, both of which have to do with fitness. In any case, humans from populations selected for agriculture and commerce engaging in this sort of behavior is the exception that proves the rule, because the only reason anybody knows about the interfamilial warfare of the Hatfields and McCoys is that it falls under the “man bites dog” rule.
I have this radical view that biological rules still apply to humans, and that we are therefore self-replicating bags of meat smart enough to understand that we are self-replicating bags of meat. I see little difference between wolves reclaiming their old hunting grounds and the Reconquista movement. Coyotes had taken over when the wolves kept getting killed by men; Spaniards took over when a storm of viruses killed off most of the Natives. Even after the Spanish admixture, the Fst values between Whites and the now-mestizos likely falls within the range of coyote-wolf Fst values. Wolves feed their kind with elk and we feed ours ultimately with money; the distribution of elk meat to wolves isn’t good for coyotes and I’m willing to bet that the distribution of money and jobs to other nations and their peoples explains much of our abysmal birth rates in the West (with birth control technologies being another primary factor). We had lots of kids back when there were blue collar jobs you could get fresh out of high school which instantaneously elevated you to the middle class. We could afford to have them, no different from the fact that European nobles had more kids on average than us commoners. If current economic, cultural, and political trends continue, though, then ethnic Europeans might go out roughly 50x faster than the Neanderthals did.
Biological organisms show preference of those who are similar at the level of self (me), family (the Kennedys), tribe or nation (Papuan tribes or Mexico), race or subspecies (Native Americans), and species (I eat pork and kill spiders more often than I eat aboriginal Australians and kill Sentinelese people). All are the same phenomenon (attempts to increase the odds of self-replication at the genetic level), all are predicted with Fst values and Hamilton’s Rule, all are observed in animals to whom “culture” doesn’t apply, and all are observed in mankind.
Now, the question is this: how would GST be detected? Numerous ways. Location, for one. Since up until around 50 years ago, most countries were monoracial, those in your general proximity will, more often than not, be more genetically similar to you than a group that’s 50 miles away. Culture, which is an expression of genetics, is yet another way that GST can be detected. Since culture is an expression of genetics, when that culture is expressed, this shows other genetically similar co-ethnics that this individual shares more genes in common than those who don’t share their culture. There is also matching by phenotype, which goes along with the location aspect. But, as I stated in my article Genetic Similarity Theory as a Cause for Ethnocentrism:
It’s clear that we are more altruistic to people who look more phenotypically similar to ourselves, to pass on and benefit copies of our genes. This evolved in spite of the negative impact on behalf of the altruist. The altruist is helping copies of his shared genes survive so that they may be copied into the next generation of progeny. The tendency to favor co-ethnics is the tendency to attempt to help pass on shared genes, as if the phenotype is similar, more often than not, the genotype is as well. This is the basis for ethnocentrism.
There is also what is called the “Grandmother’s hypothesis” in which the researchers theorize that women live past menopause to help take care of their grandchildren. In doing so, they can then make sure their grandchildren are well-fed and nourished. The researchers state that by using Hamilton’s relation coefficients (what we have been using in this article), that a grandmother should share 25 percent of genes with her grandchildren. Ted Sallis says:
Therefore (and this is the important point), a paternal grandmother, all else being equal, is genetically less related to a grandson than to a granddaughter, and less related to a grandson than is a maternal grandmother. Conversely, a paternal grandmother likely is more genetically related to a granddaughter than is a maternal grandmother, given the certainty that the granddaughter possesses an X chromosome from the paternal grandmother.
The researchers hypothesized that the grandmother’s investment in grandchildren will be directly mirrored by how genetically similar they are to each other. The authors conclude that women live past menopause to help care for their children’s offspring. Since they share 25 percent of their genes with their grandchildren, they too, have a genetic investment in making sure they get adequate nutrition and are well cared for. They found that in 7 previously studied populations that “separating grandchild survivorship rates by sex reveals that X-chromosome relatedness correlates with grandchild survival in the presences of MGMs and PGMs. In all seven populations, boys survive better in the presence of their MGM than PGM. In all bar one population, the PGM has a more beneficial effect on girls than on boys. Our X-linked grandmother hypothesis demonstrates how the effects of grandmothers could be sex-specific because of the unusual inheritance pattern of the X-chromosome.”
This is what this whole debate is about: ability to detect genetic similarity in co-ethnics. Matching by phenotype, culture, and general proximity will, with good chance, bring you together with someone who shares more alleles in common with you and someone who you would feel more altruistic towards since you have a genetic interest in ensuring that some of your genes survive to the next generation.
Mixed-race relationships don’t discredit the existence of EGI/GST, in fact, it helps to strengthen it. Americans of mixed ancestry made up for ethnic dissimilarity by matching up on the more heritable traits, whereas the correlation is lower for those traits that are more influenced by the environment. Since the correlation is higher for heritable traits, i.e., BMI, personality, alcoholism, aggressiveness, criminality, psychiatric disorders and so on. Since the correlations are higher than in the environmentally mediated traits and since mixed-race couples match on more heritable traits than on the traits more influenced by the environment, this shows us that even though they are marrying outside of their race/ethnicity, they still match up on the more heritable traits and not the traits more influenced by the environment.
JayMan brings up the concept of reciprocal altruism as if it negates the effect of racial/ethnic altruism as a whole. It does not. Reciprocal altruism and Genetic Similarity Theory go hand-in-hand as genetic similarity eliminates the need for the reciprocation to occur again. Since two related individuals share more genes in common with each other than two unrelated individuals, this then caused reciprocation and GST to evolve hand-in-hand with each other. To quote Rushton:
Thiessen and Gregg (1980) make the same point. Thiessen and Gregg state that “cooperation among `nonrelatives’ (`reciprocal altruism’) may be based in large part on genetic and phenotypic similarity” (p. 133).
Another reason that GST and reciprocal altruism go hand in hand is that genetic similarity at certain important loci can predict the efficacy of a reciprocal altruistic relationship; Fowler & Christakis find that close friends are as similar as 4th cousins, and Guo et al find the same for spouses. Selecting for phenotypic compatibility means selecting for genetic similarity at the loci which determine the relevant phenotypes (height, IQ, personality and so on). For example, different races of the world differ in Big Five personality traits, and the reason for these differences is likely genetic. If a statistically normal, introverted East Asian prefers to associate with fellow introverts, what are his odds of becoming best friends with a comparatively gregarious Black man? A gregarious Asian or an introverted Black may become fast friends with those of other races, but most of their kinsmen are more stereotypical.
Ultimately, however, what it comes down to is this: if a gene can better ensure its own survival by bringing about the reproduction of family members with whom it shares copies with, then it can also do so by bringing about the reproduction of any organism that it shares genes with. Meaning altruistic self-sacrifice. But, if there is a fitness gain for the altruist, then how is it altruism? Simple. The altruist is just protecting genetic interests. The altruist is just being driven by his genes to save copies of itself. This is basically what we humans are: organisms that only attempt to bring about those with similar genetics to ourselves.
Racial differences in Blood Donation
1050 words
Racial differences in blood donations pose a big problem for minorities. This has to do with altruism, which as I have covered extensively here, has a genetic basis. This pathological altruism has whites give and donate more than other races. This is due to evolving in colder climates with harsher environments, which high intellect evolved so our ancestors could survive. Why do minorities, blacks specifically, donate blood less?
Shaz and Hillyer (2010) observed that minorities were underrepresented as donors in the U.S., and that the cause was a higher deferral rate. Deferral reasons include: “low hemoglobin, travel, abnormal blood pressure, pulse or temperature, inability to find vein, tattoo/piercing, infection or taking antibiotics, and not being in good health.” They state that blood donation rate for blacks was 25 to 50 percent of that of white individuals.
Blacks have lower levels of hemoglobin than whites. The Red Cross defers people with low levels of hemoglobin. I don’t really know about blacks traveling too much. Abnormal blood pressure could be low or high blood pressure. Your blood pressure is determined by the amount of blood your heart pumps and the amount of resistance in your arteries.The more blood your heart pumps while arteries are clogged, the higher your blood pressure will be. The more fat and cholesterol that build up on the inner walls of the arteries, which I covered the other day, is called atherosclerosis. Called “hypertension” by the medical community, blacks also have a higher rate of this disease as well. Blacks have more genes expressed for coronary artery calcium, which is a strong indicator of atherosclerosis burden. Cardiovascular disease, more specifically coronary heart disease (CHD) is the leading cause of death for all Americans of all ages and ethnic groups (smoking is a leading cause of this). Blacks suffer the highest percentage of deaths due to CHD. And finally, inability to find a vein is due in large part to 75.6 percent of the black community being obese in America (69.2 percent for men and 82 percent for women).
Another reason for deferral is that all though Sickle Cell Disease isn’t strictly a racial disease, blacks do have the highest rate of it. Those with Sickle Cell Trait (SCT) can donate blood, though those with Sickle Cell Disease cannot.
Infections and antibiotics as well as not being in good health is yet another reason why blacks get deferred. This is due in part to “down-low bruthas” who are more likely to have diseases, and therefore cannot donate blood or plasma. Since homosexuals have some of the highest rates of disease in the country, it’s no surprise that blacks would be leading the pack in that subgroup of the country as well. This is a huge reason why blacks get deferred so much. However, in December of last year, the FDA lifted its lifetime ban of gays donating blood. I shutter to think what the deferral rates of blacks will look like in a few years due to this. That is also why “not being in good health” along with “infection or antibiotics” are such big reasons for deferrals. Blacks have all of the things they defer for, yet of course, allegations of prejudice and racism come about and the government has to step in to change things again, endangering the citizens of the country.

To quote from this AmRen article:
It has long been known that blood transfusions and organ transplants work best between people of the same race. Until the Second World War, stocks of blood were routinely segregated by race for this reason. Classification by race was ended when it was discovered to be “racist,” but blood banks are reinstituting segregation.
The distribution of the common blood types is different from race to race, and some rare types are unique to certain races. Only blacks have U negative blood; only whites have Vel negative or Lan negative blood. Dr. W. Laurence Marsh of the New York Blood Center justifies racial classification: “It makes no sense to screen 100,000 whites for U negative when no U negative white person has ever been found.”
So there is a problem with interracial blood transfusion, and they work better with co-ethnics than non-co-ethnics.
The Central Blood Bank states this about ethnicity and blood donation:
Though compatibility is not based on race, genetically similar blood is best for patients who need repeated or large volumes of blood transfusions, or those who have produced red blood cell antibodies for various diseases and conditions like sickle cell, heart disease and kidney disease.
It says that “compatibility isn’t based on race” then says immediately after “genetically similar blood is best for patients who need repeated or large volumes of blood transfusions. . .” The fact that there are differences in blood-type rate by ethnicity, and that there is a shortage of those blood types for blacks and “Hispanics” in America.
There are varying frequencies in white blood types are found in ethnicities throughout the country, and these varying frequencies in blood type are another reason why interethnic blood transfusion cannot happen; because the differing ethnic groups vary in the different blood types, there will be a low chance of having a certain blood type if it’s rare.
Another reason why blacks donate blood less is due to fear of needles and low iron. Low iron is due to vitamin and mineral deficinecies in diet. Combined with all of the aformentioned variables, this is why blacks get deferred so much. They just don’t donate as much either.
The disparity in differences in blood donation also come down to differences in giving between the races. Whites were seen to be more altruistic than were minorities in the study. This same altruistic behavior leads to more blood donations, but it also leads to the cucking of Europe due to the increase in pathological altruism.
Racial differences in blood donation are due to a whole host of factors, mainly being SCD and other diseases as a barrier for donation, as well as differing blood type frequencies between ethnic/racial groups. Since blacks have higher frequencies of SCD, SCT, and SCA this is another cause for their deferral rate. Being highly sexually active leads to higher disease acquisition, which is another reason less blacks donate blood. Moreover, blacks’ want to donate will not increase either; racial differences in blood donation and problems will persist to the forseeable future.
There Is Such a Thing As a “Male” and “Female” Brain
2100 words
Towards the end of last year, it was said that “male and female brains don’t differ“. Male and female brains differ from the number of neurons to differences in g that affect intelligence, to differences in temperament and differences in the hormones testosterone and estrogen. Other than accounting for differences in physical appearance between the sexes, the differences between the sexes in the two hormones accounts for brain differences as well. This is yet another blank slate argument, years after cognitive neuroscience affirmed that behavior is rooted in the brain and that we are not in fact “blank slates”, these same old and outdated arguments keep being pushed, of course, in part due to the growing number of “transgenders” and an influx of non-western people who are abnormal to our societies. This attempt to have the general public to believe that we have minds of Silly Puddy (to borrow a phrase from Steven Pinker) is an attempt to have us accept all of the things that get pushed on us through the media.
You may have read that having a male brain will earn you more money.
Men do make more money than women, and this isn’t the cause of the imaginary gender pay gap. Even Thomas Sowell, the liberal icon has refuted this myth. Men make more money than women due to, which I will get to below, higher intelligence.
Or maybe that female brains are better at multitasking.
Anecdotal evidence suggests it. Evolutionary evidence suggests it. Studies suggest it. But ever since the Jewish feminist push in the 20th century, this strive for egalitarianism between the sexes became mainstream, which helps to still keep the notion of “blank slatism” alive.
The idea that people have either a “female” or “male” brain is an old one, says Daphna Joel at Tel Aviv University in Israel. “The theory goes that once a fetus develops testicles, they secrete testosterone which masculinises the brain,” she says. “If that were true, there would be two types of brain.”
Anyone else surprised that someone from Tel Aviv University is making these claims? Are we supposed to believe that testosterone doesn’t affect the brain? Are we supposed to believe that higher testosterone, higher estrogen and other biologic differences in brain structure don’t account for behavioral differences between the sexes?
We have data that this is the case, though:
Sex steroid hormones exert a profound influence on the sexual differentiation and function of the neural circuits that mediate dimorphic behaviors. Both estrogen and testosterone are essential for male typical behaviors in many species. Recent studies with genetically modified mice provide important new insights into the logic whereby these two hormones coordinate the display of sexually dimorphic behaviors: estrogen sets up the masculine repertoire of sexual and territorial behaviors, and testosterone controls the extent of these male displays.
Control of masculinization of the brain and behavior (Wu and Shah, 2010)
To believe that testosterone doesn’t cause masculinization of the brain will have to have one deny all of the literature out there. Why people believe that sex differences, as well as racial/ethnic differences, are rooted in experience and not biology is truly mind boggling.
“There are not two types of brain”
And below this, they basically say that the “gender fluid” phenomenon is ‘ok’. Differences between individual boys and girls and individual men and women are extremely evident just by casual observation, so to attempt to say that individual brains cannot be shown to have full-on male or female characteristics is insincere. The fact that, as shown above, testosterone mediates the masculinization of the brain, we can see that these differences in brain structure do exist, and are accounted for by exposure to testosterone invitro, which then cause the differences in the brains of men and women.
Although the team only looked at brain structure, and not function, their findings suggest that we all lie along a continuum of what are traditionally viewed as male and female characteristics. “The study is very helpful in providing biological support for something that we’ve known for some time – that gender isn’t binary,” says Meg John Barker, a psychologist at the Open University in Milton Keynes, UK.
Gender is binary. Female and male characteristics do exist. Males and females differ in certain structures of the brain as seen in a study reviewing over 20 years of the study of sex differences in the brain.
“Across all kinds of spatial skills, we find very, very few that are sensitive to sex,” says Hausmann. “We have also identified spatial problems where women outperform men – the black-and-white idea of a male or female brain is clearly too simple.”
The sex differences on spatial skills tests are rooted in brain structure. Researchers measured a 10 percent difference between men and women in overall amount of parietal lobe surface area. Since how we process information is obviously a result of cognitive processes in the mind, differences between the sexes in brain structure show how men and women can differ in certain cognitive tasks. Of course, some spatial problems can be women can outperform men on some spatial tasks, no one disputes that. However, what the average battery of tests shows is that men have higher visio-spatial intelligence than men.
Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, head of the Gender Medicine Unit at the Medical University of Vienna in Austria, agrees that things aren’t so simple. “There are differences between men and women when you look in large groups, and these are important for diagnosis and treatment,” she says. “But there are always more differences within genders. We always need to look at culture, environment, education and a person’s role in society,” she says.
Just like there “is more difference within race than between them”, right? Culture is a product of genetics and IQ, we put ourselves into certain environments based on our genes, education is largely heritable, a person’s worth to society is based on IQ and the Big Five personality traits, which are at least 50 percent heritable, all of which are rooted in brain processes.. Those factors don’t prove that there are no differences between the brains of the sexes because all of them can be explained, in part due to genetic factors.
These findings, they claim, say that it’s impossible to say what features a person’s brain will have based on the known sex of the brain. With differences in gray matter, brain size and other regions in the brain, we can definitively say whether or not the brain is male or female. Sure some outliers will occur, but the overall bulk, we would see that the sex would be guessed with a super majority being correct.
Joel envisions a future in which individuals are not so routinely classified based on gender alone. “We separate girls and boys, men and women all the time,” she says. “It’s wrong, not just politically, but scientifically – everyone is different.”
Here we are with the point of this article: to attempt to normalize this trend of degenerate behavior that the media pushes which begins to permeate our society. Chromosomal differences between men and women show the sex differences. X means woman, Y means man. Some may point to some anomalies, but anomalies occur in nature all the time and are not a representative of the population.
This also shows with differences in brain size, that causes a difference in IQ between men and women. The study found that men had brains that were, on average, 8 to 13 percent larger than women’s. Since we know that the IQ/brain size correlation is .35, more often than not, men will have higher IQs than women due to having slightly larger brains. And the data is consistent with the finding that men and women have slightly differing IQ scores, which shows in the difference in average brain volume between men and women.
In JP Rushton’s refutation to Steven Jay Gould’s revised edition of The Mismeasure of Man, he states that Gould claims that when accounting for body size and age that the difference in brain size drops from 182 grams to 113 grams, then invokes unspecified age and body size parameters and that accounting for these differences then the sex difference in brain size will vanish. Ankney (1992) reexamined the autopsy data of Ho et al (1980) and found that uncorrected for body size, the difference between men and women’s brains was 140 grams; After correcting for body size, the difference between men and women was 100 grams. This shows that around 30 percent of the difference between men and women in brain size is attributed to body size.
In this review, Rushton did state that men and women had the same scores on tests of intelligence and that this provided a paradox due to the differences in brain size between men and women and similar IQ scores. However, Rushton and Jackson (2006) showed that men and women differ by 3.63 IQ points on average, among a multitude of other strong correlates with the difference in IQ scores.
Men have 23 billion neocortical neurons, women with 19 percent less, at 19 billion (Pakkerson and Gunderson, 1997). Seeing as cortical neuron activity moderates perception in the brain, the differences in neocortical neurons affect other processes and mental faculties in the brain as well.
All of these brain differences then manifest themselves in cultural achievement between men and women.
Charles Murray (2003), in his book Human Accomplishment shows differing societies’ human accomplishments and how these differences in human accomplishment have shaped our society today. He gathered data on women Nobel Prize winners from 1901-2000 and found this:

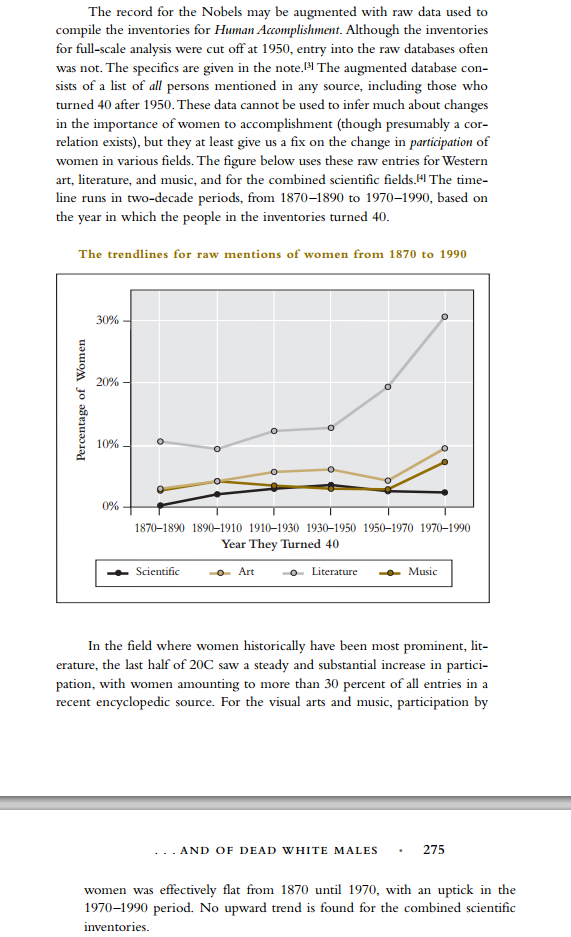
Murray states on p. 273, 274 and 275 that women have an underrepresentation in the sciences. You would figure, if this so-called “white cis male patriarchy” was out to have women be underrepresented, they wouldn’t have allowed the feminist movement to come full-swing in the early 1900s. Well, the numbers on women Nobel Prize winners from 1901-1950 is: 2 percent sciences total, 4 percent chemistry,2 percent medicine, 2 percent physics and 11 percent literature with a 4 percent representation in total. From 1951-2000, it was 2 percent sciences total, 1 percent chemistry, 4 percent medicine, 1 percent in physics and 8 percent in literature for a total of 3 percent.
Now, this does show women’s high verbal ability at play with regards to the number of literary Nobel Prizes’ they have, but this shows that after the Feminist Movement, that when they got ‘equality’, they failed to produce the same as men. This data corroborates what I noted earlier: that there is a significant amount of cortical neuronal difference between men and women, there is a 3.63 IQ point difference between men and women on average, and finally the data on Nobel Prizes corroborates this information.

The Defense Ministers of Sweden, Norway, the Netherlands, and Germany embody what is going on at the moment in these countries with the ‘migrant’ crisis. We can see with Russia’s aversion to the scenario currently happening in Europe, that with their Defense Minister, these things that are currently happening in those aforementioned countries won’t happen in Russia.
This is shown in how men and women’s overall leadership capabilities, ability to lead meetings and differing managing strategies. All of these differences, of course, are due to brain differences between men and women.
Women are more emotional than men due to biology, so in times of war with a woman Defense Minister, since men and women differ in inductive and deductive reasoning traits, women won’t be deductive, which is a logical process in which a conclusion is drawn from multiple premises that are assumed to be true, which men excel at. Women, however, excel at inductive reasoning, which is making broad generalizations from specific observations. It seems that in war time, deductive reasoning would be better, seeing as the conclusion is drawn from things that are assumed to be true. Men make better leaders than women because, since, on average, men don’t think with their emotions while women do.
Men and women’s brains differ on the individual level, of course, like all things between groups, sexes, and individuals. The push to deny human nature, and in turn, invoke a blank slate argument even in the face of science is shown in the way that our society is headed. Between differences in brain size, scholastic achievement, IQ, brain weight, Nobel Prizes, neocortical neurons and other gender-specific differences, these innate differences in brain structure manifest themselves in society and the types of jobs women want and acquire. Women cannot lead as well as men and while they ‘lead differently’, the best type of leader to have is a man as men think with logic and facts whereas women think with emotion, on average.
Gene Expression By Race
1150 words
Since all humans are less than 1 percent different, many people take this to mean that “Race is a social construct“. The stranglehold that race-denying individuals have had on our society for the past fifty years has had huge implications for our society. This egalitarian notion that “we are all the same” together with affirmative action has already begun its devastating effects on our society with this “Blank Slate“, “ghost in the machine” way of thinking.
However, when they engage in this fallacious reasoning, they fail to realize that we are 96 percent genetically similar to chimpanzees. They also don’t know that cats have 90 percent homologous genes with humans; 82% with dogs; 80% with cows; 79% with chimpanzees; 69% with rats and 67% with mice. 90% of the mouse genome could be lined up with a region on the human genome. 99% of mouse genes turn out to have analogues in humans. We share 97.5 percent of our DNA with mice (which is why lab tests get carried out on them). All of this data makes it clear: what causes phenotypic differences between species that are so genetically similar is not how much genetic distance (Fst) is between them, but how those genes that differ are expressed between these populations. Knowing this, it doesn’t seem so crazy now that with less than a 1 percent difference in the genome on average between the races that there are ways to see that race exists genetically. Moreover, the fact that geneticists estimate that there is a difference of 3 million base pairs between two humans on average, shows that there are enough genetic differences between human populations to produce phenotypic differences to be able to differentiate human populations and that since genotype is the cause for the phenotype, due to the physical diversity between human populations that it doesn’t matter how “small” these differences are, but, as mentioned previously, how those differing genes are expressed is the proof that race exists.
Cheung and Speilman collected the gene sequence of a particular white blood cell in 82 Asians and 60 Europeans. They found that the amount of genetic differences was minute, though the two races had differing amounts of gene expression. 25 percent of the overall genes tested showed differing expression between the Asians and Europeans in the sample. It was noticed on one gene that Europeans expressed it at 22 times the strength that Asians did! Since Asians and Europeans split off around 40 kya, I wonder what a study done on Europeans and Africans would show in regards to gene expression strength along with overall differing genetic expression between those two races.
Hicks et al (2013) compared gene expression levels in 4 populations (whites, blacks, Asians and ‘Hispanics’). The gene expression data consisted of 126 whites, 51 ‘Hispanics’, 13 blacks and 8 Asians. They discovered that there were 300 significantly identified genes that showed differing expression in the four populations tested. Some of the genes were: PHF6 (“Mutations affecting the coding region of this gene or the splicing of the transcript have been associated with Borjeson-Forssman-Lehmann syndrome (BFLS), a disorder characterized by mental retardation, epilepsy, hypogonadism, hypometabolism, obesity, swelling of subcutaneous tissue of the face, narrow palpebral fissures, and large ears.”, BRD3 (observed to be implicit in some forms of leukemia, as well as performing cell overlapping functions), CRLF2 (“. . . which control processes such as cell proliferation and development of the hematopoietic system. Rearrangement of this gene with immunoglobulin heavy chain gene (IGH) on chromosome 14, or with P2Y purinoceptor 8 gene (P2RY8) on the same X or Y chromosomes is associated with B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and Down syndrome ALL.”) and finally RNF135 (known to be involved in protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions). All though this study had an extremely small sample size for Asians and blacks, with further study in the future, we will see bigger sample sizes to better test these predictions.
Analysis of 639 tumor samples (270 black, 369 white), showed that 95 genes were overexpressed involving prostate cancer from blacks relative to whites and 132 were overexpressed in whites relative to Asians. This seems like testosterone is correlated with this as well. Since blacks are twice as likely to get prostate cancer than white men, this shows another reason why there is a disparity in disease acquisition between races: genetic differences, not any allegations of racism people attempt to use.
Still, there are differences in gene expression that account for more disease rate differences between blacks and whites. Huang et al (2011) observed gene expression differences between blacks and whites that lead to atherosclerosis. They discovered 409 differently expressed genes. Genes expressed lower in black Americans also tended to express lower in blacks with lower CAC. Ontological analysis also verified that of the 409 race-associated genes, a significant amount of them “revealed significant enrichment in mobilization of calcium and immune/inflammatory response”.
With differences in testosterone, estradiol and other hormones between the races, as well as looking at disease rates between human populations and studying what genes correlate with what disease, we can better understand human evolution as well as develop new and specific drugs for individuals based on their genotype.
The gene ACTN3 has been linked to athletic performance, specifically sprinting. Those descended from West African populations have it, i.e., Jamaicans and other Caribbean Islanders along with West Africa. 70 percent of those individuals have this gene variant, so, due to this, the all-time record holders in sprinting are all descended from West African populations. This holds true for Europeans as well. This is seen in World’s Strongest Man (WSM) competition wins by country, seeing as the countries with the most wins have majority white populations. A white man has also won the WSM every year since its inception, which is yet another example of gene expression in action. Whites and Asians have more slow twitch fibers (along with Kenyans) and West African descended blacks have more fast twitch fibers, accounting for these genetic differences which then manifest themselves in our athletic competitions.
Race does exist, and average phenotypic variation is the proof that there is a biological reality to race. The races differ in disease acquisition, as well as muscle fiber typing, which then accounts for disparities in professional championships won along with racial differences in the racial mix of certain sports. As we begin to fully understand the human genome, we will then begin to understand how and why the races differ genetically. The fact that the races differ, on average, on genetic expression shows that there is a reality to what we call “race”. Yes, race is a “social construct”, but it is a social construct of a biological reality. To put it simply, everything is a social construct, and if race doesn’t exist because it’s a social construct then nothing exists, since everything is socially constructed in our minds. But, we know this is not the case. There is a reality, and we use science to test that reality and confirm it with the scientific method.
Strong Evidence, Strong Argument: Race IQ and Adoption
2450 words
Commenter Salger brought this article to my attention, Weak Evidence, Weak Argument: Race, IQ, Adoption in which an environmentalist in the B-W IQ debate regurgitates the same old and boring long-refuted studies and the same long-refuted researchers, to attempt to prove that the gap in IQ is purely environmental in nature. I have written on this before, so his reasoning that there is “weak evidence” and “a weak argument on race and IQ” is clearly wrong, as we know the studies and researchers he cites have been disproven. Steele then references another discussion he had on the black-white IQ gap, speaking about people being “uninformed” about a position while arguing it.
My problem with this kind of data is as follows. It isn’t overly useful data in proving much of anything: small sample sizes, lack of effective controls and control groups, abundance of confounding factors, difficulty of replicability, etc.
Since he’s saying that there is a “difficulty of replicability” with IQ tests in transracial adoption studies, he hasn’t read the ones for the hereditarian argument and seeing how they show the biological origin of IQ or he’s just being willfully ignorant. I’ll go with the first one.
We know through other research that racial biases are immense in our society, and this other research tends to be of a higher quality than the adoption (and twin) research. Studies have found various forms of racial biases in a wide variety of areas, from education to policing. It’s well supported that this is systemic and institutional.
There are no racial biases in education nor policing. Police arrest less black offenders than are reported by the NCVS and affirmative action getting blacks ahead shows that the racial bias is for them, not whites. Saying that it’s “systemic and institutional” is a cop out since you know he doesn’t want to even entertain the idea of the hereditarian hypothesis.
It is also well supported that it is often internalized, and typically unconscious. Studies have shown that even minorities show prejudice against other minorities and that this is worse toward those with darker skin. Plus, studies show an internalized racial bias by way of stereotype threat, where the framing of a situation apparently causes the person to in a sense unintentionally sabotage themselves (because of added stress and cognitive load).
Stereotype threat, my favorite. ST can only be replicated in the lab. “Prejudice” doesn’t matter.
For any of these adoption (and twin) studies to be useful, it would require taking into account all the known confounding factors. I don’t know of a single study that does this or even attempts to come close to doing this. It would be ludicrously counterintuitive to presume that these endemic and internalized racial biases weren’t effecting the results.
All this leaves us is to speculate based on weak and probably misleading data. This means interpretation inevitably will follow ideology, as long as we limit ourselves to this data and ignore the larger context of data.
What other confounders could be controlled for that you think had a negative impact on the mean IQ of blacks at adolescence throughout adulthood? “Internalized racial biases” don’t matter since blacks have a higher self-esteeem about their physical attractiveness (Kanazawa, 2011), so “internalized racial biases” (which includes things such as one’s thoughts of one’s self physically) do not matter as they are more confident than are whites. This is due to testosterone, which makes blacks more extroverted than whites who are more extroverted than Asians (Rushton’s Differential-K Theory). If these racial biases were really to manifest themselves to actually sap 15 to 18 (1 to 1.2 SDs) IQ points from blacks, this would show in their self-confidence about themselves. Yet they are more confident, on average, than the other two major races.
All this leaves us is to speculate based on weak and probably misleading data. This means interpretation inevitably will follow ideology, as long as we limit ourselves to this data and ignore the larger context of data.
It’s been discussed ad nasueam. The data attempting to say that blacks are just as intelligent are whites are wrong, as I will show below. The data for the hereditarian hypothesis is not weak, as I have detailed on this blog extensively.
This is highly problematic, for the issues involved are complex. That is just the way reality is. If you want to deal with complex reality, you better find sophisticated ways of dealing with it. On that account, these studies fail in various ways. Still, they give us some possible insights in new directions to take with better research.
IQ has been tested for 100 years, and every time, whites outscore blacks 1 to 1.2 SDs.THAT is reality, not some made up, contorted view of reality for some egalitarian dogma.
In conclusion, my basic point is that all of this demonstrates how weak is the argument being made by hereditarians. As for those who prefer environmental explanations, they don’t need this data at all, since there is already plenty of other data that supports their position. Given what we know, all of the racial disparities, IQ or otherwise, can be explained without recourse to genetic determinism.
My basic point is that all of this demonstrates how weak the argument being made by environmentalists really is. What other data supports the environmentalist position that “they don’t need any data at all”? I’d love to see it. The gap is 80/20 genetics and environment respectively. From averaged correlations on subtests that correlate highest with g, we can say that the gap is around 80 percent genetic and 20 percent environment. Genetic determinism in terms of IQ, save extreme environmental factors, will always beat any environmental model.
This is an obvious statment, for the simple reason that race itself is a social construct, not a scientific fact. Social constructs and their social consequences need social explanations of social causes. The debate of the racial IQ gap is about as meaningful as attempting to compare the average magical intelligence of those sorted into each Hogwarts Houses by the magical sorting hat, if one were to base a society on such strange notions.
Race is not a social construct, but a biological reality. If this debate is “about as meaningful as attempting to compare the average magical intelligence of those sorted into each Hogwarts Houses by the magical sorting hat”, why waste youre time writing this post with tons of misinformation?
Steele cites Block (2005), a “philosopher of science”. Rushton and Jensen (2005, p. 279) say that those (Block) who say that gene-environment interactions are so hard to entangle, why then, do identical twins raised apart show identical signs of intelligence (among many other heritable items)?
Eyferth comes out, of course, which the study has been discredited. To be breif, 20 to 25 percent of the fathers to German women’s children weren’t sub-Saharan African, but French North Africans. 30 percent of blacks got refused in military service in comparison to 3 percent of whites due to rigorous testing for IQ in 70 years ago. One-third of the children were between the ages of 5 and 10 and two-thirds were between the ages of 10 and 13. Heritability estiamtes really begin to increase around puberty as well, so if the Eyferth study would have retested in the following 5 to 8 years to see IQ scores then, the scores would have dropped as that’s when genetic effects start to dominate and environments effects are close to 0.
He then cites Richard Nisbett, who I have discussed here, on the Moore study.
The study conducted by Elise Moore (1986) compared IQ scores of 23 7 to 10-year-old black children raised by middle-class white families and the same number of black children but raised in black families (normal adoption).The findings indicated that traditionally adopted black children raised by black parents had normal IQ scores (85), whereas those black children who were adopted by white families had IQs 1 standard deviation (100) above the black mean. Moore states that multivariate analysis indicates that the behaviors of black and white mothers were different in regards to how the black children were treated. She states that white adoptive mothers reduced stress by joking, laughing, and grinning. Whereas black adoptive mothers reduced stress in less positive ways including coughing, scowling and frowning. She also says that white adoptive mothers gave more positive reinforcement to their adoptive child’s problem solving whereas black adoptive mothers gave less (as I am arguing here, these traits are mostly genetic in origin, driven by IQ). She concludes that the ethnicity of the rearing environment exerts a significant influence on intellectual ability as well as standardized test scores. The sample sizes, however, are extremely small and to infer that the black-white IQ gap is environmental in origin because of a study with a small sample size is intellectually dishonest.
He cites a study of black children in the UK, but this is a case of super-selection, as only the most intelligent Africans emigrate.
Steele then cites this article:
These results make some common sense. We know that intelligent people tend to have intelligent children— but not always. Some studies have also suggested that intensive programs may make a large difference in disadvantaged children’s intelligence quotient (IQ) scores.
Headstart gains are temporary, and there is a fadeout over time.. Arthur Jensen was writing about this 50 years ago. IQ and scholastic achievement gains only last for a few years after Headstart, then genetics starts to take effect as the child grows older.
The article then mentions how European ancestry can be measured in American black populations. However, the studies fail to choose genetic markers with large allele frequencies between Europeans and African Americans (Jensen, 1998, p. 480).
He cites Lee Willerman and his colleagues who found that children with white mothers and black fathers scored higher on IQ tests than children with black mothers and white fathers. This is due to the mother being the best predictor of intelligence of the child. White mothers have a better prenatal environment than do black mothers.
He cites the Wikipedia article on Race and Intelligence, which brings up all the usual, Moore, Tizard (will address below) and Eyferth. The article cites Nisbett (2009) as claiming that Rushton and Jensen’s (2005) claim that the three aforementioned studies did not retest at adulthood, and that “heritability between ages 7 and 17 are quite small, and that consequently this is no reason to disregard Moore’s findings.”
That’s a lie. IQ heritability jumps from 40 percent at age 7 to 82 percent at age 18, with some studies showing heritabilities up to 90 percent.
From the same Wikipedia article:
Another study cited by Rushton & Jensen (2005), and by Nisbett et al. (2012), was Moore (1986) study which found that adopted mixed-race children’s has test scores identical to children with two black parents – receiving no apparent “benefit” from their white ancestry
As shown above, since the mother’s IQ is the best predictor of intelligence and the black-white IQ gap being 80 percent heritable, this means that the amount of white ancestry an American black has, the higher his IQ score will be.
Tizard (1972) observed 2 to 5-year-old black and white children in a nursery setting. The white and black children both had IQs at 102.6 and 106.3 respectively. She found no significant gap in the three groups tested (white, black and West Indian). However, she did note that the single significant difference was in that of non-white children. But that doesn’t mean anything as genetics doesn’t take full effect until around 18, where the IQ gap will be the largest.
Levin and Lynn (1994) disputed Weinberg et al’s conclusion with a hereditarian alternative. That the average IQ and school achievement scores of the black children directly reflected their amount of African ancestry. At both age 7 and 17, the adopted children with 2 black parents had lower average IQs and worse school achievement tests than those with one black parent and one white parent. So right here, in the MTAS, it shows that mixed-race people DO score better than just blacks, which is attributed to their white ancestry.
He then cites a bunch of quotes from Nisbett’s book Intelligence and How to Get It, yet Ruhston and Jensen have refuted this too.
Even with equalized environments these gaps still persist. Your allegations of supposed racism or any other factor you want to bring up for the racial gap in intelligence are unfounded. Environmental differences do not account for the 1.2 SD gap between blacks and whites; environment accounts for, at best, 3 IQ points, so you’ll need to explain what environmental effects cause that kind of IQ drop. In America, blacks don’t have the same environmental factors, i.e., parasitic load, bad nutrition and the high disease rate, so they can hit their phenotypic IQ, plus a bit more due to 22 percent white ancestry on average. Why you cite discredited studies and researchers to help prove your point is beyond me.
Stereotype Threat is false. Non-replicable studies outside of a lab setting, as well as a meta-analysis that looked at 55 published and unpublished studies that showed that Stereotype Threat is discredited. As shown above, blacks have higher self-confidence than do whites, so this imaginary “stereotype threat” doesn’t affect blacks taking real tests; it only affects them in a lab setting. Steve Sailer has covered stereotype threat as well.
This debate is meaningful, and environmentalist who thinks that they can attempt to explain everything away by environmental factors are being extremely disingenuous. Even giving blacks everything they want in a school system with having one of the highest budgets at 430 million dollars did nothing to close the IQ gap or do anything for integration. Why do we have to deny reality, all for egalitarian dogma based off of philosophical musings then taken by Franz Boas to deny the biological validity of race?
To quote the concluding paragraph in Rushton and Jensen’s refutation to Nisbett:
There is no value in denying reality. While improving opportunities and removing arbitrary barriers is a worthy ethical goal, we must realize that equal opportunity will result in equitable, though unequal outcomes. Expanding on the application of his “default hypothesis” that group differences are based on aggregated individual differences, themselves based on both genetic and environmental contributions, Jensen proposed “two laws of individual differences”—(1) individual differences in learning and performance increase as task complexity increases, and (2) individual differences in performance increase with practice and experience (unless there is a low ceiling on proficiency). We must recognize that the more environmental barriers are ameliorated and everybody’s intellectual performance is improved, the greater will be the relative influence of genetic factors (because the environmental variance is being removed). This means that equal opportunity will result in unequal outcomes, within-families, between-families, and between population groups. The fact that we have learned to live with the first, and to a lesser degree the second, offers some hope we can learn to do so for the third.
Arthur Jensen’s Method of Correlated Vectors
1200 words
Arthur Jensen developed the Method of Correlated Vectors in the 1980s and presents a great explanation and analysis in his 1998 book THE g FACTOR: The Science of Mental Ability. Since IQ is correlated with g, it’s not presumable that the correlation between IQ and physical variable X does not involve g. More sufficient evidence would come from the correlation between X and the g factor’s scores. So Jensen proposed the method of correlated vectors that can determine whether there is a correlation between X (or any other factor other than X) and g. Still, it doesn’t tell us about the numerical correlations between g and X, but it can prove that there is a correlation between factor X and g and show if there are any other factors independent of g that are not correlated with X (pg 143).
When a significant correlation is observed between g factors and factor X using the method of correlated vectors, which Rushton (1999) calls the “Jensen Effect”, it demonstrates that the test’s g loading is the best predictor of that correlation with a given variable. Basically, a Jensen Effect arises when there is a correlation between a large number of biological and psychological variables and the g factor. Jensen did say in his interviews with Frank Miele for the Book Intelligence, Race, and Genetics: Conversations with Arthur Jensen:
. . . it involves what I have called “Spearman’s hypothesis.” In his book The Abilities of Man, Spearman made a casual observation that the size of the average W hite-Black difference on ten diverse tests was directly related to his subjective im pression of how much each test reflected the g factor— the more g, the greater the Black-White difference. I turned Spearmans offhand conjecture into an empirically testable hypothesis by calculating the average Black-W hite difference for a number of diverse mental tests, obtaining the g loading for each test (that is, how much each test measures g), and ranking the average W-B differences and the g loadings. If the rank order of the Black White differences and the g loadings are pretty much in the same order, Spearman’s hypothesis is confirmed.
I’ve now tested Spearmans hypothesis on 25 large independent samples and it has been confirmed on every one. It has held up for many different test batteries, and at every age level from three-year olds to middle-aged adults. Nor did matching Blacks and Whites for SES diminish the effect. It even shows up in reaction-time tests that have different g loadings but require no cultural knowledge and can be performed in less than one or two seconds by elementary school children. Based on all these studies, the overall probability that Spearmans hypothesis is false is less than one in a billion! (emphasis mine)
There is less than one in a billion chance that Spearman’s hypothesis is wrong. Which brings me to the Black-White IQ gap.
Using the MCV, Dragt (2010) had his prediction confirmed when the psychometric meta-analysis of IQ batteries showed a correlation of .91, based on a large N. Their study on language bias showed a small underestimate of 2.71 points. They conclude that Spearman’s hypothesis is an empirical fact:
Spearman’s hypothesis can now be considered to be an empirical fact. Mean differences in intelligence between ethnic groups can be largely explained by the complexity of the subtests in an IQ battery. So, the present study shows clearly that there is simply no support for cultural bias as an explanation of these ethnic group differences. Apart from subtests with a strong language component, IQ batteries appear to be excellent measures of intelligence for all groups studied in our meta-analysis.
…
Conclusion: Mean group differences in scores on cognitive-loaded instruments are well documented over time and around the world. A meta-analytic test of Spearman’s hypothesis was carried out. Mean differences in intelligence between groups can be largely explained by cognitive complexity and the present study shows clearly that there is simply no support for cultural bias as an explanation of these group differences. Comparing groups, whether in the US or in Europe, produced highly similar outcomes.
This proves the hereditarian hypothesis 100 percent. Since the black-white differences on subtests are greater the more the g factor is involved (complex tasks, etc), that shows that a magnitude of the black-white difference in IQ is genetic in origin. IQ tests are also not “flawed” or “biased“, as all of the variables that continually get brought up have been controlled for, and genetic confounding wins out every time. Since testing blacks and whites both in America and Europe produces the same outcome, there is a clear genetic component in IQ between blacks and whites.
However, as with most statements and theories by Rushton and Jensen, Jensen’s MCV doesn’t come without any detractors.
Ashton and Lee (2005) state that the MCV produces spurious results as well as non-g sources of variance, producing a vector correlation of 0, even when the item is strongly correlated with the g factor. However, Nijenhuis et al (2007) state that by performing a psychometric meta-analysis on the MCV would alleviate some of the limitations with MCV. Rushton and Jensen (2010) state:
For example, Dolan et al [59] and Ashton and Lee [60] argue that the method of correlated vectors (MCV) lacks specificity so that Jensen Effects might occur even when differences are not on g, and so more powerful statistics are needed, such as multi-group confirmatory factor analysis (MGCFA). However, this criticism misses the point because there is no absolute claim that the g effects have been proven, only that what is observed is what would have been expected if an underlying g did in fact exist (see Bartholomew [61] for the logic of g inferences). Thus, the onus is on the critics of g to identify whether some other factor is operating
Which the critics cannot do. That is because the g factor encompasses all mental abilities and the lower one’s g, the lower one’s overall intelligence. The MVC shows that the black-white IQ difference is largely biological in nature, seeing as the black-white IQ gap is 80 percent genetic and 20 percent environmental (Rushton and Jensen, 2005, p. 279):
. . . is that genetic and cultural factors carry the exact same weight in causing the mean Black–White difference in IQ as they do in causing individual differences in IQ, about 80% genetic–20% environmental by adulthood.
Blacks are ahead of whites at young childhood (around 4 years of age), but at around the age of 5, whites catch up and that’s when the significant racial differences in intelligence are noticed between the races. The fact that we have this debunked “blank slate” notion on the nature of not only race and intelligence but intelligence as a whole in this era of scientific knowledge is mind boggling. Changing all variables to where environments are as close as possible still produces the same occurrence: a clear 1 to 1.2 SD difference between blacks and whites.
Methods like factor analysis and the method of correlated vectors help us to understand the magnitude and heritability of the black-white difference in IQ. Since the differences are the highest on those subtests that are correlated with g, along with correlations from the MCV, with an 80/20 (Pareto Principle in action) genetic/environmental difference in black-white IQ, we can most definitively say that the 1 to 1.2 SD (the equivalent of 15 and 18 IQ points respectively) gap in IQ between whites and blacks is genetic in origin.
Sickle Cell Anemia
950 words
Sickle Cell Anemia is a disorder in which red blood cells become hook-shaped, which causes those hook-shaped blood cells to get caught in small bloodvesselss, which then prevents oxygen and blood from getting to certain parts of the body. Since this disease is so prevalent in the African community, many people think that it is a disease that only Africans can contract and that any other population that gets SCA must have African ancestry.
I touched briefly on Sickle Cell Anemia in my post IQ, Nutrition, Disease and Parasitic Load. Mainly that SCA is correlated with decreased skull size, and therefore a decreased IQ. Though, there are some misconceptions about SCA that will be expelled today such as SCA being a marker of ancestry and the exact causes of contraction of the disease. Since most people only hear about Africans and African descended people with SCA, the misconception is that SCA is a disease that only Africans get. People then assume that any other population that gets SCA must have African ancestry, but this is not the case.
Elguero, et al (2015) took a total of 3,959 blood samples from 195 random villages dispersed throughout Gabon. They discovered that every ten-year increase in age of someone with an increase of 5.5 percent of by Sickle Cell Trait carriers. They also bring this up about evolution:
These strong associations show that malaria remains a selective factor in current human populations, despite the progress of medicine and the actions undertaken to fight this disease. Our results provide evidence that evolution is still present in humans, although this is sometimes questioned by scientific, political, or religious personalities.
[..]
Our results concern present day human populations (persons born 15–80 y ago) and clearly show that, at least in human populations of low income, such as in our study, where medical advances remain limited, biological adaptation is still an outcome driven by evolution to respond to environmental pressures imposed by pathogens, in particular malaria.
Biological adaptation is the cause for SCA developing to fight off malaria. This study proves evolution, yet, as alluded to in the quote above, Creationists still say that SCA does not prove evolution. Since selection for SCA occurs due to malaria over time, that is a clear example of evolution in action. SCA is inherited from both parents. However, if one gets the gene from one parent and not the other, they will carry the Sickle Cell Trait or SCT, and possibly pass SCA on to a future child if a partner also has the SCT.
There are many misconceptions about SCA, mainly that it is only present in black populations and those populations with some African ancestry. Since SCA evolved to fight off malaria, SCA will be prevalent in those populations that have high rates of malaria. It is mostly prevalent in areas where it is warmer and there is a lot of still water due to that being the best breeding ground for mosquitoes. The mosquitoes then transmit malaria, and those with SCA and the SCT can better fight off the malarial infection. SCA is also prevalent in Sicily and Southern Italy, Greece, Turkey and parts of India, showing that it’s not a ‘black disease’, but a disease that arises due to a higher rate of malaria due to more mosquitoes and still water being around.
- stroke – where the blood supply to part of the brain is cut off
- increased vulnerability to infection
- acute chest syndrome – where the lungs suddenly lose their ability to breathe in oxygen (often the result of an infection)
- pulmonary hypertension – where the blood pressure inside the blood vessels that connect the heart to the lungs becomes dangerously high
Since American blacks have higher rates of hypertension (among the highest rate in the world), this causes more complications when SCA arises due to already impaired blood vessels due to the higher blood pressure from hypertension, which is exacerbated by smoking. Higher rates of hypertension can then be attributed as another cause of death of those who die from SCA since their blood vessels were already put under pressure due to their hypertension.
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) affects around 100,000 Americans, is found in 1 out of 365 black or African American births, occurs in one out of 16,300 ‘Hispanic’ births (other populations from a tropical area), and 1 in 13 blacks are born with the SCT. Since 1 in 13 blacks are born with the Sickle Cell Trait, the prevalence of blacks with SCA in America will only increase due to the SCT being more prevalent in black populations.
So far, the only known prevention of Sickle Cell Disease is not to have children. This is because it is a genetic disorder, one that evolved in populations that evolved in areas with more mosquitoes and malaria-infected mosquitoes. Though, in the future with CRISPR Cas9, it will be able to circumvent the genetic mutation that causes SCD. Researchers discovered that changes to a small patch of DNA in the enhancer region of the BCL11A gene show that it is possible to circumvent the genetic defect that causes SCA and other blood diseases such as thalassemia.
SCA, SCT, SCD and any other Sickle Cell disorder traits are not exclusive to African populations. They were selected to fight malaria and is more proof of human evolution at work. SCA evolved to fight off malaria and is prevalent in places with high amounts of mosquitoes (i.e., places with a lot of still water) as well as tropical and semi-tropical locations due to those areas being the best breeding ground for mosquitoes. Creationists deny the evolution of SCA, however, we know that they will do and say anything to prove their case that evolution does not exist.
Can You “Hear” Race?
650 words
I’ve been wondering about this for a while now. Whenever you hear a black speak, nine times out of ten, you can tell whether or not it’s a black who is speaking. The differences come down to testosterone and morphological differences in vocal cords.
This study compared vocal tracts in 140 white, black and Asian speakers who were divided amongst the three races. The researchers controlled for age, gender, height and weight. They measured six dimensions in vocal tracts with acoustic reflection technology. They discovered that significant gender and racial differences exist in certain vocal tract dimensions. These findings will help researchers with a new anatomical database of those from different races and how their voice tracts differ for more study into it.
In this study, they measured volumetric differences in males from different races. They investigated vocal tracts, such as length differences in them, to see which would contribute to racial differences in acoustic characteristics. The findings help to support the hypothesis that those from different races may possibly have morphological differences when it comes to vocal tract dimensions. Those same dimensions could also be responsible for differences in vowel sound of specific dialect/speech.
People use everything from their throats to noses when they speak, and since there are morphological differences there, one would reason that there would be differences in the voices between races, on average. Basically, those with different facial features should have different voices. Since the races have different facial features, as well as morphological differences in vocal tracts and larynx and everything in between, then there are obvious differences in voices.
Taking 50 blacks and 50 whites and having them say an ‘a’ sound which was then recorded. The researchers paired one black subject with one white subject and the individuals in the study were able to guess the correct race 60 percent of the time. The researchers then gave an acoustic analysis of the voices. What was then discovered was that all though the voices for the black subjects was within normal ranges, the black subjects had “greater frequency perturbation, significantly greater amplitude perturbation, and a significantly lower harmonics-to-noise ratio than did the white speakers.” The listeners were most successful in distinguishing voice pairs when the differences in vocal perturbation and additive noise were greatest (obviously) and least successful when those differences were minimal or absent (again, obviously). Since there was no fundamental difference in the mean fundamental frequency and format structure of the samples, it’s extremely likely that the listeners relied on spectral noise to differentiate black and white speakers.
Even blind people “see” race!! Yet more proof that the races differ in speech as well as have morphological differences between them.
I’ve always noticed that, on average, you can tell a black from a white and a white from an Asian. Testosterone also plays a part. In Rushton’s debate with Joseph Graves, he says that testosterone differences are the cause for racial differences in voice. Testosterone mediates a lot of things in the human body. Testosterone levels also mediate the deepness of an individual’s voice. Those with more testosterone have a deeper voice, and those with less testosterone have a higher voice. East Asians have the least testosterone out of the three races, and they have the highest-pitched voices. Conversely, blacks have the highest testosterone and have the deepest voices, as well as the most distinct voices between the races. Whites, as usual, fall in the middle.
Black males have a smaller overall size gradient, Asians the biggest, and of course, whites fall in the middle. The sound of voices doesn’t just vary between races, but by gender within races as well.
Can we “hear” race? The answer is yes!! Whether it’s morphological differences in the voice tract or larynx or testosterone differences between races, we definitely can discern someone’s race on average when speaking to them.