Home » 2016 (Page 8)
Yearly Archives: 2016
White Men Can’t Jump? That’s OK; Black Men Can’t Swim
1200 words
Everyone sees how athletic blacks are, for instance in football, but why don’t blacks like swimming? Black children drown at a rate almost three times higher than white children. 70 percent of black children can’t swim, compared to 60 percent of ‘Hispanic’ children and 40 percent of white children. A combination of genetic and environmental factors are involved in this.
JP Rushton writes in Race, Evolution and Behavior (pg. 163):
Body structure differences likely account for the differential success of blacks at sporting events. Blacks are disproportionately successful in sports involving running and jumping but not at all successful at sports such as swimming. For example in the 1992 Olympic Games in Barcelona, blacks won every men’s running race. On the other hand, no black swimmer has ever qualified for the U.S. Olympic swim team. The bone density differences mentioned above may be a handicap for swimming.
Rushton noted above this paragraph that there are bone density differences between blacks and whites which have been noted at all ages and skeletal sites, remaining even after controlling for body mass. These differences even appear before birth, prenatally. Divergence in length and width of the bones in black and white fetus is followed by greater weight of black infants in comparison to white infants. These skeletal differences in weight obviously persist into adulthood, which then have implications for blacks with swimming, but give them advantages in other sports.
At the time of the writing of Race, Evolution, and Behavior in 1997, no black had ever qualified for the U.S. Olympic Swimming Team. However, Anthony Ervin became the first black swimmer to qualify for the Olympic swim team in the year 2000. The fact that it took so long for a black swimmer to make the Olympic swim team shows a genetic component.
Also contributing to this phenomenon is the fact that blacks have narrower chest cavities along with heavier skeletons (as mentioned above), this makes it harder for blacks to stay afloat and swim in the water. A smaller chest cavity brings with it less mobility while doing strokes in the water in comparison to one with a wider chest cavity.
Hochberg (2007) notes that fracture risk, particularly hip fractures, in whites is higher than for blacks in both sexes at 10.1 and 4.1 percent for white and black women respectively while the percentage is 4.3 and 3.1 percent for white and black men respectively. Other analyses of people aged 65 to 90 show 16.3 and 5.3 percent in white and black women while the percentage is 5.5 and 2.6 percent for white and black men respectively. Why do white women suffer more fractures? When women hit menopause, the drop in estrogen coincides with bone loss and osteoperosis. Moreover, in 2010, the Food Surveys Research Group published Fluid Milk Consumption in the United States, which shows women drink less milk then men, with seniors drinking less milk than all age groups (pg. 4). We can then infer from this that senior white women drink less milk, which is then another cause for more hip fractures and weaker bones. Though, there is of course a genetic component with blacks having stronger bones. However, stronger bones means heavier bones, which is a disadvantage when it comes to swimming.
Another funnier reason for blacks non-ability for swimming is that since blacks have a higher single mother rate (72 percent) they didn’t take them to the pool and teach their kids how to swim because they “didn’t want to get their hair wet”, as they put so much time in their hair. This may contribute to this slightly, but the physiological and biological differences mentioned above contribute a far greater amount of variance.
Blacks also wouldn’t be good swimmers due to them having more type II muscle fibers than type I, meaning their muscles fire off quicker and therefore tire quicker. This is why blacks are good sprinters, but would suffer in swimming events. Blacks also have a higher fat free bone density than whites, which leads to blacks not being able to float since fat floats.
For the same reasons why blacks wouldn’t be good swimmers, whites can’t jump, on average. Type II muscle fiber doesn’t allow for the explosive power needed to be able to jump as well as blacks. Even though blacks have a heavier skeletons than whites on average, they can still jump due to their muscle fiber typing. This is also why whites are underrepresented in the NBA (which is 74.4 percent black). Testosterone and musculoskeletal differences are the causes for racial differences in sports.
Whites drown more than blacks before 5 years of age, but after 5 years, more blacks drown in comparison to whites. Drowning in natural water settings was significantly higher for blacks than for whites, with blacks drowning more than whites at ages 7-8 through 17-18 years of age. Swimming pool drowning rates was also shown to be elevated for black children This data shows that after 5 years of age, blacks drown at a significantly greater amount than whites or ‘Hispanics’, which is attributed to the data above.
In our ‘post-racial society’, it’s become taboo to study, and even speak of differences so prevalent in our society, seeing as sports is a huge part of many peoples’ lives around the world. Most of the stars everyone speaks of are black. They must, subconsciously atleast, notice that these differences are there seeing the racial differences on the screen (except for baseball). Of course practice has a part in becoming elite in whatever sport is chosen, however, the best also have a higher inclination to want to do better as well as already being genetically gifted. Those who are more genetically different are, obviously, on the right side of the bell curve, thus, are extremely rare. Though, we can see these genetic disparities in racial differences in sports, with swimming being a huge tell.
It’s not just “a racist joke” that blacks can’t swim, there is biological and physical evidence that blacks, on average, have a more difficult time in the water due to difference in fat-free body mass as well as more narrow chest cavities and heavier skeletons than whites. The same reasons why blacks dominate other sports (football, soccer, boxing, basketball) is the same reason why blacks are underrepresented as swimmers: their biology. However, the trope that white men can’t jump is true as well, and also has it’s origin in genetic differences between the races.
The cause for racial disparities in drowning, as well as in swimming competitions is due considerably to genetic factors such as bone density and chest cavity narrowness. Other environmental factors include children not being taught how to swim due to them being more likely to be raised by single mothers. Bone density and heaviness also shows why blacks suffer less fractures than whites, with white women suffering from it the most. That same bone heaviness is also a reason why blacks are not good swimmers. Muscle fiber typing play a difference in racial differences in sports ability, which the races also vary in significantly. For these reasons, “White men can’t jump.” That’s OK, because “Black men can’t swim.”
Transvestic Disorder and Gender Dysphoria Identification and Prevention
2150 words
Abstract
Transvestic Disorder comes about in early childhood and manifests itself in sexually deviant actions. Men suffering from TD who aren’t homosexual, more likely than not, show attraction to themselves dressed in women’s clothing. The signs of TD are noticed at an early age when the individual begins to cross dress. TD is also correlated highly with numerous sexually deviant actions. Fluoxetine and serotonin reuptake blockers may be able to lessen TD since it is an impulsive disorder. With TD being co-morbid with OCD, by treating OCD we can better treat TD itself and give a better quality of life to the patient suffering from the disease. Since autogynephilia and transgenderism are related, measures taken to alleviate TD and autogynephilia could be taken to alleviate symptoms of gender dysphoria, since autogynephilia leads to transgenderism.
Transvestic Disorder and Gender Dysphoria Identification and Prevention
Transvestic disorder is a paraphilic disorder, classified by the American Psychological Association (2013), in which males dress up as women to gain sexual gratification. The individual suffering from TD suffers from compulsions to want to dress as a woman, which causes distress due to the individual not wanting their secret to come out. This then leads to the quality of life of the individual to decrease due to constantly being worried about his secret coming out. TD is diagnosed when a male has sexual feelings and gets sexual arousal from dressing in women’s clothing. It is only diagnosed when these activities are ongoing for at least six months. TD is also similar to another paraphilic disorder called ‘autogynephilia’ (Lawrence, 2011), in which the subject is aroused at the thought of himself being a female, so he, therefore, then begins to dress as a woman to fulfill his sexual desires. Blanchard (1989) proposed that most gender-dysphoric males who do not show sexual arousal to men, instead show sexual arousal to themselves dressed in the opposite sex’s clothing. He concludes that the hypothesis is supported that major types of those men who cross-dress are nonhomosexual, and do so because they become aroused at the thought of dressing as a woman. The DSM V says that autogynephilia is a specifier to transvestic disorder. This is because they are characterized by the same things (American Psychological Association, 2013).
The signs of TD are noticed at very early ages. Most notable are when children begin to cross-dress at or before puberty. This then continues into their adult lives where it begins to be a problem and cause dysfunction due to needing to keep their secret. Dr. Mark Griffiths (2012) states that all though children may engage in transvestic behavior, what differentiates it between an adult suffering from TD is that the child who cross-dresses does so for excitement and pleasure, not for sexual pleasure. Though some researchers say that the disorder is brought on through childhood trauma, i.e., accidental exposure to women’s clothing or exposure to a woman who is undressing. Numerous studies have also concluded that many men who suffer from TD have had to deal with parental separation during childhood.
The American Psychological Association (2013), reports that fewer than 3 percent of males are characterized as having transvestic disorder. TD is most always seen in males, though Moser (2009) noted that in his study using the Autogynephilia Scale for Women (ASW), that out of the 29 respondents that sent back questionnaires, 90 percent would be classified as having autogynephilia. Though, by using a more meticulous definition, only 28 percent were seen to be autogynephilic (Moser, 2009).
Langstrom and Zucker (2005) observed in a sample of 2,450 18 to 60-year-olds in Sweden that transvestic disorder was correlated significantly with being separated from their parents, homosexual relations, higher masturbatory frequency, being easily aroused sexually and pornography use. Also noticed, was a positive attitude in regards to sexual arousal from pain, exposing oneself to a stranger and voyeurism were all positively correlated with TD. Langstrom and Zucker observed how TD is co-morbid with many other paraphilic disorders as well as other deviant behavior. By attempting to treat what TD is correlated with, symptoms of TD can be lessened.
Men suffering from TD and autogynephilia are told that women are the standard of beauty. They then look at themselves in the mirror and see a male and not the standard of beauty they were told of growing up. They then turn to cross-dressing to finally see their “beauty standard” in the mirror but keep it a secret. This strong want to keep their disorder a secret then leads to dysfunction. Men suffering from TD will go to any lengths to hide their secret. This then causes extreme dysfunction in their lives, which leads to a lessened quality of life.
Less than three percent of males suffer from TD in the American population, as such, it is classified as a deviant lifestyle as it deviates from the norm of the population. It causes distress due to them not wanting their secret to be discovered. This, in turn, leads to dysfunction where the individual cannot live their daily lives to the fullest due to their abnormal disorder. It finally leads to danger due to their secret beginning to consume their lives so that they’re not discovered.
There are ways to treat TD. Usmani et al (2012) follow a case study in which a 17-year-old Indian male who had occurring desires to wear his mother’s clothes. He then would masturbate in his mother’s clothes to alleviate himself. This continued on for two years so he could pleasure himself. He was caught by his parents wearing his mother’s clothes and was beaten by them for it. He then said that it is a compulsive behavior and cannot be helped. This case also shows the obsessive compulsive side to TD. They have an urge so strong they cannot help but to do it compulsively to alleviate their sexual desires. He also said that the occurring thoughts then affected his schoolwork as he was so preoccupied with the thought of wearing women’s clothes. All of his brain scans were found to be normal, so what brought on this case in the individual in the case study? He was then diagnosed with TD and prescribed fluoxetine, an antidepressant SSRI. The dose was started at 20 mg and increased by 40 mg once a day for two weeks. In his six-month follow-up, he reported lessened desire to masturbate with women’s clothes (Usmani et al, 2012).
Paraphilias and other related disorders have been thought of as sexual addictions. Though it has been argued that they are not sexual addictions, but are sexual compulsions (Stein et al, S 1992). The researchers reviewed 13 patients who showed signs of TD and were administered serotonin reuptake blockers. The symptoms of those individuals were then divided into paraphilias, non-paraphilic sexual addictions, and sexual addictions. Stein et al discovered that paraphilias had the least improvement with the reuptake blockers whereas sexual compulsions showed the best improvement. They end up concluding that paraphilias and other related disorders are on the impulsive end of the spectrum compared to the compulsive end. These impulsions, then, have those men suffering from TD have the urge to dress in women’s clothes to fulfill their sexual impulsion.
TD is co-morbid with obsessive compulsive disorder (Abdo, Hounie, de Tubino Scanavino, and Miguel, 2001). They used longitudinal case studies in which they assessed two individuals who had OCD as well as TD. They conclude that some cases of TD may be OCD related and not always be caused by gender dysphoria. Since OCD and TD are co-morbid, by treating symptoms of OCD, the want to cross-dress will lessen, which will then lessen the symptoms of TD. Treatments could include SSRI and fluoxetine, as previously stated in the paper. Other treatment for TD should be looked at, such as treatment for OCD due to the co-morbidity between the two. By doing so, feelings of wanting to cross-dress may lessen due to one of the underlying causes (OCD) of TD being treated.
Autogynephlia could also explain transgenderism.Transvestism can be called both a paraphila and a sexual orientation. Lawrence (2004) says that it can explain mid-life MtF transitions, progression from transvestism to transgenderism, the prevalence of other paraphilias among MtF transsexuals and the late development of male intrest in MtF transsexuals. However, when Lawrence says that “Hormone therapy and sex reassignment surgery can be effective treatments in autogynephilic transsexualism”, that is incorrect. The prevalence of suicide attempts among transgenders is 41 percent according to the Williams Institute, UCLA School of Law, in comparison to 4.6 percent for the average population. That’s almost ten times higher than the national average. Clearly, surgery doesn’t do anything to alleviate the feelings of gender dysphoria, and as shown in this paper, therapy and drugs like Prozac can better help to alleviate feelings of gender dysphora in transsexuals due to them being extremely similar to eachother. These two disorders greatly mirror each other. Since Lawrence (2004) observed that there is a progression from transvestism to transgenderism, using similar techniques that work on those with TD may also work on those with gender dysphoria.
Discussion
TD can be helped with the correct therapy as well as right medication. With those, impulsions to wear women’s clothes, as well as impulsions to commit abnormal acts will be greatly lessened and quality of life will be restored to a somewhat normal level. Due to co-morbidity between TD and OCD, treating OCD will, in turn, better help the patient suffering from TD. When more studies are carried out on those suffering from TD, we can see whether or not SSRI drugs and fluoxetine will have the desired effect in alleviation of the symptoms of TD. The individual in the Usmani study reported lessened symptoms and impulsions of cross-dressing, so by identifying which parts of the brain are and were activated during the fluoxetine therapy, we can then better give better care and treatment to those suffering from TD. We can also use some data from TD cases for transgenders, as TD and transgenders have a lot of things in common. With therapy as well as, maybe even fluoxetine (which is just Prozac), and high doses of testosterone/estrogen, this could possibly help to alleviate ‘gender dysphoria’. It could also lower the suicide rate as it’s completely possible that these interventions could fix them mentally.
Conclusion
There is little current literature in treating TD, due to it being a shameful disorder and many men not speaking about what they suffer from. One major way in which to help those with TD is to administer SSRI drugs, in which compulsion to cross-dress, and other attitudes associated with TD lessened. Blanchard (1989) proposed the autogynephilia theory for those transgenders who are not attracted to men. With the obseration by Lawrence (2004) on how autogynephilia and transgenderism are related, this can better help those with transgenderism, as they can get correct help and the right hormones they need, instead of the opposite hormones. SSRI therapy is a good candidate in treating TD, as drastic changes in deviant behavior are seen while the patient is taking the SSRI drug. Seeing as most cases of TD begin in childhood before puberty, by better identifying warning signs of these disorder, we can better treat those children who are at risk of developing these disorders before they become a big problem later in life. As more men come out and say that they suffer from these disorders, more studies can be carried out that corroborate the findings in the studies laid out here. It is extremely promising that these disorders can be treated with common drugs already on the market. In those individuals suffering from TD as well as OCD, by treating the OCD first (which may be an underlying cause) the symptoms of TD may be lessened and the individual may eventually have the ability to lead a life without TD. In using these measures on those with transgenderism, this could possibly alleviate suicide rates and other negative variables associated with these paraphilic disorders and sexual orientations.
References
Abdo, C.H.N., Hounie, A., de Tubino Scanavino, M., & Miguel, E.C. (2001). OCD and transvestism: Is there a relationship?. ACTA Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 103(6
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
Blanchard, R. (1989). The Concept of Autogynephilia and the Typology of Male Gender Dysphoria. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 177(10), 616-623. doi:10.1097/00005053-198910000-00004
Griffiths, M. (2012, February 28) Dressed to thrill? A brief overview of transvestic fetishism. Retrieved from https://drmarkgriffiths.wordpress.com/2012/02/28/dressed-to-thrill-a-brief-overview-of-transvestic-fetishism/
Lawrence AA . Autogynephilia: An Underappreciated Paraphilia . In: Balon R, Hrsg . Sexual Dysfunction: Beyond the Brain-Body Connection. Adv Psychosom Med 2011 ; 135 – 148
Långström, N., & Zucker, K. J. (2005). Transvestic fetishism in the general population: Prevalence and correlates. Journal of Sex and Marital Therapy, 31, 87–95
Moser, C. (2009). Autogynephilia in Women. Journal of Homosexuality, 56(5), 539-547. doi:10.1080/00918360903005212
Stein DJ, Hollander E, Anthony DT, Schneier FR, Fallon BA, Liebowitz MR, Klein DF: Serotonergic medications for sexual obsessions, sexual addictions, and paraphilias. J Clin Psychiatry 1992; 53:267–271
Usmani et al, (2012) Treatment of Transvestic Fetishism With Fluoxetine: A Case Report. Iran J Psychiatry Behav Sci. 2012 Autumn-Winter; 6(2): 100–101
Human Intelligence, Child Rearing and r/K Selection Theory
1300 words
In a paper titled Extraordinary intelligence and the care of infants, Piantadosi and Kidd (2016) add to the other hypotheses of higher cognition in humans (Cold Winter Theory and farming) by positing higher cognition evolved to better take care of offspring.
Their theory is that big brained parents have big brained children, with the big brained children needing to be born earlier as their head has to be small enough to pass through the birth canal. A lot of animals can stand up immediately after birth, when humans can’t even hold their head up (I will return to this point later). Human babies are born less mature than other primates, which means they are more vulnerable, thus higher cognition evolved to better care for children. All of the variables coalesce into the need for more intelligent parents, which lead to humans growing more intelligent as a result of this.
They found that weaning time, which acts as a measure of the prematurity of infants, was a much better sign of a primate’s intelligence than any other variable they looked at, including brain size. Piantadosi said “One of the motivating puzzles of our research was thinking about those theories and trying to see why they predict specifically that primates or mammals should become so intelligent, instead of other species that faced similar pressures.”
The researchers also state that this may explain how humans developed good social reasoning and the “theory of mind” which is the ability to anticipate the needs of others as well as recognizing that other’s needs may not be the same as their own. Kidd also says how the theory of mind is especially helpful since human babies won’t talk for a couple of years. Since women took care of the children, they had to evolve a higher verbal IQ to better care for them. Along with being better able to care for children, men had to evolve high intelligence to care for both the children and women as well as hunt for food and defend his family and other co-ethnics.
Piantadosi and Kidd’s (2016) data shows that the helplessness of a primate’s newborns predict their intelligence, as well as accounting for human uniqueness in intelligence and why this level of cognition took so long to evolve. They also show how dinosaurs, who evolved in the same conditions and had a longer time to do so, did not evolve the same level of super intelligence as primates did. They also matured in eggs, showing that there is no link between intelligence and infant immarurity and birth. Humans also mature slower and need longer parental care. Due to these pressures, a bigger brain evolved. Babies are born earlier and mature slower than other animals, leading to higher intelligence. This also shows how human intelligence is so different from our closest primate ancestors.
This theory compliments the cold winters theory as well as Cochran and Harpending’s argument that higher intelligence evolved due to the advent of farming. Adequate nutrition lead to the development of higher intelligence and bigger brains as well. It also compliments other theories, including that we evolved higher intelligence due to social reasoning and reproductive pressures (sexual selection).
This theory also shows more evidence for Rushton’s Differential-K Theory. As the researchers noted, babies were born less mature than other primates babies. We can also apply r/K selection theory to this as well. Black babies are born one week earlier than white babies who are born one week earlier than Asian babies. Despite black babies being born one week earlier than white babies, black babies can support their heads at 24 hours earlier than white babies. For Asians it’s unknown, as Rushton notes in Race, Evolution, and Behavior (pg. 148). Asian children are slower to develop than white children who are slower to develop than black children, with Asian children having the biggest brains of the three races. This theory of Piantadosi and Kidd (2016) perfectly compliments Rushton’s r/K selection theory. Asians are born one week earlier than whites who are born one week earlier than blacks, which correlates with the average intelligence scores of the three races.
The cold winters theory also shows another reason for bigger brains, as those who evolved in colder climates evolved bigger brains, and therefore higher intellect. The more intelligent parents who could provide more for their offspring prevailed over those less intelligent who could not survive. This lead to more mutations developing in those with high IQ alleles making higher intelligence more prevalent in those populations who evolved further away from the equator, as well as having an adequate population for more births to occur leading to more genetic mutations which leads to higher intelligence. Since those with higher intelligence can survive more efficiently than those with lower intellect, they were able to spread their genes more by having more offspring than those with low IQ alleles (the opposite of what is happening today).
As noted previously from Rushton’s data, those with higher intelligence are born earlier and mature slower than those with lower intelligence. Black children being able to, for instance, lift their head at 24 hours sooner than white children, along with all of Rushton’s data that shows that blacks mature the fastest on all variables. Black children have to mature faster due to a higher mortality rate, which is correlated with low IQ. This is also why black girls have an earlier menarche than white girls. Since black children are born with smaller heads, they, according to Piantadosi and Kidd’s data, have lower intelligence as a result. Black children average smaller brains than white children who averahe smaller brains (and heads) than Asian children. This shows with how Asians are born one week earlier than whites who are born one week earlier than blacks.
This study shows how r/K selection theory is not dead, nor is it not a theory to take seriously, as other researchers have stated since Rushton applied it to race, since it is shown to have good predicitive power. Piantadosi and Kidd’s data corrobarates Rushton’s findings on earlier births between the races, vindicating Rushton and his r/K selection theory. Piantadosi and Kidd show that a) helpless children need intelligent parents, b) intelligent parents must have large brains and c) large brains necessitate having helpless children. This would show, in accordance with r/K selection theory that a) helpless Eurasian children need more intelligent parents, b) Eurasian parents must have large brains and c) large brains nescisstate having helpless Eurasian children.
Piantadosi and Kidd’s theory compliments other theories of human intelligence, which strengthens the cold winters theory of intelligence more, as those with higher intellect have bigger brains, and are therefore born earlier than those with lower intellect and smaller brains. As time goes on, more and more researchers will, unknowingly to them, corroborate more and more of Rushton’s r/K Life History variables. As noted by E.O. Wilson (co-founder of r/K selection theory) in defense of Rushton in the early 90s:
“I think Phil is an honest and capable researcher. The basic reasoning by Rushton is solid evolutionary reasoning; that is, it is logically sound. If he had seen some apparent geographic variation for a non-human species – a species of sparrow or sparrow hawk, for example – no one would have batted an eye. … when it comes to [human] racial differences, especially in the inflamed situation in this country, special safeguards and conventions need to be developed.
As we understand human development more, Rushton’s r/K Life History Theory will be corrobarted. This three-way pattern Rushton noticed, “Rushton’s Rule of Three“, has been corroborated yet again by other researchers. As time goes on, the true nature of humanity, as well as human races, will be revealed unbeknownst to them.
I wonder if Piantadosi and Kidd realize that they have just corroborated one of Rushton’s theories?
Polar Bears, Inuits, Evolution and Fst
1150 words
The Daily Stormer published an article today that claimed that “Polar bears are miscegenating with grizzly bears“. When polar bears and grizzly bears mate, they produce a “pizzly bear“. Due to this, the polar bear population is shrinking and the grizzly bear population is growing.
Scientists say this doesn’t look good for the polar bears; though these hybridizations are not due to ‘climate change’, as is suggested. Using a computer model, the researchers generated a prediction of the Earth’s climate from 2071 to 2100. The model analyzed how different species of birds, mammals and amphibians would need to migrate to find new territory. Birds had the highest overlap with 11.6 percent, attributed to their range from flying. Mammals and amphibians were 4.4 and 3.6 percent likely to encounter a hybridization event. Overall, about 6.4 percent of all species are expected to come into contact to even have the chance to hybridize with other compatible species. Meaning, the polar bear is not in danger of ‘dying out’ due to ‘miscegenation’.
What is missed in the article mentioned at the beginning is that polar bears and grizzly bears are even able to produce offspring at all. This is due to the two splitting around 350 kya to 6 million years ago. This article then says something vaguely familiar:
After beginning to branch off from brown bears, the polar bear’s ancestors under went a series of evolutionary changes in order to survive in the Arctic. The bears adapted to a life of hunting seals and surviving extreme cold. One of the most remarkable adaptations was the ability to thrive on a fat-rich diet withoutapparent heart damage. (sounds like the Inuit or other Eskimo tribes; emphasis theirs)
‘The bears’ could be switched to ‘the Eskimoes’ or ‘The Inuit’and make complete sense. The Inuit also live off a high-fat diet. The higher n-3 gives immunity and boosts in health to a slew of diseases as well.
The Inuit and their ancestors evolved special genetic mutations that allowed them to partly counteract the effect of a diet high in fat. Nearly 100 percent of the Inuit have these genes, while 2 percent of Europeans and 15 percent of Han Chinese do, which means that they synthesize n-3 differently than the Inuit. Over time eating a diet high in fats, the Inuit evolved these genetic adaptions to better adapt to their environment. The genes they have also lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and fasted insulin levels, which presumably has an effect on cardiovascular disease and diabetes. This used to be the case, but “exposure to a more Western lifestyle” has made Diabetes Mellitus in the Inuits comparable to that of the general population. Since growth is reliant on a person’s whole fatty acid profile, the Inuits are, as a result of these mutations, 1 inch shorter than they should be. The same mutations causing shorter height in the Inuit have also been found in Europeans. Researchers have found many genes responsible for height, but this was “one of the strongest effects ever found by geneticists”.
These genetic mutations are around 20,000 years old and originate with their Siberian ancestors. They think that the adaptation came about in the last Ice Age, but the selection is far stronger in the Inuit, due to them being one of the furthest populations away from the equator.The researchers have also found that the Inuits have another common mutation in their population that is involved in the differentiation of brown, subcutaneous fat cells and brite fat cells. Brite fat cells burn fat for more heat, showing another adaptation they had from their diet and direct environment. This helped them survive the harsh climate.
A strict Inuit diet shows evolution in action, that populations forced to subsist mostly on one type of food/macronutrient can and will adapt to their environment over time, proving that evolution exists. However, you cannot infer from the Inuits that the effect they gain from this diet will carry over to the general population.
The Science Daily article then goes on to say people have asked themselves whether they “Should be on a Stone Age diet”. My answer to that is a resounding “No” if you think the diet will do anything different from any other diet and weight training. As stated in the SD article, you cannot say that other populations, for instance, evolved to eat a certain way cannot be made as the Inuit have certain genetic mutations that no other populations have, in the frequency they do, for that matter.
The DS article, more interestingly, doesn’t bring up how two different species are interbreeding. Humans have a Fst distance of less than .5. The Fst for polar and grizzly bears is 0.2688. Two differing populations separated anywhere between 350 kya to 6 million years ago, can interbreed, and so can humans. Sewall Wright, the creator of the Fst concept, has said that if this differentiation was noticed in any other species, that they would be noted as distinct subgroups. When it comes to human genetics and science, science chooses to take the “egalitarian route” and deny the existence of race. However, when it comes to polar and grizzly bears, talking about how polar bears are a subspecies of grizzly bears and the polar bears adapted to the cold leading to physical and physiological differences, this is fine. Just like when Rushton proposed Differential-K Theory, which is the application of r/K selection theory to humans, it got shot down, despite E.O. Wilson who co-founded r/K selection theory stating “I think Phil is an honest and capable researcher. The basic reasoning by Rushton is solid evolutionary reasoning; that is, it is logically sound. If he had seen some apparent geographic variation for a non-human species – a species of sparrow or sparrow hawk, for example – no one would have batted an eye. … when it comes to [human] racial differences, especially in the inflamed situation in this country, special safeguards and conventions need to be developed.” Rushton’s main thesis has also never been refuted. No other explanation can fully explain the variables Rushton describes in Race, Evolution, and Behavior like r/K selction theory does.
Polar bears are not going away, and if they were, it’d just be evolution in action as the point of life is to breed and carry on your lineage (however, fitness is increased for the grizzly bear as he is gaining more habitat, yet decreasing for the polar bear due to a warming planet). The strongest populations get selected for, while the weakest become absorbed/wiped out. Since the planet is warming, as well as the grizzly bears looking for more environment some, not all, are mating with polar bears. This does not mean that polar bears will go extinct due to inbreeding with grizzly bears. Inuits are proof of the existence of evolution with how they adapted to their high-fat diet and cold environment, but you cannot use this information on their diet and say that the benefits from a high fat diet would be the same in other populations.
Even More Evidence for GST: Speed Daters Match on Genotype
850 words
Your success at speed-dating might be influenced by your genetic make-up and your potential partner’s ability to detect so-called ‘good genes.’ The research team found that participants who were more likely to be asked on a second date had genotypes consistent with personal traits that people often desire in a romantic partner.
Coming off of a successful refutation of JayMan (check comments too), more evidence for our claim came out the other day. Us humans can match on genotype, which we, of course, match with people with other similar heritable characteristics. Since humans match on these traits that are more heritable than the ones that are more influenced by environment, then we can say that we are seeking out partners who are like us, therefore matching on genetic similarity.
Wu, et al (2016) examined 262 Asian Americans in a speed-dating setting. The researchers predicted that there would be considerable matching by genotype between the genders. They found that the gene A118G, which is linked to submissiveness and social sensitivity, whereas for the men, the minor variant with the -1438 A/G allele, which is linked to social dominance and leadership, were shown to have greater success. They also discovered that men and women with genotypes consistent with “prevailing gender norms were more likely to receive second date offers”
The researchers say that “These results suggest that personal attributes corresponding to A118G and −1438 A/G can be detected in brief social interactions, and that having a specific genetic variant or not plays a tangible role in dating success,” Those with the A118G polymorphism had greater capacity for experiencing social pleasure and pain as well as their need to have social contact. This also shows how Men and women with the opposite of each allele (men having the A118G allele and women having the -1438 A/G allele) were seen as less desirable mates, showing good evidence that each allele is gender-specific. Wu also believes this effect could also expand to other social interactions, such as job interviews.
This study shows more evidence for Rushton’s theory of spouses matching phenotypically by genotype. Spouses are as similar as 4th cousins. Spousal genetic similarity is a significant driving force for human civilization, as it selected for certain traits over others that then lead to things such as higher IQ in Eurasian men to beauty in Eurasian women, vice versa for Africans. In Eurasian societies, men hunted and while women took care of the children. Higher intelligence then evolved in men due to needing to strategize, among other things such as surviving the frigid temperatures. Women took care of the children, and thus developed a higher verbal IQ as a result of this. In Africa, women gathered food, selecting them for slightly higher intelligence than their male counterparts. Conversely, the African males were selected for attractiveness (Fuerle, 2008).
Those K-selected have lower birth rates, and thus, must be more rigorous in choosing a mate. Choosing a mate based on intelligence showed that the male could provide food as well as protect the family against predators and other bands of humans. R selected humans have more children and show less care, so they have higher birth rates to counter this. They are less rigorous in mate selection due to need to have more children due to a higher death rate. This is mirrored still, even today in modern society. Human sexual selection is one of the reasons why human evolution progressed to the point is has, with the driver being evolution in harsher climates. Eurasian women needed to be more stringent in choosing mates due to a higher chance of death in choosing the wrong mate. Over time, this lead to a ‘genotype sensor’ if you will, which by matching by certain phenotypic traits (facial symmetry, skin color, height, health, etc), chances for intelligent children, better care and more food will come as a result of this stringent selection by women, which in turn lead to evolution of certain traits in Eurasian men and women.
This shows that these human differences in how we select our spouses to how our civilizations ultimately end up is due to a) climate, b) sexual selection and c) genetics. Passing on the best genes lead to an ultimately better society, and as a result, this lead to those genes that were more successful having a chance to produce more copies of themselves, assuring that society would be run well in the future. This is also why government systems such as monarchies have hereditary rulers.
I have said numerous times that the tendency to favor co-ethnics is the tendency to favor shared genes. Benefiting those similar to yourself ensures that you’re benefiting copies of your genes, ensuring your genetic legacy for the future. Matching with those who appear similar to us by genotype when there is such phenotypic similarity shows that this is a trait we humans have to seek out those co-ethnics genetically similar to ourselves.
The Black-White IQ Gap
3300 words
(This goes along with my refutation of Steele here: Strong Evidence, Strong Argument: Race IQ and Adoption)
There is a 15 point, 1 standard deviation between black and white IQs. I will argue that they are not biased towards any group, as well as there being both positive and negative life outcomes based on IQ, crime included. This is due to false ideas of equality, some “blank slate” idea that we all have the same capacity for cognitive ability, athletic ability and so on. These egalitarian ideas, in turn, have devastating effects on our society, as we a) deny the reality of intelligence and b) deny any type of racial gaps in intelligence.
The famous words “Compensatory education has been tried and has apparently failed” in Jensen’s paper in the Harvard Educational Review that reignited the firestorm on the race/IQ debate called How Much Can We Boost IQ and Scholastic Achievement? is the reason why this debate got thrown back into the public eye (Jensen, 1969). It will be argued in this paper that he was correct and that his main thesis that blacks need differing education than do whites is correct and needs to be done.
IQ tests were first developed off of Army Aptitude Tests in the early 1900s by French psychologist Alfred Binet. They were originally used to identify at-risk populations in terms of who is mentally retarded. People then say that due to this, that IQ tests don’t test anything of worth due to the reason why they were originally developed.
In 1976, a study was conducted called the Minnesota Transracial Adoption study where they took children of different races who were adopted into different families and tested their IQs at age 7 and again at age 17. A follow-up study was published in 1992. What was found, was that IQs of transracially adopted children didn’t differ at all from children raised by their biological parents in the same area.
Dr. David Duke states in his book My Awakening: A Path to Racial Understanding (1998), that the authors waited about 4 years to publish these findings. This, of course, has to do with the political climate of today. Any allegations of “racism” can and most likely will end someone’s career; so most individuals just go the politically correct route to play it safe and keep their credentials. Blacks raised in white families hardly did any better than blacks raised in black families. If the differences supposedly were environmental in the way environmentalists say it is, how come blacks raised in rich white families didn’t reach the IQ of whites if “IQ is malleable by the immediate environment?” Because the differences are genetic.
Though, there are other studies that state that environment matters more than genetic factors. These three studies (Moore 1986; Eyferth 1961; and Tizard, 1972) all conclude that the black-white IQ gap is environmental in nature.
A study was conducted that compared IQ scores of 23 7 to 10-year-old black children raised by middle-class white families and the same number of black children but raised in black families (normal adoption) (Moore, 1986). The findings indicated that traditionally adopted black children raised by black parents had normal IQ scores (85), whereas those black children who were adopted by white families had IQs 1 standard deviation (100) above the black mean. Moore states that multivariate analysis indicates that the behaviors of black and white mothers were different in regards to how the black children were treated. She states that white adoptive mothers reduced stress by joking, laughing, and grinning. Whereas black adoptive mothers reduced stress in less positive ways including coughing, scowling and frowning. She also says that white adoptive mothers gave more positive reinforcement to their adoptive child’s problem solving whereas black adoptive mothers gave less (as I am arguing here, these traits are mostly genetic in origin, driven by IQ). She concludes that the ethnicity of the rearing environment exerts a significant influence on intellectual ability as well as standardized test scores. The sample sizes, however, are extremely small and to infer that the black-white IQ gap is environmental in origin because of a study with a small sample size is intellectually dishonest.
One study conducted in Germany in 1959 observed IQ scores of out-of-wedlock children fathered by US soldiers stationed in Germany during WWII and reared by white German mothers (Eyferth, 1961). Mean IQ scores for 83 white children and 97 mixed-race children were 97, 97.2 for the whites and 96.6 for the mixed-race children (Rushton and Jensen, pg. 261). However, these results are disputed. One, the children were extremely young, one-third of the children in the study were between the ages of 5 and 10 whereas the remaining two-thirds of the children were between the ages of 10 and 13. The malleability of intelligence is very well-known in regards to children. The heritability of IQ at age increases with age (a phenomenon known as ‘the Wilson Effect’), which Arthur Jensen states that as a child ages, social environment can increase IQ (as heritability for children aged 5 is 22 percent and children aged 7 at 40 percent). Though, as the child ages, genes activate, and they fall to their genetic potential, with genetic effects accounting for a lion’s share of intelligence (80 to 90 percent) and environment having no effect. Second, 20 to 25 percent of the ‘black’ fathers were French North Africans (Caucasians). This shows why the mixed-race children had higher IQs in the sample: about a quarter of the sample was Caucasian (Rushton and Jensen, pg. 261). Finally, rigorous selection was done on both the white and black soldiers. With 3 percent of whites getting rejected compared to 30 percent of blacks, it is shown that high IQ blacks were selected for, therefore, skewing the sample.
Yet another study on black and white children observed 2 to 5-year-olds in a nursery setting (Tizard, 1972). The white and black children both had IQs at 102.6 and 106.3 respectively. She found no significant gap in the three groups tested (white, black and West Indian). However, she did note that the single significant difference was in that of non-white children.
All three of the above studies that get cited ad nauseum have something in common: they did not retest the children again at age 17 like was done in the Minnesota Transracial Adoption Study. This is very critical. As it was alluded to earlier, as children mature, genetics exerts more of an effect than does socialization. Any IQ differences that are brought about by socialization will be mediated by genetics at adulthood, falling to the racial mean. It also noted how the age of adoption does not influence children’s IQ scores after age 7 (Jensen 1998b). This is due to, again, genetic effects being heightened as age increases.
What the Minnesota Transracial Adoption Study (Weinberg, Scarr, and Waldman, 1992) and the Eyferth study (1961) had observed was that the children born to a white mother and a black father had statistically significant differences in IQ in comparison to those birthed by a black mother and white father. This is attributed to prenatal environment. It was observed that mothers who had higher IQs and were more educated (which both correlate highly with each other), had children which, in turn, had higher IQ scores as well (Erikson, 2013). The results of the study suggest that mothers who are more educated have children who have higher intelligence. This should end this debate right there. Since, clearly, a white mother is more conducive to foster a higher IQ than is a black mother, this shows that racial differences in IQ are largely genetic in origin.
The black-white IQ gap has been noticed for over 100 years, ever since the test has been first conceptualized. Egalitarians may say that “they’re biased against minorities” or “they don’t learn the right things on the test”, all of these are easily refutable. This was true in the 70s, according to Herrnstein and Murray, but today there is no bias of that magnitude on these tests of cognitive ability.
Jensen states that genetic and cultural factors influence the black-white IQ gap the same as individual factors (80 percent genetic factors, 20 percent environmental). Since both individual differences in IQ, as well as the mean difference in the black-white IQ gap are genetic, this shows that some individuals are genetically predisposed to have lower IQs. Moreover, a multitude of traits in life fall on a bell curve, you will have some individuals at one end, and others at the opposite end, but you’ll see a majority fall in the middle of the racial mean (85 for blacks, 100 for whites, 104 for East Asians and 107 for Ashkenazi Jews). So, with equalized environments, the gap can be closed by around 3 points, but still a lion’s share of the gap is still there, which again gives credence to the genetic hypothesis.
Those who disbelieve the validity of IQ tests at the individual level, as well as the between-group level, say that test biases are the cause for lower scores in certain individuals in minority populations. Gottfredson et al state in their publication that was released after the controversial book The Bell Curve, Mainstream Science on Intelligence, that if you speak the language, IQ tests are not biased. If you don’t speak the language, you then get a special IQ test that is culture free, based on pattern recognition called Raven’s Progressive Matrices. Even then on these culture-free, word-free IQ tests, there is still a one SD gap, 15 points, between blacks and whites.
People have tried to bridge the gap, even going so far to make a test that’s ‘culture fair’ to blacks called the B.I.T.C.H. (Black Intelligence Test of Cultural Homogeneity) IQ test (Williams, 1972). What was found was that blacks scored highly, whereas whites lagged behind. But, the thing is, this test has ridiculous concepts that don’t test actual intelligence. The way that people say that regular IQ tests are biased towards blacks don’t even realize that the way the B.I.T.C.H. IQ test is set up does not mirror the supposed biased nature of regular IQ tests on blacks.
Flynn noticed that no matter which country you look IQs have gained around 3 points per decade. Herrnstein and Murray then coined the term The Flynn Effect, after the man who focused the most attention on the phenomena. Flynn argues that since IQ scores have been gaining the same amount of points in any population no matter where you look, that the black-white IQ gap has to be environmental in origin.
However, the Flynn Effect is a fallacy and is overstated. In 1945, the average IQ of whites in America was 85, the same as the black average today. That statement is supposed to show that the between-group differences are environmental in origin and since there haven’t been any big genetic changes in both populations to account for this difference, then the gap must be environmental in origin. Just because a change in one group over time is due to an environmental change, doesn’t mean, or even make it probable, that a difference between 2 groups at the same time is due to an environmental change. The Flynn Effect make’s that highly unlikely and here’s why.
Any country you look at, the rate of increase is 3 IQ points per decade; but gaps in IQ stay the same. This shows that this same uniform factor affects all groups the same throughout the world. And due to this uniform factor, as a result, you have a difference in IQ that’s being preserved. This suggests that the response on the parts of blacks and whites is due to non-environment factors, a genetic factor, which makes the difference in IQ remain as the Flynn Effect goes into effect.
Blacks and whites also have a similar environment, especially since segregation ended. Since environments are similar, the more and more similar the environment, the less and less differences are due to environment and the more and more they are due to genetic factors. So the 15-point gap surviving this change in environments proves that the racial gap is genetic in origin.
Dickens and Flynn state that black Americans have closed the gap in recent years, but this, however, is not the case. Most of those studies were done on children; Jensen states that the black-white IQ gap becomes more noticeable as they get older because genetic effects take over at adulthood with the environment having little if no effect on IQ (Rushton and Jensen, 2005). Jensen concludes that the SD gap between blacks and whites at early adulthood is about 1.2 SDs or about 17 IQ points. In Rushton and Jensen’s 2005 paper, Flynn and Dickens sidestepped a theoretical analysis in which it’s showed that the higher amount of white admixture a black has, the higher his IQ score is.
The Flynn Effect is not on g, or the general intelligence factor, which the most heritable items on the subtests show the most differences between blacks and whites (Rushton and Jensen, 2010). Since the Flynn Effect does not fall on g, this should not even be in the discussion. A Flynn Effect is not a Jensen Effect, which is real gains in g over time (Rushton, 1998). Rushton found it ridiculous that we had a nation of mentally handicapped children 100 years ago. This was enough for him to disregard the Flynn Effect.
Other proposed causes for this gap involve a mechanism called ‘stereotype threat’ (Steele and Aronson, 1995). Stereotype threat is a situational predicament in which people find themselves falling into the stereotype of whatever group their group is a part of. Though, this is not the case for blacks. Blacks are rated as seeing themselves as more attractive, which a) shows more self-confidence and b) shows that the so-called effects of white racism making blacks feel ugly and inadequate in their own skin are simply not true. Kanazawa (2011) noted that both male and female blacks rated themselves higher than other groups; showing that there are no lingering effects of racism as well as this silly belief that just by thinking you’re going to fall into a stereotype means that you will fall into it.
Still, others may state that poverty is a cause for the IQ disparity between the races. People have causalities mixed up when they make this statement. Since lower IQ is correlated with lower SES, the cause of poverty is people being born with low intellect which manifests itself in the wealth attainment of the individual. Many recent studies have come out saying that poverty decreases IQ, yet the only environmental factors that can do such a thing is malnutrition, extreme abuse, and extreme isolation. Other than that, all a parent needs to do is just give the child an ‘OK’ environment and genetic factors will take care of the rest.
Critics of the public school system have said for decades that you can’t solve educational problems by throwing money at them, but those who believed in the public schooling system said it has yet to be tried. They did try, in Kansas, MO, and failed miserably (Ciotti, 1998). This desegregation experiment cost 11,700 dollars per student, more money spent per individual on a cost of living basis than 280 school districts around the country. This tax-payer money bought “higher teachers’ salaries, 15 new schools, and such amenities as an Olympic-sized swimming pool with an underwater viewing room, television and animation studios, a robotics lab, a 25-acre wildlife sanctuary, a zoo, a model United Nations with simultaneous translation capability, and field trips to Mexico and Senegal. The student-teacher ratio was 12 or 13 to 1, the lowest of any major school district in the country.”
Despite all of these variables to enrich the environment of the black students, even bussing in white kids from out of district, the gap did not diminish, test scores did not change and there was less, not more, integration. Moreover, numerous individuals say that poverty and schooling systems are the cause for anti-intellectualism in the black community. I, however, argue that there is a considerable genetic component to the black-white IQ gap (Rushton and Jensen, 2005 p. 279).
Where does all of this leave us? Yes, blacks are less intelligent than whites, but what does this mean for our society that we refuse to acknowledge the existence of innate intelligence, as well as racial differences in intelligence? The average IQ of a repeat juvenile criminal in America is 92 (Herrnstein, Murray, and Cullens, 1998). At adulthood, the average IQ for a repeat criminal is 85. The reason for the IQ of a repeat adult offender being lower than that of teenaged offenders is due to as you age, the environment doesn’t matter as genetics takes over at adulthood.
The fact that we are disregarding g (intelligence) and its multiple covariates is extremely alarming. The fact that America is headed down the path to dysgenesis (Lynn, 2006) and we are not doing a thing about it troubles me greatly. The way we treat black underachievement in America is completely wrong. To succeed as a country, we need to recognize biological truths in that certain groups achieve highly whereas others have low levels of academic achievement, we need to recognize that there is no insidious plot to hold down others; we need to realize that some groups are less intelligent as others due to evolution in differing climates over tens of thousands of years. The trillions of dollars we have spent on all of these programs have not worked. We have tried them, and they have failed. No matter what we do, black underachievement will always be around. By recognizing black underachievement, they will be better able to succeed relative to themselves and not compare themselves to other high-achieving groups. There is a considerable genetic component to the gap (80 percent genetic) and that due to this, blacks should have differing standards in comparison to the rest of the population (Jensen, 1969).
References
Ciotti, P. (1998) Money and School Performance: Lessons from The Kansas City Desegregation Experiment http://www.cato.org/pubs/pas/pa-298.html
Cullens, F.T., Herrnstein, R., Murray, C. Does IQ Significantly Contribute to Crime? (From Taking Sides: Clashing Views on Controversial Issues in Crime and Criminology, Fifth Edition, P 30-51, 1998, Richard C. Monk, ed. — See NCJ-183062)
Dickens, W. T., & Flynn, J. R. (2006). Black Americans Reduce the Racial IQ Gap: Evidence From Standardization Samples. Psychological Science, 17(10), 913-920. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01802.x
Duke, D.E. (1998). My awakening A path to racial understanding. Covington, LA: Free Speech Press.
Eriksen, H. F., Kesmodel, U. S., Underbjerg, M., Kilburn, T. R., Bertrand, J., & Mortensen, E. L. (2013). Predictors of Intelligence at the Age of 5: Family, Pregnancy and Birth Characteristics, Postnatal Influences, and Postnatal Growth. PLoS ONE, 8(11).
Eyferth, K. (1961). Leistungen verscheidener Gruppen von Besatzungskindern in Hamburg-Wechsler Intelligenztest fu¨r Kinder (HAWIK) [Achievement of children on the Hamburg-Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children]. Archiv fu¨r die gesamte Psychologie, 113, 222–241.
Flynn, J. R. (1987). Massive IQ gains in 14 nations: What IQ tests really measure. Psychological Bulletin, 101, 171–191.
Gottfredson, Linda S. “Mainstream science on intelligence: An editorial with 52 signatories, history, and bibliography.” Intelligence 24.1 (1997): 13-23.
Herrnstein, R. J., & Murray, C. A. (1994). The bell curve: Intelligence and class structure in American life. New York: Free Press.
Jensen, A. (1969). How Much Can We Boost IQ and Scholastic Achievement. Harvard Educational Review, 39(1), 1-123.
Jensen, A. R. (1998). The g factor: The science of mental ability. Westport, CT: Praeger.
Kanazawa, S. (2011). Why Are Black Women Less Physically Attractive Than Other Women? The Scientific Fundamentalist
Lynn, R. (1996) Dysgenics: Genetic Deterioration in Modern Populations, Human Evolution, Behavior and Intelligence Praeger, 1996
Moore, E. G. J. (1986). Family socialization and the IQ test performance of traditionally and transracially adopted Black children. Developmental Psychology, 22, 317–326.
Murray, C. (2014) Our Futile Efforts to Boost Children’s IQ http://www.aei.org/publication/futile-efforts-boost-childrens-iq/
Rushton, J. P., & Jensen, A. R. (2005). Thirty years of research on race differences in cognitive ability. Psychology, Public Policy, and Law, 11(2), 235-294.
Rushton, J. P., & Jensen, A. R. (2010). The rise and fall of the Flynn Effect as a reason to expect a narrowing of the Black–White IQ gap☆. Intelligence, 38(2), 213-219. doi:10.1016/j.intell.2009.12.002
Steele, C. M., & Aronson, J. (1995). Stereotype threat and the intellectual test performance of African Americans. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 69(5), 797-811. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.69.5.797
Tizard, B. (1974, February 1). IQ and race. Nature, 247, 316.
Weinberg, R. A., Scarr, S., & Waldman, I. D. (1992). The Minnesota transracial adoption study: A follow-up of IQ test performance at adolescence. Intelligence, 16(1), 117-135.
Williams, Robert L. (1972) The BITCH-100: A Culture-Specific Test.
“Philosophers of Science” and Race/IQ
1500 words
“Philosophers of Science” attempt to stick their heads into the race/IQ debate to give their field more credence than it should get with the hard sciences. They use bad arguments like saying that “gene-environment interactions are widespread and hard to entangle” (Block, 1995), not knowing that identical twins reared apart grow up to be so similar (Rushton and Jensen, 2005, p. 279). The only time they should stick their heads in this debate is when they’re affirming that the methodology used to test IQ as well as racial differences in IQ are sound; otherwise, they do not have the training to assess this. Most “Philosophers of Science” defend claims that disintegrate when presented with the relevant scientific evidence (Sesarardic, 2000). I will be referencing this paper for the length of this article.
Half of the paper analyzes Lewontin’s argument to Jensen in which he uses his now famous “seed argument” in which he says you can take two seeds from the same heterogeneous population and plant them in rich and poor soil and “. . . as a result, the phenotypic differences within each of the two groups of plants will be 100 percent heritable, but the difference between the two groups will be entirely due to differences in two environments (zero heritability).” The fact of the matter is, this argument is parroted by “Philosophers of Science” when Jensen never made that argument.
Jensen then systemically dismantled every environmental argument with empirical evidence that they don’t hold up.
Other researchers then made accusations of “racism” the reason for Jensen’s overlooking of this. James Flynn, a big opponent of the hereditarian hypothesis and Rushton and Jensen in general, say that Jensen is not a “racist”. There is also something called the “X-Factor”, which is when phenotypic differences between two groups can be explained by an environmental factor that has no within-group variation at all, a 0 heritability. Racism, however, is a poor excuse for the “X-Factor”. Both Flynn and Jensen rule out discrimination as being the cause for the “X-Factor” as well.
Simply put, Jensen doesn’t make inferences that the black-white IQ gap is genetically based on one or a few variables on their own, but everything put together, that’s where the remaining evidence put. “Philosophers of Science” don’t understand heritability coefficients to be saying what they do; they wouldn’t be saying that if they knew how they worked.
Sesardic brings up how Block (1995) only mentions three pieces of empirical evidence: The “Flynn Effect”, “data about caste-like minorities”, and the small amount of genetic variation between races.
- The Flynn Effect happens uniformly in all populations at a rate of 3 points per decade but has slowed considerably. This increase began starting around 1880, coinciding with the industrial revolution. Better nutrition increased brain size in all populations, which lead to an increase in IQ. The Flynn Effect is not on g, so to make any claims that the differences in IQ between blacks and whites, or global differences in IQ for that matter, can be changed with more favoring towards environmentalist positions are not consistent with the scientific literature. In 1945, the average white IQ in America was 85, the same as the average American black IQ today. Since the differences in IQ have stayed consistent despite better nutrition in all groups, this proves that the gap is genetic in origin. Just because a change in one group over time is due to an environmental change, doesn’t mean, or even make it probable, that a difference between 2 groups at the same time is due to an environmental change. Since the Flynn Effect does not occur on g, it should be a non-factor.
- Minorities are only “caste-like” because differences in IQ are heritable, leading to racial disparities in social class differences. We can see when we match blacks, whites, and “Hispanics” for IQ (100), that some differences disappear, other differences decrease dramatically, and even blacks and “Hispanics” beat out whites in a couple of variables. Through multiple IQ tests averaged over time as well as seeing that test differences between races stay mostly the same, we can then make the inference, with all of the other evidence, that racial and ethnic differences in IQ are mostly genetic in origin with the environment having very little effect. To say that “racism” or “stereotype threat” has any bearing on these racial differences in IQ is laughable because 1) stereotype threat is only replicable in the lab and 2) racism as a variable does not exist in IQ testing.
- The small amount of genetic variation between races as an argument for the non-existence of race is meaningless. There are around 3 billion base pairs in the human genome. The human races differ on around .1 percent of the genome, or around 3 million base pairs. This is more than enough genetic difference to show phenotypic differences (obviously) as well as genotypic differences (again, obviously). Richard Dawkins in the Ancestor’s Tale writes: “What is not correct is the inferene that race is therefore a meaningless concept.” Race is a perfectly valid concept, anyone who denies it has doesn’t know of all of the studies that show the existence of race and how it’s a scientifically taxonomic concept.
Sesardic then brings up how “Philosophers of Science” continuously cite The Mismeasure of Man and Steven Jay Gould in an attempt to denigrate scientists long dead. A few “glowing reviews” from two “Philosophers of Science”:
No one has done as much as Stephen J. Gould to expose race and intelligence studies for the garbage that they often are. (Brown 1998, 5)
Stephen Jay Gould has lucidly analyzed how filling the skulls with lead shot, and comparing the weights of the lead, could easily be infected with unconscious biases. (Kitcher 1997, 171)
The garbage that they often are? Steven Jay Gould is a long discredited ideologue who put his politics before actual science, ironically giving HIM the same bias he falsely accused Samuel Morton of having. James Flynn even says that Gould’s book evades all of Jensen’s best arguments (as most always happens with this debate) with his false belief that g is “reified” therefore leading to the study of race and IQ being meaningless since he has “rebutted the g factor”. I proved the existence of Spearman’s hypothesis the other day using Jensen’s writings that he empirically verified that Spearman’s hypothesis exists in 25 independent samples of blacks and whites along with the study by Dragt (2010) who used the method of correlated vectors to empirically prove the existence of Spearman’s hypothesis. In meta-analyses of Spearman’s hypothesis, he found that differences in intelligence between groups are largely based on cognitive complexity and any so-called “biases in mental testing” cannot account for these racial differences in cognitive ability.
In the definitive refutation of Steven Jay Gould’s “reanalysis” of Morton’s skulls, Lewis, et al definitively prove by remeasuring 308 of the 670 skulls that he had no implicit biases. They also found that if Morton’s biases were true, then there would be considerable overestimates of white skulls while there would be considerable underestiamates of non-white skulls. Ironincally enough, he considered his Egyptian skulls “Negroid” and overmeasured by 12 percent. He overmeasured three of those skulls, along with Seminole (by 8 percent) and native African Nergro (by 7 percent), falsifying the claim that Morton had a bias in measuring his skulls!! As I have brought up here numerous times, as Rushton has refuted him (and defended Morton’s results) as well as Jensen giving Gould a definitive rebuttal to his book. Gould should not be being cited seriously anymore. He should only be brought up as an example of extreme bias in the context of race as well as racial differences and a whole slew of other things that are politically motivated.
He finally rounds up the paper by bringing up how TJ Bouchard, showing that the Big Five Personality Traits have a high heritabilty, gets told that they are traits that carry a social judgment. However, we now know that 40-60 percent of the variation the Big Five is heritable, so this is a meaningless claim.
Sesardic ends the paper as follows:
Why is this small segment of contemporary philosophy of science in such a sorry state? On reflection, I prefer to leave this question as an exercise for the reader. My aim in this paper is to criticize a deviant philosophical trend, not to explain how it came about or why it spread.
My answer to this question is that most philosophers seem to be leftists. We can see with the vehement race denial that they want to believe so strongly that racial differences, as well as race as whole, does not exist. The fact that they attempt to say that these things are not a reality and based on faulty methodologies shows that they do not know what they are talking about. They show large misconceptions about heritability, and continuously cite Steven Jay Gould, even when Gould has been refuted numerous times as well it being shown that they don’t correctly understand heritability. They show large misconceptions of what is understood in the field of psychometrics and heritabilities and make faulty claims about the hereditarian hypothesis.
If the hereditarian hypothesis is to be refuted (it won’t), it will be from science and not philosophy or “Philosophers of Science”.
Science Daily: Mom’s Exposure to BPA During Pregnancy Can Put Her Baby on Course to Obesity
1750 words
Science Daily came out with an article today that exposure to BPA invitro for babies is correlated with obesity at age 7. 94 percent of the women tested had detectable levels of BPA. BPA is also linked with early onset puberty, which I will also speak on later in this article as it has implications for one of my theories.
I briefly touched on BPA in my article What’s the Cause of the Cucking of Europe? where I said:
I advise all of you (women included, there are many deleterious effects of BPA on the mother as well as the baby prenatally), to discontinue use of plastics with BPA in them.
The above-linked study shows that preeclampsia is correlated with elevated levels of BPA in the blood levels in the pregnant mothers, fetal blood, and the placenta. BPA was found to be elevated in mother’s fetal tissue with preeclampsia in comparison to the mothers with lower levels of BPA in their fetal tissue. I will come back to the BPA link with preeclampsia later in the article as it has implications for ethnic groups in America.
The paper, which was just released on the 17th, called Bisphenol A and Adiposity in an Inner-City Birth Cohort, carried out tested BPA in three differing subjects: 375 babies invitro, (3rd trimester) children aged 3 (n=408) and aged 5 (n=518) (Hoepner, et al, 2016). They measured the children’s bodies as well as measuring body fat levels with bioelectrical impedance scales.** Prenatal urinary BPA was positively associated with waist circumference as well as fat mass index, which was sex-specific. When analyzed separately, it was found that there were no associated outcomes in body fat for boys (however it does have an effect on testosterone), but there was for girls (this has to do with early onset puberty as well). They found that after controlling for SES and other environmental factors, they discovered that there was a positive correlation with fat mass index – a measure of body fat mass adjusted for height, body fat percentage and waist circumference. The researchers say that since there was no correlation between BPA and increased obesity, that prenatal exposure to BPA indicates greater vulnerability in that period.
The researchers then conclude that BPA exposure invitro “may be an important underlying factor in the obesity epidemic” and that “Endocrine disrupting chemicals like BPA may alter the baby’s metabolism and how fat cells are formed early in life.”
If true, this has huge implications for the way we look at the obesity epidemic in this country. Who are the most likely to be obese? “Hispanics” and blacks (Ogden et al, 2014).
Returning to what I brought up earlier about early onset puberty: in my article on the hormone leptin being a cause for earlier menarche in black girls, I noted that since black girls were more likely to be heavier as well as mature faster than white girls, that differences in leptin were the cause of differences in menarche between the two groups. Elevated levels of serum leptin were correlated with body fat and differences in maturation between the two groups. Differences remained, but lessened, after controlling for differences in fat mass, maturation, age, and physical fitness.
Since BPA is correlated with adiposity in children and black girls have earlier menarche DUE to there being a higher chance of black girls being overweight in comparison to white girls, BPA is yet another piece to the puzzle of this phenomena, along with, of course, evolution. Ingestion of BPA is an environmental factor, however, with these changes in body chemistry in the children invitro due to increased BPA consumption by the pregnant mothers, it leads to one cause that can be prevented from further occurring due to our new knowledge.
The study was carried out on a cohort from NYC. In 2010 in NYC, the city was: 44 percent white, 25.5 percent black, 12.7 percent Asian with the rest being filled out by ‘Hispanics’ (not a racial category) and mixed-race people. Even after they matched for SES and other environmental factors, these differences persisted. However, this study was only carried out on those women who self-identified as either Dominican (basically African) and black. To quote the researchers:
Women were included if they self-identified as either African American or Dominican and had resided in Northern Manhattan or the South Bronx for at least 1 year before pregnancy. Exclusion criteria included mother’s report of: cigarette smoking or use of other tobacco products during pregnancy, illicit drug use, diabetes, hypertension, known HIV, or a first prenatal visit after the 20th week of gestation.
So, we have a full sample of Caribbean Africans and African Americans in this study. What else can we learn about those two populations and their consumption of things with BPA in them?
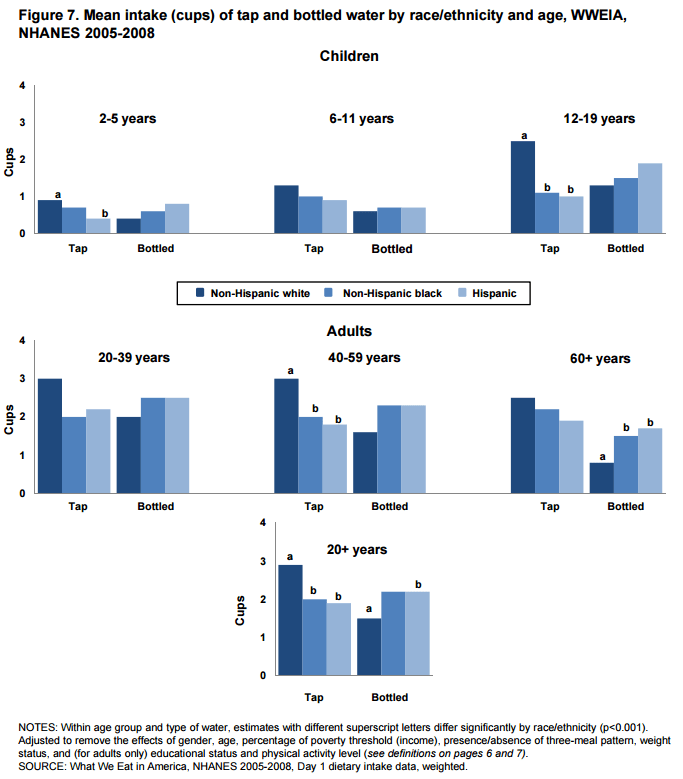
The above Figure (7) is taken from the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the Food Surveys Research Group study on differences in drinking tap and bottled water.in different populations in the country. As you can see in this figure (what is notable is the ages 12-19 and 20 to 60 in the table), whites at all age groups drink more tap water. Blacks and ‘Hispanics’ were pretty much even in consumption of bottled water. However, Mexican American girls, like black girls, are also entering puberty earlier. Since both populations have a substantial percentage of them overweight and obese (factor for serum leptin production which then causes early onset puberty), this again shows a strong correlation between body fat gain and early onset puberty. Moreover, this also shows that both Dominican and black populations consume more bottled water than do white populations, both populations are more likely to be obese or overweight (even after controlling for SES) which causes leptin production earlier causing periods to happen much sooner than in populations who drink less bottled water and use other products with BPA in them. .
Going back to preeclampsia, it is a condition that pregnant women develop that’s characterized by hypertension (high blood pressure) and protein in the urine. It’s known that black women suffer from it the most. More interestingly, over the past ten years, rates of preeclampsia have been increasing in the black female population. As the researchers note in the article, BPA is correlated with preeclampsia. Blacks have a higher rate and chance of being diagnosed with hypertension as well. All of these differing variables coalesce into our current obesity epidemic. With blacks and “Hispanics” being more likely to be overweight/obese drink more bottled water, have a higher risk for hypertension, higher risk for preeclampsia and having earlier menarche, these help explain, in part, racial/ethnic differences in obesity.
These differences can be attributed to consumption of bottled water, i.e., consuming things with made with and packaged in plastic as well as canned foods. From my experience with Dominican and black New Yorkers, they tend to have horrible lifestyles, tend to drink tons of bottled water and also tend to be overweight or obese at a higher rate in comparison to the general population. This leads to biologic factors changing (i.e., earlier menarche in younger girls) in these young girls, leading to devastating effects on their body chemistry.
This study, yet again, proves another underlying factor for obesity in certain populations in the country. And what do you know? It’s the populations that already have the highest rate of obesity in the country. When it becomes definitive that BPA consumption by pregnant mothers does lead to underlying factors in obesity. To quote the researchers: “Endocrine disrupting chemicals like BPA may alter the baby’s metabolism and how fat cells are formed early in life.” This will be HUGE for our understanding of underlying causes to obesity! Moreover, if (when) this is fully corroborated, it can then be said that by mothers exposing their children in the womb to excess levels of BPA, there is a chance that they are “giving their own choice to make their children have a higher chance of being obese, as they know the dangers of BPA consumption during pregnancy and all of the negative variables associated with it.”
This is an extremely interesting and important study for our understanding of obesity. Since BPA consumption invitro is correlated with higher fat mass index in girls at age 7, and since those girls who tend to be more overweight and obese than other populations, we can then say that BPA has a hand in obesity in children, which then causes serum leptin to be released, causing way menarche in these populations. An increase in sexual maturation has been linked to the obesity epidemic, which began around 60 years ago. The cause of this is due to the demonization of the fat macro and carbohydrates, all the while it was reversed. This destroyed insulin sensitivity for many Americans, leading to a huge majority of our health problems today.
In conclusion, underlying factors for obesity keep appearing. Due to racial/ethnic differences in bottled water consumption (one of the most common BPA products in households), which the effects of BPA may alter how fat cells are formed in early life, this accounts for, in part, excess adiposity in differing populations. These underlying factors could help show where some of these racial/ethnic differences in obesity come from. Since the two populations in the study (black American and Dominican) both have high levels of adiposity, both drink a lot of bottled water and both have earlier menarche than do whites (who drink LESS bottled water), this shows that some (a lot?) of the variation in obesity between ethnic/racial groupings can be explained by these underlying factors.
** I have one problem with this study. They assessed fat mass index with bioelectrical impedance.The machine sends a light electrical current through the body and measures the degree of resistance to the flow of the current, which body fat can then be estimated. Problems with measuring body fat this way are as follows: it depends on how hydrated you are, whether you exercised that day, when you last ate, even whether your feet are calloused. Most importantly, they vary depending on the machine as well. Two differing machines will give two differing estimates. This is my only problem with the study. I would like if, in a follow-up study, they would use the DXA scan or hydrostatic weighing. These two techniques would be much better than using bioelectrical impedance, as the variables that prevent bioelectrical impedance from being a good way to measure body fat don’t exist with the DXA scan or hydrostatic weighing.
More g Denialism and more Gould Refuting
1750 words
It seems like every day something new comes out that attempts to discredit the reality of g (This paper came out in 2012.). Steven Jay Gould (in)famously wrote in The Mismeasure of Man:
The argument begins with one of the fallacies—reification, or our tendency to convert abstract concepts into entities (from the Latin res, or thing). We recognize the importance of mentality in our lives and wish to characterize it, in part so that we can make the divisions and distinctions among people that our cultural and political systems dictate. We therefore give the word “intelligence” to this wondrously complex and multifaceted set of human capabilities. (emphasis mine)
Which is the same thing that the researchers of the paper Fractioning Human Intelligence said to The Independent:
“The results disprove once and for all the idea that a single measure of intelligence, such as IQ, is enough to capture all of the differences in cognitive ability that we see between people,”
“Instead, several different circuits contribute to intelligence, each with its own unique capacity. A person may well be good in one of these areas, but they are just as likely to be bad in the other two,”
Just like The Mismeasure of Man is “the definitive refutation to the argument of The Bell Curve”, right?
In the above paper, they cite Gould twice writing:
It remains unclear, however, whether population differences in intelligence test scores are driven by heritable factors or by other correlated demographic variables such as socioeconomic status, education level, and motivation (Gould, 1981; . . .
They have been shown over numerous studies that population differences in intelligence are driven by heritable factors (Rushton and Jensen, 2005; Lynn and Vanhanen, 2006; Winick, Meyer, and Harris, 1975; Frydman and Lynn, 1988; Rushton, 2005)
More relevantly, it is questionable whether they relate to a unitary intelligence factor, as opposed to a bias in testing paradigms toward particular components of a more complex intelligence construct (Gould, 1981;
I will prove the existence of g in this article. There is also an empirical basis for the g factor.
It’s getting old now that researchers still think that they can “disprove g”, as a multitude of studies have already corroborated Spearman’s hypothesis as an empirical fact. That is, applying the scientific method, using the same hypothesis over a multitude of different studies and testing those predictions by experiment or further observation and modify the hypothesis when new information comes to light. Then, repeat the aforementioned steps until there are no discrepancies between the theory and experiment/observations.Then when consistency is obtained it then becomes a theory that provides a coherent set of premises that explain a class of events.
How many times has the Hampshire et al hypothesis been corroborated? I doubt it has been corroborated as many times as Spearman’s hypothesis has.
As I said the other day, Jensen tested Spearman’s hypothesis on 25 large independent samples, with each sample confirming Spearman’s hypothesis. Even matching blacks and whites for SES didn’t diminish the effect. Jensen then concludes that the overall chance for Spearman’s hypothesis being wrong is over 1 in a billion. Pretty high odds.
Even then, if this study were to be replicated the amount of times that Spearman’s hypothesis has, it still wouldn’t disprove g.
On page 558-559 of the Afterword to The Bell Curve, Charles Murray responds to many of Gould’s criticisms of the book. He writes:
He (Gould) continues: “The fact that Herrnstein and Murray barely mention the factor-analytic argument forms a central indictment around The Bell Curve and is an illustration of its vacuousness.” Where, Gould asks, is the evidence that g “captures a real property in the head?
Murray states that they “barely brought up the factor-analytical argument” because it was out of date; Gould was using statistics on g that were 50 + years old. Also, a reviewer of his book for the journal Nature said that Gould’s “discussion of the theory of intelligence stops at the stage it was more than a quarter of a century ago.” Gould was using old arguments, and, as Arthur Jensen states in his response to Gould:
Of all the book’s references, a full 27 percent precede 1900. Another 44 percent fall between 1900 and 1950 (60 percent of those are before 1925); and only 29 percent are more recent than 1950.
More than half of Gould’s references in The Mismeasure of Man are outdated by more than 50 years. Clearly, he was attempting to denigrate the old studies of intelligence, i.e., phrenology, even though this recent paper in the journal Nature recently said:
The genomic regions identified include several novel loci, some of which have been associated with intracranial volume
So, we have several loci that are associated with intracranial volume; this shows that those skull studies of yesteryear weren’t crazy. Moreover, the fact that Rushton and Ankney (1996) “reviewed 32 studies correlating measures of external head size with IQ scores or with measures of educational and occupational achievement, and they found a mean r .20 for people of all ages, both sexes, and various ethnic backgrounds, including African Americans” shows that there is a correlation of .20, albeit not too high but there, with external head size and IQ. This shows that Gould’s argument on phrenology is bunk, as modern studies confirm that there is a slight correlation between head size and IQ, and therefore g.
The fact that researchers are still bringing up Gould’s arguments on g show that there really is no good argument to discount it. Basically, any and all arguments that attempt to discredit g are bunk as Spearman’s hypothesis has been empirically verified:
Conclusion: Mean group differences in scores on cognitive-loaded instruments are well documented over time and around the world. A meta-analytic test of Spearman’s hypothesis was carried out. Mean differences in intelligence between groups can be largely explained by cognitive complexity and the present study shows clearly that there is simply no support for cultural bias as an explanation of these group differences. Comparing groups, whether in the US or in Europe, produced highly similar outcomes.
Along with Jensen’s 25 large independent studies that showed that the probability that Spearman’s hypothesis is false is 1 in a billion, this proves that Spearman’s hypothesis is an empirical scientific fact.
Newman and Just, (2005) state in verbal and spatial conditions that the frontal cortex revealed greater activation for high-g in comparison to low-g, supporting the idea that g reflects functions of the frontal lobe. The “seat” of general intelligence is the prefrontal cortex (Cole, et al, 2011, Roth, 2011). This can also be verified with MRI scans that show that those who have higher g have bigger prefrontal cortexes than those with lower g.
Moreover, the fact that Colom, et al (2006) show that in their sample that neuroanatomic areas underlying the g factor could be found across the entire brain including the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes, shows that this factor is present throughout the brain and all are correlated with g and work together in concert to manifest intellectual ability.
Other researchers have also used the method of correlated vectors on functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), which measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique is proven useful due to the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal action are correlated. Lee, et al write:
In conclusion, we suggest that higher order cognitive functions, such as general intelligence, may be processed by the coordinated ability may be attributable to the functional facilitation rather than the structural peculiarity of the neural network for g. In addition, our results demonstrated that the posterior parietal regions including bilateral SPL and right IPS could be the neural correlates for superior general intelligence. These findings would be the early step toward the development of biological measures of g which leads to new perspectives for behavior interventions improving general cognitive ability.
They also used the MCV to find that the frontal and parietal lobes are associated with g. Even these studies show that g shows up throughout the brain and not in one solitary spot (though, the PFC is still the seat of intelligence), this shows yet another biological basis for g.
Hampshire, et al write:
Thus, these results provide strong evidence that human intelligence is a construct that emerges from the functioning of anatomically dissociable brain networks.
However, with the above studies confirming that the seat of intelligence is the prefrontal cortex, along with great g ability possibly be attributable to the functional facilitation rather than the structural peculiarity of the neural network for g, this shows, along with the study proving Spearman’s hypothesis, that g is a real and measurable thing. g’s seat is the prefrontal cortex, and exceptional g may possibly be attributed to the functional facilitation of the neural network for g . What all of these studies show is that all though the Hampshire paper showed how they “demonstrate that different components of intelligence have their analogs in distinct brain networks.” that a) higher order cognitive functions may be processed by the coordinated activation of widely distributed brain areas (disproving the above quote), b) the seat of g is the prefrontal cortex, c) those with more g have bigger prefrontal cortexes and therefore bigger brains since the prefrontal cortex is the ‘seat’ of intelligence and d) Spearman’s hypothesis has been corroborated numerous times by many different researchers not named Arthur Jensen.
Highfield (one of the researchers in the study) ends the article as follows:
“We already know that, from a scientific point of view, the notion of race is meaningless. Genetic differences do not map on to traditional measurements of skin colour, hair type, body proportions and skull measurements.
This is something that never ends; it always comes up no matter how many times it’s been said. People can say “race is a social construct” all they want, it doesn’t make it true as there is a biological reality to race.
Now we have shown that IQ is meaningless too,” Dr Highfield said.
IQ is not biased, nor is it “meaningless“.
When will people learn not to cite men who have smeared their legacy in an attempt to defame men who they disagreed with ideologically? Citing Steven Jay Gould in 2016 shows a bias to want to discredit g as a main factor for many things in life including SES, educational attainment, wealth attainment and so forth. The g factor is a measurable thing, with the seat of the factor being the prefrontal cortex. No amount of attempting to dispute this factor can be done, as it’s been empirically verified numerous times.
Ethnic Genetic Interests and Group Selection Does Exist: A Reply to JayMan
6350 words
JayMan has said that ““Ethnic Genetic Interests” Do Not Exist (Neither Does Group Selection)“. It’s clear from what he says towards the end that he has some sort of bias to attempt to disprove Ethnic Genetic Interests and Group Selection. This will be a definitive refutation of JayMan’s belief of the non-existence of GST and GS. Along with Dr. Swaggins from the CoonU Blog, both of us today will prove that EGI and GS do in fact exist and that JayMan has an implicit bias in the denial of EGI and GS. I will also address JayMan’s comment to me in that same article that I never responded to save it for this article.
I first wrote an article, Genetic Similarity Theory, in reply to his denial of EGI. It was short, but I got my point across with the Price Equation. JayMan then comments:
Ethnic altruism can’t evolve through genetic similarity because the coefficient of relationship between co-ethnics (who aren’t close family) is pretty small. Even kin selection itself is pretty weak in general. How much time do you spend with your second and third cousins?
In-group favoritism likely evolved through individual selection for reciprocal altruism. Overall similarity simply allowed individuals to recognize likely partners for trading favors (shared language and customs may help). This may have even co-opted systems designed to act towards close kin – misfiring kin altruism, if you will.
Rebutting Jayman’s denial of the ethnic kinship coefficient requires an explanation of the concept of relatedness as a whole. How, for example, can I be 50% identical to my father if I’m 99.8% identical to all living humans? The answer is that I am not 50% identical to my father; rather, I am 50% identical to my father by comparison to the baseline level of relatedness of all living humans. If all living humans are 99.8% genetically identical then I’m 99.9% identical to my father. Jayman’s argument that two random co-ethnics aren’t related fails to factor this into account: a calculation of relation needs a baseline level of relatedness for comparison. So he’s correct in stating that two co-ethnics are not similar to one another- but only by comparison to the baseline level of relatedness of their entire population.
Since the ethnic kinship coefficient has been worked out to the equivalent of half siblings, it may be useful to frame the issue in those terms. If I am 25% identical to my half sibling by comparison to any other co-ethnic, it is because there is a quarter of my genome that I share with my half sibling due to our common descent. Specifically, our mutual descent from our mutual parent gives us a specific combination of genes that nobody else is likely to have. 25% of my genome is 100% identical to his alleles of the same genes and the other 75% is as similar to his as it is to any other co-ethnic, but taken as an average across my entire genome, any given allele is 25% more likely to be shared with him than it is everyone else in our race.
The ethnic kinship coefficient works in an uncannily similar way. Instead of inheriting those 25% identical genes from recent common ancestors, the two co-ethnics inherit the same genes due to the fact that people of their race usually have those genes (think melanin, keratin, microcephalin, EDAR, HERC2, or any other gene for which the frequency of alleles differs overpopulation). In spite of that difference in the origin of ethnic vs familial similarity, the mathematics are shockingly similar: according to Henry Harpending in his review paper Kinship and Population Subdivision, “Many studies agree that Fst [genetic distance between populations] in world samples of human populations is between ten and fifteen percent,” with “a conservative general figure” being 12.5%. What’s more, Fst “is computed for each allele at each locus, then averaged over all loci.” In other words, 1/8th of human genetic diversity is at the between-group level.
To put things into perspective, a 1/8th reduction in diversity within a family occurs when two half siblings (25% identical) have a child. There is a 1/16th chance that the common parent will pass a given allele to both children and that both children will pass that allele to their child, and a 1/16th chance for the same to occur for the other allele of the same gene; when computed allele for allele, “diversity” (odds of heterozygosity) goes down by 1/8th among a population that is 25% identical by descent.
One such calculation finds, for example, that a Frenchman is 24% identical to another Frenchman if your baseline for comparison is the genetic similarity between the French and Japanese.
This is the inevitable implication of the central tenet of HBD: that the various races of the world are genetically different from one another. It is also the inevitable implication of Lewontin’s famous finding that 15% of all human genetic variation is racial; if it were 100% then all co-ethnics would be identical and it were 0% then race wouldn’t exist at all. If it were 15%, though, then that 15% would be composed of genes whose alleles vary in frequency across populations; these are genes you share with co-ethnics much more often than you share with anyone else. If you’re more likely to share a lot of genes with co-ethnics than you are with anyone else, then you’re more genetically similar to co-ethnics than you are anyone else. When they sequence the genes of people of different races and compute the odds of similarity locus for locus, you’re much more likely to share some genes (ABCC11, MC1R, etc) with co-ethnics than you are others, but taken as an average across both copies of the entire genome, it’s about 25%. Apply those odds to the 20,000 or so genes in the human genome and the result will be consistent with the data that members of a given race are about 25% identical by comparison to members of other races.
We are not the first people to predict that these genetic differences would result in kin selection expressed as altruism towards co-ethnics and discrimination towards others; to quote an article by the late Henry Harpending posted in March 2012, “In the new diverse community the average person can find someone related as f~0.06, corresponding roughly to a great-grandchild at f=1/16. Suddenly there is a fitness payoff to discrimination.” (In this hypothetical population, an individual is 1/8th more related to a co-ethnic than to the average and 1/8th less related to some of a different race than to the average.) In an ethnically homogeneous population, discrimination of this kind will not occur because the fitness payoff of benefiting one co-ethnic or the other is the same, but in a heterogeneous population, you suddenly have people in whom you have comparatively more or less genetic interest. In December 2012, Harpending and Salter published “JP Rushton’s Theory of Ethnic Nepotism,” a paper predicting that the Fst data would support Rushton’s theory of ethnic genetic interest, by providing evidence for kin selection. Towards the end of this article, I will provide evidence for human altruistic behavior fitting the patterns predicted by kin selection, and I will present a likely animal model for subspecies competition over resources. In the meantime, however, there are more misconceptions to clear up.
JayMan says:
I suppose a key misunderstanding in the matter is the failure to realize that each individual gene contributes to fitness independently. Each gene is “out for itself”, so to speak. It just so happens that in any given organism, genes achieve success by working together (most of the time). As sucheach individual gene’s “aim” is to make more copies of itself. What’s going on in the rest of the genome is tangential to this. ((—>Each gene would be just as happy to mix with any other gene, so long as its own fitness is increased in the process.<—)) (Additions in last sentence for emphasis are mine)
Individual genes don’t always contribute to fitness independent of one another; the venerable Nicholas Wade has pointed out that there is at least one gene which confers different levels of selective disadvantage depending on the other genes they’re mixed up with: an allele that slightly increased risk of heart problems in Europeans causes big problems whenever it introgresses into Africans. Naturally, the population which has had this allele for longer has more genes elsewhere in the genome compensating for its negative effects, meaning that said allele will cause fitness problems after it introgresses into another population. Introgression is just a fancy word for race mixing, though, and there are other problems with it, as follows:
In a study of 100,000 mixed-race adolescent school children, those who identified themselves as such had higher health and behavior instances than those of one race. The effect was still observed even when SES and other factors were controlled for. A problem with an obvious genetic component.
Yet another study done on white-Asian mixes notes that they have a two times higher rate to be diagnosed with psychological problems such as anxiety, depression and substance abuse.
It was found, in agreement that black-white mixes engaged in more risky behavior than did monoracial children. They also observe that mixed-race adolescents are stark outliers in comparison to whites and blacks, which still holds true despite being raised in similar environments to monoracial children.
Fitness doesn’t look increased in that process, seeing how mulatto children show more health problems and negative behavior than monoracial children. And given the data relating to the allele mentioned above, we can’t rule out the possibility that health problems in biracial children arise because their parents’ genes don’t necessarily work together.
There is no impact on one’s fitness from the race of one’s mate (or an offspring’s mate) so long as close relatives are off the table as mates (aside from the fitness impact of the particular genes such mates were bringing in the environment in question). The fitness impact to a White man’s genes if his daughter marries a Black man is the same as if she married an unrelated White man (again, fitness from gene function notwithstanding).
Do you really believe that? As shown above, mixed-race children show more health and behavior problems than do monoracial children. Africans were not selected for resistance to the negative effects of certain European genes as Europeans were, and we have no reason to believe that any race is selected to compensate for the negative effects of genes they don’t even have.
Just the same, the inclusive fitness impact to a White American is the same whether he focuses his altruistic act on an unrelated White American or on a Namibian; it is zero in both cases. If you adopt children rather than have your own, the fitness hit to you is the same whether your adopted children are White, Black, Chinese, or Venezuelan.
Again, this assumes that there are no genetic differences between populations, but there are, so your fitness is probably higher if you adopt a co-ethnic than if you adopt someone else.
Hence, there is no human ethnic group that exhibits ethnic nepotism. This includes Ashkenazi Jews. But these have nothing to do with ethnic nepotism, didn’t arise via kin selection, and don’t depend on genetic relatedness per se. This includes Ashkenazi Jews.
Ashkenazi Jews evolved their nepotism through thousands of years of getting driven out of countries. Along with being barred from certain jobs, this led to them being only able to do banking jobs and those jobs that took more intellect, which they then evolved their higher IQ as well as more group favoritism to help them in societies where they are the minority. This is clearly evident today with Jewish overrepresentation at elite universities; their average IQ of 110 suggests that they shouldn’t be that much of the student body since they’re six times as likely to be geniuses but many more times likely to make it into the top institutions. Odds are pretty good that that’s ethnic nepotism in action. We’re talking about a group of people 38% likely to consider themselves religious but 70% likely to believe the old mythos that the omnipotent, omniscient creator of everything that ever existed prefers them to literally everyone else, and judge whether someone is worthy of this inconceivably lofty status purely on the basis of their genetics; before they had handy-dandy PCR machines and enzymes, Jews determined someone to be Jewish by matrilineal descent, not cultural custom. If the Ashkenazim lacked any ingroup preferences of any kind during their time in Europe, they would’ve literally copulated themselves to death by marrying Gentiles until their population was totally absorbed by ours. What would you call it then, JayMan, if not EGI? They’re one of the best examples FOR the existence of EGI. See, the thing is, if someone is an Ashkenazi Jew, more often than not, they will be more related to each other than some other random person from another population.
This particular fact – that co-ethnics share genes – is why they have a genetic interest in one another.
The Ethnic Kinship Coefficient has been corroborated literally every time anybody calculated Fst values between different human races, and by JayMan’s understanding of kin selection it disproves his assertion that ethnic genetic interests do not exist:
This [relatedness] is the probability that a given relative of an individual possesses a copy of an allele the individual possesses.
Co-ethnics are about 25% more likely to share the statistically average allele than people of different races are, so the Hamiltonian drive to confer benefit on co-ethnics is comparable to the drive to confer benefit on secondary relations (half siblings, grandchildren, etc). In other words, it doesn’t matter that the frequency of altruistic alleles is unaffected by the presence of outsiders, because people have a genetic imperative to assist the genes they share with their co-ethnics either way (and are therefore selected for altruism/ethnic nepotism either way); since they are related to their co-ethnics regardless of context, they are selected for the desire to confer benefit on co-ethnics regardless of context, and they only have a genetic interest in derogating an outgroup if doing so will increase the fitness of the ingroup. This is why Harpending and Salter observe, in the paper linked above, that racial solidarity “strengthens in response to attacks perceived to be aimed at group identity, especially invasion of the homeland and physical harm done to co-ethnics.” Observe Donald Trump or Marine Le Pen excoriating the bureaucrats they deem responsible for an alleged invasion, or Black Lives Matter being more enraged about a Hispanic killing a black than by thousands of blacks killing thousands of other blacks. A supposed shift in altruistic allele frequencies was never the point, and to argue against it is to battle with strawmen.
If altruism is the result of kin selection, then an organism will confer benefit on the criterion of relatedness. If a European man saves a daycare with 8 Asian babies in it from some freak accident, then he saves as much of his own genes as were shared by those babies. If he saves a daycare with 8 European babies in it, he just saved a collection of his own copies of HERC2 or ABCC11 or EDAR or some other such gene which he previously failed to save as well. If he saves 8 of his co-ethnic first cousins, the proportion again goes up, this time by 12.5%. By the same mathematical model we use to explain kin selection (Hamilton’s Rule), we predict and observe that altruism will be expressed to various degrees depending on the degree of relatedness.
The adaptation to this would have nothing to do with magical altruism genes which change in frequency when Japanese people arrive in France. Rather, the selection pressures predicted by the kin selection model would select for organisms that exhibited compassion and cooperation in proportion to relatedness.
The fact that co-ethnics share so many genes means that they do have a genetic interest in one another, if kin selection is real. I personally believe that kin selection is a clearer and more likely explanation for altruism than group selection in most cases, but due to the difficulty of determining causality in processes that occurred thousands if not millions of years ago (namely the original evolution of altruistic behavior), I doubt that the scientific community can put this one to bed yet. For the purposes of this issue, however, JayMan has already professed his belief that group selection has never occurred, meaning that one of a few different things must be true.
- Humans are not altruistic at all. Untrue.
- Humans are altruistic, but not due to kin selection or group selection. Unlikely; we can talk about mutual back-scratching all we want but the fact that people take bullets and jump on grenades for one another means that mutual benefit cannot be our only reason to confer benefit upon others.
- Humans are altruistic due to kin selection. This explanation is consistent with genetics and evolutionary theory; evolution holds that survival is a matter of passing on genes and genetics show that related organisms have many of the same genes. It also has pretty good predictive power (it predicts familial love, racism, and other real phenomena). For these reasons, I’m going to be arguing from the assumption that kin selection is a primary reason for human altruism, and that it, therefore, must exist in humans.
Due to the genetic similarity between co-ethnics, there is a genetic interest between them. Each has a Darwinian interest in the other comparable to roughly 25% of their own survival. Operating from the assumption that kin selection is the reason for human altruism, one would predict one of the following possibilities:
- Humans will prefer to confer benefit to their co-ethnics over others due to the fitness advantage gained by doing so,
- That humans cannot perceive genetic similarity and have therefore been selected to benefit one another regardless of genetic similarity in hopes that they hit the mark by accident,
- Humans do prefer those who are genetically similar but are incapable of perceiving the genetic differences between the various human subspecies, or
- Humans understand the genetic differences between themselves and others but for whatever reason will not take the 25% fitness advantage. I’m going to go ahead and throw this one out.
We know that humans prefer others on the basis of genetic similarity, and we know that nearly all human cultures have considered those of different ethnicities to be “the other,” or at least different in some significant way. We know that people can determine someone’s biological race based on their appearance, in any case, and in his 1996 book Race in the Making: Cognition, culture, and the child’s construction of human kinds, Lawrence Hirschfeld found that even children could do so. All of which means that humans can get a rough idea of genomic similarity (or difference) using phenotype and family history as a proxy, and that race is among the types of genetic difference that humans are capable of perceiving. If humans prefer one another based on the criterion of genetic similarity (they do), and race is a genetic difference that humans can perceive (it is), then we expect humans to generally prefer those of their own race (they do).
Even in studies of bereavement, Littlefield and Rushton (1986) put forth ten hypotheses (I will only bring the ones up that prove the case for EGI) to make the case for Genetic Similarity Theory:
- A mother will grieve more than the father: this is due to the mother having finite number of ova, have a more limited reproductive potential than do men and also bear the burden of bearing children, this shows that each offspring of a mother is more important to the overall success to her genes than the are to the father’s.
- Male children will be grieved for more intensely than female children. This is due to a male having a higher chance to have more children and spread his genes to more progeny.
- Similar children will be grieved for more intensely than dissimilar children. GST explains the phenomenon of assortative mating, the phenomenon that spouses will be genetically similar on those traits more influenced by genetics. One consequence of assortative mating is that one parent may be more similar to the child than the other. This can be illustrated as follows: Rushton and Littlefield: “If a father gives his child 50% of his genes, 10% of which are shared with the mother, and the mother gives the child 50% of her genes, 20% of which are shared with the father, the child would be 60% similar to the mother and 70% similar to the father (Rushton et al., 1984)”. So we can see that depending on the amount of genes a child gets from his parent will infer whether or not they are genetically similar to which parent, and in the case of a possible surprise death, the parent who believes the child looks (shares more alleles in common with) like their selves, will grieve longer and more intensely due to having a greater fitness hit due to the increased GST.
This study shows good evidence that the more genetically similar the child is to the grieving parent, the more strong and intense the grieving process will be. How mothers and fathers will risk their lives for their children, their genetic endowment, shows another truth to this phenomenon: altruism. Altruism for those who are genetically similar to yourself. We can then take this and show that since co-ethnics are closer to each other than they are to distant populations, and that since they are more genetically similar to themselves, the same kind of derogation and suspicion that parents give strangers who come around their children, co-ethnics will give to non-co-ethnics when they appear in their homeland. Robert Putnam’s research corroborates this.
Altruism/nepotism does increase when out-groups come to the land. When this occurs, the native population of the country will, in theory, become more altruistic to co-ethnics since their genetic interests are at stake. This is currently occurring in Eastern and Southern Europe in countries like Hungary, Poland, Spain, and Italy.
The model has pretty good predictive power since it predicts racism and other phenomena, which I’ll dive into now. Applying the kin selection model to humanity we expect that altruism will not only be doled out proportionally with respect to genetic similarity, but also to the number of babies the recipient is likely to have. I wouldn’t do as much for my DNA by saving the residents of a retirement home as I would by saving a daycare. And saving women is smarter than saving men. Hence, when the Titanic sinks, the rallying cry of the day is literally “save the women and children!” (Because the people who didn’t do that throughout our biological history had less of an impact on our gene pool than the ones who did.)
So you’re going to see innumerable charities for the benefit of children, and comparatively, nobody trying to solve the conundrum of how terrible life is in nursing homes for the elderly. On the Forbes list of top US charities, numbers 1-4 all frequently work with children (as do many others) and numbers 5, 6, 12, and 14 are specifically for children. None of them are specifically for the elderly; making sure that Grandpa isn’t miserable and alone registers nowhere in the top 50 items of our society’s to-do list.
And you’re going to see things like this, in spite of the fact that men are equally likely if not a hair more likely to get lung cancer and it’s a big killer in both sexes because people care more about “women” than they do about “people.” And I’m not joking or cherry-picking: Lung Force’s blog is seemingly more about women’s feelings than about lung cancer, no doubt because these people are aware that breast cancer research receives way more funding than prostate cancer research does in spite of similar death rates . In other words, it’s a well-known fact among people whose jobs are to stir up altruism that people will give more resources for the well-being of women than for the well-being of men.
All of which is just another case of altruism that “just so happens” to confer group and/or kin benefit, and does so proportionally to the expected increase in fitness, precisely as kin selection would predict. I would expect people to donate more to co-ethnics as well, were it not for the facts that:
a) It’s fashionable in our society to virtue signal niceness to swarthier folks, and
b-z) Haitian children literally eat dirt for breakfast.
In any case, you can look at where rich nonwhites send their donation dollars, be it the fitness benefit gained by JayZ when he donates to clean water causes in Africa, or by George Lopez in his “contributions to the Latino community“. This isn’t a cherry-picked trend of statistically irrelevant anecdotes: Blacks donate to other Blacks, “Identity-based giving is gaining momentum in the Latino, Asian American, Arab American, and Native American communities,” and “Latino’s motivation to give is embedded in a sense of responsibility and desire to give back to their community.” Much of the work of such people may end up benefiting Whites who happen to be there when a catastrophe hits a bunch of the donor’s co-ethnics (observe a Black donating to Hurricane Katrina; New Orleans is majority black, but not devoid of Whites), or occasionally they’ll donate to other nonwhites. But I’m not holding my breath for the day they raise awareness for the White squatter camps in South Africa.
Basically, any time that a person does a nice thing for another person, it will be proportional to any combination of three factors: genetic similarity, assumed number of offspring, and/or how bad the recipient needs help. All three of these are predicted by kin selection since all three are factors which predict the fitness gained by engaging in an altruistic act.
Importantly, virtually every culture on Earth preferred co-ethnics to others prior to the Communist subversion of the West, at which point accusations of racism became something of a social death sentence. (You don’t believe me on the Communist subversion thing- think it’s a conspiracy? Google up where all of this “social construct” ideology we keep encountering ultimately came from, and look up who’s promoting it today.) One could claim that whether a culture is “racist” or not depends on “culture” rather than biology, and point to the modern West as an example of an “anti-racist” culture, but in that case, it’s one hell of a coincidence that every race on Earth generally preferred themselves to everyone else, and did so for 10,000 years or more if you count prehistory. Considerably more likely is that populations with no ingroup preference are subsumed by other populations who gain a fitness advantage by doing so (they mounted no defense because they didn’t understand the need to do so) and that the majority of modern humans are therefore descended mostly from passionate racists.
Co-ethnics have a real genetic interest in one another due to large amounts of shared DNA, meaning that ethnic genetic interest is real. Humans do act on genetic interests in general, as the family studies show, and they are capable of perceiving racial genetic differences, as the ethnicity studies show; it is, therefore, likely that they will act on these ethnic genetic interests as they do with other genetic interests, because racism is caused by the innate preference for genetically similar people. In other words, racism is a biological phenomenon instead of a cultural one.
That, or nearly every culture ever in the history of forever was racist by pure coincidence.
To put subspecies competition into perspective, I will point out that wolves and coyotes have a Fst value between 0.056 and 0.121 and can interbreed. We can call subspecies and other taxonomic classification a social construct if we like; technically we’d be correct in the case of canids, to whom the words “species” and “subspecies” are doled out in a pretty arbitrary fashion. We can say that the admixture is proof that the wolf and coyote DNA doesn’t care about which other genes it’s combined with, if we like. But everything we say about it does absolutely nothing to change the fact that the biological fitness of coyotes massively drops when they share territory with wolves.
Understatement of the week: the implications of having to compete for the same resources is probably why canids fight for territory. Wolf packs, being direct family, would no doubt have a high Fst with other wolf packs, no different from how I’m more similar to my grandpa than I am my housemates. They fight for territory on a familial level because of genetic interest, and they have been observed fighting for territory on the level of subspecies as well, with a clear genetic interest in doing so. The only difference between them and us in this respect is that our method of acquiring resources relies on commerce rather than hunting, and so we weren’t selected for the propensity to wander around a given territory fighting off other families who intrude. That’s not good for business; in fact, I’d be willing to bet that warfare usually occurs in humans when the profit incentive for conquest is greater than the profit incentive for trade. Humans who don’t engage in a lot of commerce and belong to inbred populations, though, have fewer incentives towards peace and higher Fst values relative to others- and they aren’t above killing the guys from the next tribe over. What a surprise that these village’s conflicts had to do with territory and breeding, both of which have to do with fitness. In any case, humans from populations selected for agriculture and commerce engaging in this sort of behavior is the exception that proves the rule, because the only reason anybody knows about the interfamilial warfare of the Hatfields and McCoys is that it falls under the “man bites dog” rule.
I have this radical view that biological rules still apply to humans, and that we are therefore self-replicating bags of meat smart enough to understand that we are self-replicating bags of meat. I see little difference between wolves reclaiming their old hunting grounds and the Reconquista movement. Coyotes had taken over when the wolves kept getting killed by men; Spaniards took over when a storm of viruses killed off most of the Natives. Even after the Spanish admixture, the Fst values between Whites and the now-mestizos likely falls within the range of coyote-wolf Fst values. Wolves feed their kind with elk and we feed ours ultimately with money; the distribution of elk meat to wolves isn’t good for coyotes and I’m willing to bet that the distribution of money and jobs to other nations and their peoples explains much of our abysmal birth rates in the West (with birth control technologies being another primary factor). We had lots of kids back when there were blue collar jobs you could get fresh out of high school which instantaneously elevated you to the middle class. We could afford to have them, no different from the fact that European nobles had more kids on average than us commoners. If current economic, cultural, and political trends continue, though, then ethnic Europeans might go out roughly 50x faster than the Neanderthals did.
Biological organisms show preference of those who are similar at the level of self (me), family (the Kennedys), tribe or nation (Papuan tribes or Mexico), race or subspecies (Native Americans), and species (I eat pork and kill spiders more often than I eat aboriginal Australians and kill Sentinelese people). All are the same phenomenon (attempts to increase the odds of self-replication at the genetic level), all are predicted with Fst values and Hamilton’s Rule, all are observed in animals to whom “culture” doesn’t apply, and all are observed in mankind.
Now, the question is this: how would GST be detected? Numerous ways. Location, for one. Since up until around 50 years ago, most countries were monoracial, those in your general proximity will, more often than not, be more genetically similar to you than a group that’s 50 miles away. Culture, which is an expression of genetics, is yet another way that GST can be detected. Since culture is an expression of genetics, when that culture is expressed, this shows other genetically similar co-ethnics that this individual shares more genes in common than those who don’t share their culture. There is also matching by phenotype, which goes along with the location aspect. But, as I stated in my article Genetic Similarity Theory as a Cause for Ethnocentrism:
It’s clear that we are more altruistic to people who look more phenotypically similar to ourselves, to pass on and benefit copies of our genes. This evolved in spite of the negative impact on behalf of the altruist. The altruist is helping copies of his shared genes survive so that they may be copied into the next generation of progeny. The tendency to favor co-ethnics is the tendency to attempt to help pass on shared genes, as if the phenotype is similar, more often than not, the genotype is as well. This is the basis for ethnocentrism.
There is also what is called the “Grandmother’s hypothesis” in which the researchers theorize that women live past menopause to help take care of their grandchildren. In doing so, they can then make sure their grandchildren are well-fed and nourished. The researchers state that by using Hamilton’s relation coefficients (what we have been using in this article), that a grandmother should share 25 percent of genes with her grandchildren. Ted Sallis says:
Therefore (and this is the important point), a paternal grandmother, all else being equal, is genetically less related to a grandson than to a granddaughter, and less related to a grandson than is a maternal grandmother. Conversely, a paternal grandmother likely is more genetically related to a granddaughter than is a maternal grandmother, given the certainty that the granddaughter possesses an X chromosome from the paternal grandmother.
The researchers hypothesized that the grandmother’s investment in grandchildren will be directly mirrored by how genetically similar they are to each other. The authors conclude that women live past menopause to help care for their children’s offspring. Since they share 25 percent of their genes with their grandchildren, they too, have a genetic investment in making sure they get adequate nutrition and are well cared for. They found that in 7 previously studied populations that “separating grandchild survivorship rates by sex reveals that X-chromosome relatedness correlates with grandchild survival in the presences of MGMs and PGMs. In all seven populations, boys survive better in the presence of their MGM than PGM. In all bar one population, the PGM has a more beneficial effect on girls than on boys. Our X-linked grandmother hypothesis demonstrates how the effects of grandmothers could be sex-specific because of the unusual inheritance pattern of the X-chromosome.”
This is what this whole debate is about: ability to detect genetic similarity in co-ethnics. Matching by phenotype, culture, and general proximity will, with good chance, bring you together with someone who shares more alleles in common with you and someone who you would feel more altruistic towards since you have a genetic interest in ensuring that some of your genes survive to the next generation.
Mixed-race relationships don’t discredit the existence of EGI/GST, in fact, it helps to strengthen it. Americans of mixed ancestry made up for ethnic dissimilarity by matching up on the more heritable traits, whereas the correlation is lower for those traits that are more influenced by the environment. Since the correlation is higher for heritable traits, i.e., BMI, personality, alcoholism, aggressiveness, criminality, psychiatric disorders and so on. Since the correlations are higher than in the environmentally mediated traits and since mixed-race couples match on more heritable traits than on the traits more influenced by the environment, this shows us that even though they are marrying outside of their race/ethnicity, they still match up on the more heritable traits and not the traits more influenced by the environment.
JayMan brings up the concept of reciprocal altruism as if it negates the effect of racial/ethnic altruism as a whole. It does not. Reciprocal altruism and Genetic Similarity Theory go hand-in-hand as genetic similarity eliminates the need for the reciprocation to occur again. Since two related individuals share more genes in common with each other than two unrelated individuals, this then caused reciprocation and GST to evolve hand-in-hand with each other. To quote Rushton:
Thiessen and Gregg (1980) make the same point. Thiessen and Gregg state that “cooperation among `nonrelatives’ (`reciprocal altruism’) may be based in large part on genetic and phenotypic similarity” (p. 133).
Another reason that GST and reciprocal altruism go hand in hand is that genetic similarity at certain important loci can predict the efficacy of a reciprocal altruistic relationship; Fowler & Christakis find that close friends are as similar as 4th cousins, and Guo et al find the same for spouses. Selecting for phenotypic compatibility means selecting for genetic similarity at the loci which determine the relevant phenotypes (height, IQ, personality and so on). For example, different races of the world differ in Big Five personality traits, and the reason for these differences is likely genetic. If a statistically normal, introverted East Asian prefers to associate with fellow introverts, what are his odds of becoming best friends with a comparatively gregarious Black man? A gregarious Asian or an introverted Black may become fast friends with those of other races, but most of their kinsmen are more stereotypical.
Ultimately, however, what it comes down to is this: if a gene can better ensure its own survival by bringing about the reproduction of family members with whom it shares copies with, then it can also do so by bringing about the reproduction of any organism that it shares genes with. Meaning altruistic self-sacrifice. But, if there is a fitness gain for the altruist, then how is it altruism? Simple. The altruist is just protecting genetic interests. The altruist is just being driven by his genes to save copies of itself. This is basically what we humans are: organisms that only attempt to bring about those with similar genetics to ourselves.